* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Net Start Class
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
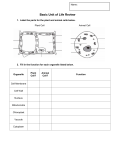
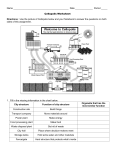
Name____________________ Period___________________ Spring 2016 Benchmark Study Guide Key Food webs Write where they get their energy and give an example using the provided food web: Producer- An organism that can produce its own food. Plants. Primary consumer- An organism that eats plants. Beetle, Grasshopper Ect.. Secondary consumer- A consumer that eats a Primary consumer. Bird, Mouse Ect. Decomposer-An organism that breaks down large molecules from dead organisms into small molecules and returns nutrients back to the soil. Scavenger (Not on this food web)-A carnivore that feeds on the bodies of dead organisms What do they eat and give an example: Herbivore- Eats plants only. Rabbit, panda Carnivore- Eats meat (animals) only. Lion Omnivore- Eats plants and animals. Human, bear Compare and contrast Food web vs. food chain: What is the difference between a food web and a food chain? A food web shows more possible combinations of how energy flows through an ecosystem, a food chain shows only one possibility. Food web is a combination of many food chains. Energy Pyramid: Which part of the pyramid has all of the energy for the ecosystem? Why? The bottom, the producers. All of the energy is made by producers using energy from the Sun. What percentage of energy is transferred up to the next level? 10% Body systems Match the system to the correct description Respiratory Nervous Circulatory Excretory Endocrine Integumentary Reproductive Digestive 1. Reproductive facilitates the continuation of a species 2. Endocrine uses hormones to help regulate the body’s activities 3. Excretory filters waste from blood to be expelled form the body 4. 5. Respiratory acquires oxygen for the body and releases carbon dioxide Circulatory works with the above system to move oxygen to all cells and removeCarbon dioxide 6. Digestive 7. Nervous breaks down large molecules so it can be absorbed by the body uses electrical impulses to control the body’s activities What three systems aid in body movement (Not part of matching) _Muscular_______, __Skeletal___, and __Nervous_____ systems. Fill in the chart: Body System Respiratory Nervous Endocrine Excretory Circulatory Function Organs Exchange of gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide Coordinate body functions, receive information, deliver messages Coordinate body functions using chemical messages, hormones Remove liquid waste from body Carry nutrients to all cells, carry waste away form all cells lungs Brain, spinal cord, neurons Glands – pituitary, adrenal, ovaries, testies, thyroid etc. Kidneys, urinary bladder Heart, veins, arteries, blood, capillaries Cells Match the cell organelle to the correct description: Nucleus Membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole Lysosome Cell Lysosome similar to digestive system because it breaks down molecules Cell Membrane similar to the skin because it can protect by keeping things out Vacuole similar to excretory system because it stores waste for removal Nuclus similar to the brain because it directs all activities of the cell Fill in the Venn Diagram using the words below: Plant Mitochondria Nucleus Chloroplast Small vacuole Large vacuole Cellular Membrane Cellular Wall Animal Gives off oxygen Gives off Carbon dioxide Makes own food Can not make own food Made up of cells Cell organelle Function Mitochondria Powerhouse of the cell Nucleus Brain of the cell Ribosome Produce protien Cell Membrane Allows certain things in and out of the cell Cell Wall Support and protection in plants Vacuole Store water and some waste, turgor pressure in plants List the levels of organization starting with organelle: Organelle, Cell___, _Tissue__, Organ______, _Organ system__, __Organism_. Genetics Define and give an example: Trait___A characteristic that an organism can pass on to an offspring through its genes. Blue eyes Selective BreedingChoosing to parents to breed to give the offspring desired traits. Large cows to take to market Dominant Allele – the version of a gene whose trait is always expressed (seen) when at least 1 is present Recessive Allele – the version of the gene whose trait is “masked” (not seen) unless both genes present are recessive Cell Theory List the three parts of cell theory. 1)___All living things are composed of cells 2)___Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3)___All cells are produced from other cells Fill in the boxes using the words below (Hint not all boxes will be used): Sexual Reproduction vs. Asexual Reproduction Genetically diverse offspring Genetically identical offspring Two parents One parent Egg and Sperm Cell division Budding Genetically identical offspring, Genetically diverse offspring, One parent, Two parents, Egg and sperm, Cell division, Budding Abiotic vs. Biotic Define and list 3 examples of each Abiotic-__A non-living part of an ecosystem ___air, rocks, sunlight Biotic- _A living part of an ecosystem Bear, Tree, Fungi Scientific Method DRYMIX Read the experiment below and answer the questions that follow. Students made paper helicopters that had rotors of different lengths then followed the procedure below: 1. they dropped each helicopter 4 times form a set height 2. timed how long it took for the helicopters to each the ground 3. averaged the time for each helicopter 4. compared average drop time to rotor length What is the independent variable in this experiment? Rotor length What is the dependent variable in this experiment? Drop time Name at least 2 controlled variables in this experiment? Drop height and number of times dropped Using the experiment above, write a hypothesis using an IF Then Statement If the rotor length is longer Then the time to land will be longer Label the Graph below using the information above. Helicoptor rotor length vs time to drop Drop time in seconds DV Helicopter rotor length in cm IV 1. An object must move when a force is applied for WORK to have been done. 2. The work done on an object is the AMOUNT of the force applied and the distance moved. 3. Regardless of whether you use a ramp or lift from the ground to move a box into a moving van, the amount of WORK required is the same. 4. The goal of a simple machine is to reduce the amount ofFORCE (effort) needed to move an object 5. A student pushes against a tree with a force of 10 newtons (N). The tree does not move. What is the amount of force exerted by the tree on the student? 10 x 0 = 0J no work because the tree did not move. Define the following and give 2 examples of each. 6. Chemical Change –When an chemical reaction takes place that changes the original substance into something new. Burning, Rusting, Saliva breaking starches down into sugars,. Evidence includes production of a gas (bubbles, fizzing), temperature change (increase or decrease), formation of a solid, color change 7. Physical Change-When the original substance changes shape, size, texture, volume, state of matter etc. still the same thing just looks different. Chewing a cookie, tearing paper, freezing, melting, boiling etc. Indicate if mechanical or chemical digestion (or both) is taking place by placing a check mark in the appropriate column and explain. Location Mouth Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Mechanical Chemical Explanation Digestion Digestion X X Chewing – cuts into smaller pieces Saliva- changes starch into sugars X X Peristalsis – squeezes, mushes Acids – breakdown proteins X X Peristalsis – squeezes Bile – cuts fats into smaller pieces Enzymes and Gastric Juices – breakdown proteins No chemical digestion only absorption Peristalsis compacts the remaining materials for elimination from body