* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics Questions
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
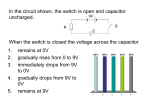
Electronics Questions 1. Copy and complete the block diagram of an electronics system. Input Process Output 2. The diagram below shows the block diagram representing an electronic thermometer. Thermistor CPU LCD display Which part is the input device? Which part is the process device? Which part is the output device? 3. Draw a block diagram to represent the school tannoy system. The parts are Amplifier, Microphone, Loudspeaker. 4. Microphone, Buzzer, LED, LDR, Lamp,Thermistor, Switch, Motor, Loudspeaker. Arrange the devices above into two groups, Input and Output devices. 5. What is the energy change in a microphone? 6. What happens to the resistance of a thermistor if the temperature goes up? 7. What happens to the resistance of an LDR if the light level goes up? 8. Microphone, LDR, Switch, Thermistor From the above list what would be the best input device for an electronic thermometer? From the above list what would be the best input device for an automatic night light? From the above list what would be the best input device for a baby monitor? 9. What is the energy change in a motor? 10. What is the energy change in a loudspeaker? 11. What is the energy change in a lamp? 12. What is the energy change in an LED? 13. Buzzer, LED, Lamp, Motor, Loudspeaker. From the list above what would be the best output device for a radio? From the list above what would be the best output device for an automatic fan? From the list above what would be the best output device for an automatic night light? 14. Draw the symbol for a NOT gate. 15. Draw the symbol for an AND gate. 16. Draw the symbol for an OR gate. 17. What logic value represents a high voltage? 18. What logic value represents a low voltage? 19. Write down the output value for the gate shown Logic 1 output 20. Write down the output value for the gate shown Logic 1 Logic 1 output 21. Write down the output value for the gate shown Logic 1 Logic 1 output [19,20,21 change logic input as required] 22. Explain how the following control circuit works. The light sensor gives a logic 1 in the dark. The switch gives a logic 1 when switched on. Interchangeable gates Light Sensor Security Light Switch Movement 1. What device would you use to measure a force? 2. Describe how you would use a newton balance to measure a force. 3. What is meant by weight? 4. A pupil has a mass of 45 kg. What is the weight of the pupil? 5. What is the name of the force that causes a moving object to slow down? 6. What is the name of the force that makes it difficult to push a brick along a bench? 7. Describe how you could increase the force of friction. Give an example of where this could be used in a practical situation. 8. Describe how you could decrease the force of friction. Give an example of where this could be used in a practical situation. 9. How would you describe the forces in the diagrams below. 300 N 300 N 100 N 500 N 400 N 10. How could you tell if the forces acting on an object are balanced? 11. What three effects does an unbalanced force have on an object? 12. Describe how you would measure the average speed of a naughty pupil running along the science corridor. 13. A car drives past the school. A pupil times how long it takes to travel 50 metres between two lamp posts. The time is 3.1 seconds. Calculate the speed of the car. 14. What is meant by instantaneous speed? 15. Describe how you could measure the instantaneous speed of a trolley in the lab. 16. What happens to an object when it accelerates? 17. Which vehicle would cause more damage in a crash, a bus travelling at 15 m/s or a car travelling at 15 m/s? Explain your answer. 18. Which vehicle would cause more damage in a crash, a car travelling at 15 m/s or an identical car travelling at 25 m/s? Explain your answer. 19. You have to push a car. Give two ways that would make the car travel faster. 20. When you throw a ball what affects the distance the ball travels before it lands? 21. A ball lands on a surface and bounces upwards. What will affect the height that the ball reaches when it bounces? Telecomm Questions 1. What is transferred by radio signals? 2. What speed do radio signals travel through the air? 3. Name the missing parts of the radio on the diagram below. Aerial X Decoder Y Speaker 4. What does the aerial do in a radio? 5. What does the tuner do in a radio? 6. What does the decoder do in a radio? 7. What does the amplifier do in a radio? 8. What does the speaker do in a radio? 