* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download growth and development notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
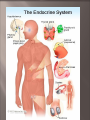
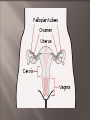
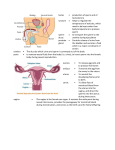
Endocrine System- made up of glands that produce hormones. Hormones- chemicals the circulate thru the bloodstream and regulate body activities such as growth and development. Glands of the Endocrine System Pituitary- mater gland, located at the base of the brain. Controls other endocrine glands, secretes growth hormone and regulates the thyroid, adrenal, ovaries and testes. Thyroid- located in the lower neck, regulates metabolism (the rate at which food is converted to energy). Parathyroid- attached to thyroid, regulates the amount of calcium in the body. Adrenal- on top of each kidney, regulate the body’s response to stress, release adrenaline. Pancreas- near the stomach, produces insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood. (Diabetes) Ovaries- (female), located in the abdomen, produce female hormone estrogen which controls female reproductive functions, including the production of eggs. Testes- (male) Controls reproduction in males. Produce testosterone- male hormone responsible for sexual development and secondary sex characteristics. Also produce sperm cells. Adolescence- is the period in life between childhood and adulthood, during which many physical, mental and emotional changes take place. Puberty- A period of growth during which males and females become physically able to reproduce. However, at puberty, they are NOT emotionally or socially ready for reproduction. Primary Sex Characteristics- Physical characteristics of males and females that are present at birth. Secondary Sex Characteristics- Characteristics of adult men and women that develop during puberty. See page B19. Group Dates- some people may feel more comfortable going with a group on their first date. WHY? Discuss Dating Guidelines with your parents… -find out what age you are allowed to go on one-on-one dates. How late you are allowed to stay out Your parents set dating guidelines because they care about you. If your date encourages you to break these guidelines, this person is not right for you. Function is to produce and store egg cells, to allow fertilization to occur, and to nourish & protect fertilized egg until it’s ready to survive outside the body. Major Organs involved: * ovaries- contains eggs (ova) and hormones that allow eggs to mature. * fallopian tubes uterus - carry eggs from ovaries to * uterus- (womb) shelters & nourishes the fetus. * endometrium- lining of uterus * cervix-opening of the uterus * vagina- passageway from uterus to outside of body. Other Important Info & Terms Estrogen: hormone responsible for female sexual development and the mentrual cycle. *Using a calender to chart your cycle can help to determine predictibility. *Irregular cycles are normal during the 1st year of menstruation. Ovulation- the release of a mature egg from an ovary. During this time period, a woman is at her most fertile point. Usually happens midcycle. Menstruation- process through which the built-up lining of the uterus sheds itself and leaves the body. This is a monthly process. Secondary Sex Characteristics develop and prepare the body to produce sperm. Sperm are the male reproductive cells. The hormone testosterone regulates these changes. Testes- Sperm cells are produced here and travel to the epididymis and are held here for 4-6 weeks. Epydidymis- located on top of the testes. Stores sperm. Vas Deferens- Narrow passageway through which sperm travels into the urethra. Seminal Vesicles- 2- add semen that nourishes sperm and help them move. Prostate Gland- produces fluid that helps the sperm stay alive. Urethra- narrow tube inside the penis through which urine and semen leave the body. Scrotum- Pouch of skin that holds the testes and helps to regulate temperature. Females • • • • Keep track of menstrual cycles During menstruation, use pads or tampons to absorb menstrual flow. Take a warm bath or exercise moderately to reduce cramps. Make breast self exams a monthly habit to check for any irregularities. • • • • • Males Follow rules of good hygiene. Wear protective clothing for sports. Perform testicular self exams, checking for irregularities. Have regular medical checkups. Seek medical attention for any problems. Each person begins as a single cell produced by fertilization. • Conception- the union of a sperm and egg. This cell begins to divide multiple times. Pregnancy is divided into 3 month long phases called trimesters. Embryo- refers to a developing baby during the 1st eight weeks after conception. Fetus- term for a developing baby after the 1st eight weeks and until birth. Placenta- outer cells develop to form this organ that attaches the embryo to the inner wall of • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Amniotic Sac- is a pouch filled with fluid (called amniotic fluid) that surrounds and protects the developing fetus. Labor- is a series of stages that result in the birth of a baby. Cervix dilates 10 cm. Baby passes into the vagina Once outside the body, the baby takes its first breath on it’s own. Doctor cuts the umbilical cord Mother delivers the placenta. Parenthood is a serious responsibility. Both parents are responsible for the well-being of their child. Fathers- fathers who are involved in the infant stage are more likely to stay involved as their child gets older. Mothers- The 6-8 week period of time after birth is called postpartum. During this time, the mother’s body is adjusting to the end of pregnancy and beginning to return to normal. Infants- require constant attention. Feelins fo frustration and anxiety are common for the new parents. You will continue to grow and change throughout your life. A person passes through a series of stages between birth and death, known as the Life cycle. Infancy (birth-1year)- involves the most rapid period of growth. Early Childhood (1-3 years) Children are learning from adults, socialization skills, and how to be safe. Middle Childhood (3-6 years) Phase of originality, learning, and skill development, and making good choices. Late Childhood (6-12 years) Children explore their physical surrounding and learning to develop new skills. Adolescence (12-18 years)