* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faulkner University Science Department
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
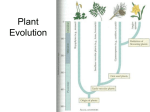
Faulkner University Science Department Principles of Biology (BIO 1402) C hapter Notes Ch 23: Plants Overview of a complex kingdom: from simple and small to complex and large and back again Fibers, cellulose and lignin Vascular system, the xylem and phloem Rhizoids to roots and root systems Stems to trunks and shoots to shoot systems Leaves with waxy cuticles and stomata In the alternation of generations a shift toward diploid dominance from gametophyte to sporophyte Seeds and seed dispersion mechanisms Pollen and pollination Flowers Storage organs C-3, C-4 and CAM carbon fixation Nonvascular plants Bryophytes (18,600 spp.) Mosses (10,000), liverworts and hornworts Special “plant” adaptations Cuticle Water-holding “jacket” around reproductive structures Sporophytes grow from free living gametophytes Other traits Spore case (Fruiting body) Slow growth Short Cushiony and feathery growth habits Water required for sexual reproduction Gemmae formed (asexual propagules) Peat bogs Vascular plants but seedless Ferns (Pterophytes) (12, 000 spp) “fern allies” whisk ferns (Psilophytes) club moss (Lycophytes) Horsetails (Sphenophytes) Special “plant” adaptations Independent sporophyte Sporophyte is larger and longer lived than gametophyte True vascular system Other traits Rhizomes Strobili and sori Fiddleheads and fronds Some are tree-sized Vascular, seed-bearing plants Special “plant” adaptations Pollen Megaspores Gymnosperms – seed-bearing but no flowers Conifers (550 spp) Cycads (185 spp) Ginkgos (1 sp) Gnetophytes (70 spp) Angiosperms – seeds and flowers Dicots (180,000 spp) Monocots (80,000 spp)