9. What is meant by the frequency of a radio signal? 10. What is the unit of frequency? 11. How does the frequency of a TV signal compare with a radio signal? 12. What colours of paint light up on a TV screen? 13. Which colours are combined to produce cyan on the screen? 14. Which colours are combined to produce yellow on the screen? 15. Which colours are combined to produce magenta on the screen? 16. Which colours are combined to produce white on the screen? 17. Describe how a signal could be sent from Scotland to USA using a satellite. 18. What is meant by a geostationary satellite? 19. What effect does a curved reflector have on a recieved signal? 20. Draw a diagram to show how a curved reflector makes a signal stronger. 21. Draw a diagram to show a light ray being reflected from a mirror. Label the diagram. 22. What is an optical fibre? 23. What speed does light travel along an optical fibre? 24.Draw a diagram to show a ray of light travelling along an optical fibre. 25. Give an advantage of using optical fibres for transmission of signals. 26. Give a disadvantage of using optical fibres for transmission of signals. 27. What does a transmitter do in a telecommunications system? 28. What does a reciever do in a telecommunications system? 29. Give three methods that a signal can be sent between two telephones. 30. Give an advantage of using a mobile phone. 31. Give a disadvantage of using a mobile phone. 32. What device is in the mouthpiece of a telephone handset? 33. What device is in the earpiece of a telephone handset? 34. What is the useful energy change in a microphone? 35. What is the useful energy change in a loudspeaker? 36. What speed do telephone signal travel in a metal wire? 37. How would it be possible to send a document using the telephone system? 38. Draw a simple wave that may be seen on an oscilloscope. Now draw a wave representing a louder sound. 39. Draw a simple wave that may be seen on an oscilloscope. Now draw a wave representing a quieter sound. 40. Draw a simple wave that may be seen on an oscilloscope. Now draw a wave representing a higher frequency sound. 41. Draw a simple wave that may be seen on an oscilloscope. Now draw a wave representing a lower frequency sound. Practical Electricity 1. Draw the circuit symbol for a battery. 2. Draw the circuit symbol for a lamp. 3. Draw the circuit symbol for a switch. 4. What does a battery supply to an electrical circuit? 5. What is the energy change in a lamp? 6. What is the energy change in a heater? 7. What is the energy change in a motor? 8. Draw a series circuit containing a battery, lamp and a switch. 9. What device is used to measure current? 10. What device is used to measure voltage? 11. Draw the circuit symbol for the device that is used to measure current. 12. Draw the circuit symbol for the device that is used to measure voltage. 13. Draw a parallel circuit containing a battery and two lamps. 14. What is an electric current? 15. What is the unit of electric current? 16. What is the unit of voltage? 17. Write down the missing values from the following circuits. 12 V 6V 2A __ A __V __ A __V __ A __V 4A __V 3A __V __ A 18. Draw a series circuit containing a battery a lamp and a resistor. Include a voltmeter and ammeter to measure the voltage across the lamp and the current in the lamp. 19. Draw the circuit symbol for a resistor. 20. Draw the circuit symbol for a variable resistor. 21. What energy change takes place in a resistor? 22. What device is used to measure resistance? 23. What is the unit of resistance? 24. What is the symbol for the unit of resistance? 25. What happens to the current in a circuit if the resistance is increased? 26. Give two practical uses for a variable resistor. 27. The voltage across a lamp is 6 volts when the current in it is 2 amperes. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. 28. Why are hoeshold appliances connected in parallel? 29. What is the value of the mains voltage? 30. Draw the circuit symbol for a fuse. 31. Name the three terminals in a plug and identify the colour of wire that should be connected to each terminal. 32. How does the fuse act as a safety device? 33. What is used in many homes now instead of fuses? 34. What factors affect the cost of electrical energy in the home? 35. A kettle has a power rating of 2 300W. What current will flow in the kettle when it is connected to the mains supply? 36. What happens to the conductivity of the human body when it gets wet? 37. What is the purpose of the earth wire? 38. What type of appliances do not need an earth wire? 39. Draw the symbol for double insulation. 