* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Wsfcs
Transmission (mechanics) wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
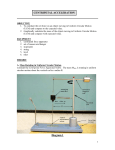
Name ______________________________________ Unit 8 Notes: Circular Motion Velocity has both magnitude and direction, so if an object’s direction changes, it _________________________ even if the speed remains constant. When an object moves in a circular path, it is accelerating because its direction is always changing. This is called ___________________________ __________________________________. Centripetal means _______________________ _______________________. The force making or allowing the object to move in a circular path is called a ________________________ ____________________. It can come from friction, gravity, the tension in a string, etc. Useful equations for circular motion: 1. A 615 kg racing car completes one lap in 14.3 s around a circular track with a radius of 50.0 m. The car moves at a constant speed. a. Calculate its centripetal acceleration. b. How much friction is necessary to keep the car traveling in a circle? c. What is the coefficient of friction between the tires and the track? 2. A carnival ride has a 2.0 m radius and rotates once each 0.90 s. a. Find the speed of a rider. b. Find the centripetal acceleration of a rider. c. Find the centripetal force exerted on a 75 kg rider. ___________________________ ________________________pulls an object toward the center of a circle instead of letting it move in a straight path. _________________________causes a rigid, rotating object to change its velocity. It does NOT come from the center of a circle. You apply torque to objects that have a circular path because of their construction. (door on hinges, merry-go-round, wrench, pencil sharpener, etc.) Torque is most effective if it is applied _______________________________ and ___________________________ to the object. Torque can __________________, _____________________, or ___________________________ of rotating objects. Equation: 3. You apply 40 N of force perpendicular to a wrench that is 0.25 m long. Calculate the torque. 4. If the angle that the force is applied changes to 30o, how is the torque affected? If a rotating object is in equilibrium, the __________________________________ ________________ must balance the _____________________________________ ____________________. Equation: 5. Four children are riding on a see-saw. On one side of the see-saw, Jack (22 kg) sits 1.3 m from the pivot point and Kate (20 kg) sits 1.5 m from the pivot point. On the other side of the see-saw, Andrew (21 kg) sits 1.2 m from the pivot point. Where should Sally (19 kg) sit to balance the see-saw?