* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation glossary File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
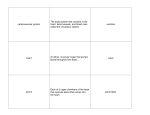
Blood Antigens The unique proteins on the surface of a cell. They are recognised by the immune system as ‘self’ or ‘non-self’. Blood Liquid that transports nutrients and oxygen to tissues and removes wastes. Contains red and white blood cells, plasma and platelets. Blood plasma The clear yellow liquid part of the blood which carries dissolved substances and blood cells around the body. Fibrin Insoluble protein that creates a mesh and catches blood cells to produce a blood clot Fibrinogen Soluble protein in blood plasma that turns to fibrin when activated by clotting mechanisms Immune system The body system which recognises and destroys foreign tissue such as invading pathogens. Immunisation Giving a vaccine which allows immunity to develop without exposure to the disease itself. Lymphocytes White blood cells that destroy pathogens by producing antibodies to them Oxyhaemoglo bin The molecule formed when haemoglobin binds to oxygen molecules. Pathogen A harmful micro-organism Phagocytes white blood cells that engulf and digest harmful bacteria and other pathogens Phagocytosis The process of engulfing and ingesting foreign particles, such as bacteria, by phagocytes such as the white blood cells. Platelets Cell fragments present in blood that release chemicals to make blood clot when we cut ourselves Red blood cells Blood cells which contain the red pigment haemoglobin. They are biconcave discs in shape and they give the blood its red colour. Vaccination A biological preparation that gives artificial immunity to a disease without contracting the disease itself White blood cells Lymphocytes and phagocytes Blood vessels Artery Thick-walled blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart Blood vessels The tubes which carry blood around the body, i.e. arteries, veins and capillaries. Capillaries Tiny blood vessels specialized for exchanging materials by diffusion Lumen Space in the centre of a tube, e.g. a blood vessel or the intestine Vein Blood vessel with a wide lumen and valves that carries blood towards the heart Circulati on Double circulation High pressure systemic circulation moves blood around the body, low pressure circulation (from right side of heart) moves blood around the lungs Pulmonary artery Blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs Pulmonary vein Blood vessel that carried oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart Vena cava The vein carrying blood from all of the body, apart from the lungs, to the heart Aorta The main artery through which blood passes from the heart to the body Renal artery The artery supplying blood to the kidneys Renal vein The artery taking blood away from the kidneys Hepatic artery The artery supplying blood to the liver Hepatic vein The artery taking blood away from the liver Hepatic portal vein The artery carrying absorbed nutrients from the small intestine to the liver Heart Coronary arteries Arteries that deliver blood to the heart muscles Coronary heart disease Disease in which the coronary arteries get blocked or damaged Ventricle Chamber that pumps blood out of the heart into an artery Atrium Chamber that receives blood into the heart from a vein Semilunar valve Valve between the ventricle and the artery it pumps blood into. Closes to prevent blood flowing backwards from the artery. Tricuspid valve Valve between the right atrium and right ventricle, which prevents blood flowing backwards into the atrium when the ventricle muscle contracts Bicuspid valve Valve between the left atrium and left ventricle, which prevents blood flowing backwards into the atrium when the ventricle muscle contracts Heart Muscular organ that pumps blood to the lungs and around the body. Heart rate Medulla Part of the brain that controls important body function such as breathing and heart rate Adrenaline Hormone released in stressful situations that increases the heart rate