40. Give three examples of dangerous situations involving electricity. 41. Draw a circuit diagram for a simple continuity tester. 42. Describe how a continuity tester could be used to identify an open circuit. Radiations 1. How many colours of light are produced from a laser? 2. Give one practical use of a laser. 3. What happens to light when it hits an object? 4. Give a use of optical fibres in medicine. 5. Draw the shape of a converging lens. 6. Draw the shape of a diverging lens. 7. Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens effects parallel rays of light. 8. Draw a diagram to show how a diverging lens effects parallel rays of light. 9. Draw a simple diagram of the eye to show short sight. 10. Draw a simple diagram of the eye to show long sight. 11. Draw a diagram to show how a lens can be used to correct long sight. 12. Draw a diagram to show how a lens can be used to correct short sight. 13. What can be used to detect X-rays? 14. Why must photographic film be used to detect X-rays? 15. Describe one use of X-rays in medicine. 15. Describe one use of X-rays in industry. 17. Why are X-rays dangerous? 18. Give a safety precaution that should be taken when using X-rays. Explain your answer. 19. What effect does gamma radiation have on living cells? 20. What would be needed to stop gamma rays? 21. Describe how gamma radiation can be used as a tracer. 22. What happens to the strength of a source of gamma radation as time passes? 23. Describe three safety precautions that should be taken when dealing with gamma radaition sources. 24. What is the name given to the gamma radiation all around us? 25. What is background radiation? 26. What is infrared radiation also known as? 27. Describe one use of infrared radiation in medicine. 28. Describe one non-medical use of infrared radiation. 29. Describe one use of ultraviolet radiation in medicine. 30. What do you see when you place a £10 note under a UV lamp? 31. Explain how you can use a UV pen to security mark your possessions. 32. What is the danger of over exposure to UV radiation? Sound and Music 1. What must happen for a sound to be produced? 2. What is transferred by a sound wave? 3. What is meant by the frequency of a sound wave? 4. What is the unit of frequency? 5. What happens to the pitch of a sound if it’s frequency increases? 6. Look at the oscilloscope patterns of sound waves below. Describe how sounds A and B compare with the original pattern. B A original 7. A pianist plays a note of frequency 256 Hz. What is the frequency of a note one octave higher? 8. Describe two ways a guitarist could increase the ferquency of a note produced by a single guitar string. 9. Which of the cylinders below would produce the highest note when you blow across the top of the cylinder? Explain your answer. A B C water water water 10. Give an example of a situation which shows that sound travels slower than light. 11. Describe how you could do an experiment to measure the speed of sound. 12. A tourist is 1 km away from the castle in Edinburgh when the 1 o’clock gun is fired. They notice a time difference of 3 seconds between seeing the flash from the gun barrel and hearing the sound of the gun. Calculate the speed of sound from this information. 13. Give an example of sound travelling through a solid. 14. Give an example of sound travelling through a liquid. 15. Give an example of sound travelling through a gas. 16. Why was the tag line for the film Alien “ In space no one can hear you scream.” good physics? 17. What is the normal frequency range of human hearing? 18. What do we call sounds of frequencies above the upper range of human hearing? 19.Describe a medical use of ultrasound. 20.Describe a non-medical use of ultrasound. 21. What is the unit of sound level measurement? 22. Give two examples of noise pollution. 23. Why is it important that we are not exposed to long periods of loud noise? 24. An amplifier is used in a stereo system.The amplifier has a gain of 20. The frequency of the input signal is 400 Hz. What is the frequency of the output signal? 25. What is the function of the microphone in a tannoy system? 26. What is the function of the amplifier in a tannoy system? 27. What is the function of the loudspeaker in a tannoy system? 28. An amplifier has a gain of 50. What does this mean? 29. An amplifier has an input voltage of 0.01 volts. The output voltage is 4 volts. Calculate the voltage gain of the amplifier. 30. Why does your voice always sound different to you when you hear yourself speak on a video? 31. Give two advantages of a CD over a cassette for listening to music.