* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download what is management
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
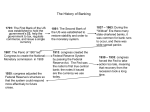
B. Basics about the Federal Reserve OBJECTIVE 3 ► ► LEARNING Explain the functions of the Federal Reserve. (Text pages 423-427) 1. 2. The FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM (“THE FED”) is the organization that oversees the money supply of the United States; it consists of five major parts: a. The Board of Governors administers and supervises the 12 Federal Reserve System banks. i. Seven members are appointed by the President. ii. The primary function is to set monetary policy. iii. MONETARY POLICY includes policies used by the Federal Reserve to control factors such as inflation, deflation, exchange rates, and economic growth. b. the 12 Federal Reserve Banks c. three Advisory Councils d. the member banks of the system e. The Federal Open Market Committee has 12 voting members and is the policy-making body. Overseeing the monetary system a. The FEDERAL OPEN MARKET COMMITTEE (FOMC) is the group that oversees the entire Federal Reserve process. i. The FOMC is the policymaking body of the FRS. ii. The advisory councils give 13.1 POWERPOINT 13-5 Basics about the Federal Reserve (Refers to text pages 423-427) TEXT FIGURE 13.1 The 12 Federal Reserve District Banks (Box in text on page 424) 3. 13.2 suggestions to the board and to the FOMC. iii. The councils represent the district banking districts, consumers, and member institutions. b. The Federal Reserve: i. Buys and sells foreign currencies; ii. Regulates various types of credit; iii. Supervises banks; iv. Collects data on the money supply and other economic activities. c. The tools used to regulate the money supply include: i. reserve requirements; ii. open-market operations; iii. the discount rate. The reserve requirement a. A RESERVE is an amount of money that must be kept on hand and not lent to individuals or institutions. i. The RESERVE REQUIREMENT is a percentage of commercial bank’s checking and savings accounts that must be physically kept in this bank. ii. For example, cash in the vault or a non-interest-bearing deposit at the local Federal Reserve district bank. TEXT FIGURE 13.2 The Four Functions of the Federal Reserve (Box in text on page 424) BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 13-2 Researching the Federal Reserve Tools This Internet exercise asks the student to go online and obtain up-to-date information about the Fed’s money supply management tools. (See complete exercise on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) TEXT FIGURE 13.3 How the Federal Reserve Controls the Money Supply (Box in text on page 427) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual 4. iii. The reserve requirement for U.S. banks is between 3-10%. b. Changing the reserve requirement is one of the Fed’s most powerful tools. c. When the Fed increases the reserve requirement: i. Banks have less money for loans and make fewer loans, which reduces inflation. ii. The money supply would be reduced and prices would likely fall. d. When the Fed decreases the reserve requirement: i. Banks have more money available for loans and make more loans. ii. An increase in the money supply stimulates the economy for higher growth, but it can also create inflationary pressures. Open-market operations a. Another commonly used tool is OPEN-MARKET OPERATIONS, the buying and selling of U.S. government bonds. b. When the Fed wants to decrease the money supply, it sells government securities to the public. c. When the Fed wants to increase the money supply, it buys government securities from individuals, corporations, or organizations willing to sell. CHAPTER 13: Money, Financial Institutions, and Securities Markets LECTURE LINK 13-7 Wrenching Inflation Out of the Economy The U.S. inflation rate in 1979 was almost 15%. Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker was appointed in 1980 with a mandate to bring inflation under control. (See complete lecture link on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) 13.3 5. The discount rate a. The Fed is called the banker’s bank. i. Member banks can borrow money from the Fed and then pass it on to their customers. ii. The DISCOUNT RATE is the interest rate that Fed charges for loans to member banks. b. Increasing the discount rate discourages banks from borrowing and consequently reduces the number of available loans, resulting in a decrease in the money supply. c. Lowering the discount rate encourages banks borrowing and increases the amount of funds available for loans, resulting in an increase in the money supply. d. The Fed also sets the rate that banks charge each other (the federal funds rate). C. Global Exchange of Money 1. A falling dollar means that the amount of goods and services you can buy with a dollar goes down compared to other currencies. 2. A rising dollar means that the amount of goods and services you can buy with a dollar goes up. 3. For example, a strong Canadian dollar would drive up the cost of a vacation to Canada. 4. What makes the dollar weak or strong is the position of the U.S. economy 13.4 TEXT REFERENCE Ethical Challenge: To Return the Money or Not (Box in text on page 427) If an ATM machine incorrectly dispensed $200 to you instead of the $100 on the receipt, what would you do? POWERPOINT 13-6 Global Exchange of Money (Refers to text page 428) BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 13-3 Currency Trading This exercise asks the student to research currency values and calculate some currency conversions. (See complete exercise on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) LECTURE LINK 13-8 Protecting Your Money INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual 5. relative to other economies. a. In a strong economy, the demand for dollars is high and the value of the dollar rises. b. When the country’s economy is perceived as weakening, the demand for the dollar declines and the value falls. When the dollar is weak compared to other currencies: a. It takes more dollars to buy factory equipment from France, for example. b. Companies are then not able to trade as much. c. Foreign competitors can use the weaker dollar to their advantage. SELF CHECK QUESTIONS (Text page 429) 1. Explain the meaning of the money supply. 2. What are the three ways in which the Federal Reserve can control the money supply? Why is control of the money supply important? 3. 4. What does it mean if a news report says, “the dollar is falling against the euro”? CHAPTER 13: Money, Financial Institutions, and Securities Markets After the Great Depression in the 1930s, several organizations were created to protect depositors and investors from being completely wiped out during an economic downturn. (See complete lecture link on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 13-3 Financing Options A small company is considering expansion. Which financing option would be best? (See complete exercise on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) BONUS CASE 13-3 State Farm Bank: Would You Like Banking with That Insurance? (Video Case) This bonus case ties in with the video available for use with this chapter. State Farm Bank is a new type of financial institution: a virtual bank. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 13.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual.) 13.5