* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for the LS
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
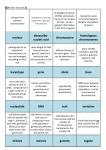
Study Guide for the Heredity Test Date of Test: _________ heredity: the passing of traits from parents to offspring offspring- the young (or baby) of two parents probability: the mathematical chance that an event will occur phenotype: an organism’s inherited physical appearance (blue eyes, tall, curly hair) genotype: an organism’s inherited combination of alleles (BB or Tt) alleles: two forms of the same gene (represented by letters such as TT, Tt, or tt) These may be dominant or recessive. Alleles make up your genotype dominant trait: a trait observed when at least one dominant allele (capital letter) for a characteristic is inherited (for example Rr or RR). When present a dominant trait will cover up a recessive trait and will ALWAYS appear in the first generation offspring. recessive trait: a trait that is apparent only when two recessive alleles (small letters) for the same characteristic are inherited (for example rr or bb) This trait recedes into the background in first generation offspring. generation: all of the people born at about the same time (example brothers and sisters) Genes: set of instructions donated by parents to offspring (genes are found on chromosomes) Sex cell: sperm and egg cells which hold half the number of chromosomes as body cells Sex chromosomes: The X and Y Chromosomes that are responsible for determining an organism’s gender. XX= female XY= male Mitosis: is the process in which one cell copies its DNA and divides into two identical body cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. (produces 2 identical daughter cells) Meiosis: is the process in which one cell goes through two divisions to become four separate sex cells (sperm and egg cells have half the amount of chromosomes) Back Important People: - Punnett developed a square that is used to visualize all the possible combinations of alleles in offspring resulting from a genetic cross. - Gregor Mendel was the first to discover genetics. He used plants to study the way traits are passed from one generation to the next Know the difference between mitosis and meiosis Kind of cell made Number of cells made Mitosis body cell 2 Meiosis sex cell (egg or sperm) 4 A= Red apples Number of chromosomes made same as original cell Half as many as the original cell Purpose of cell Growth and Repair Reproduction a= green apples Statistics: Genotype Ratio Phenotype Ratio 1 : 2 : 1 AA Aa aa 3 : Red apples Phenotype Percentage 1 green apple 75% or 3 red apples 4 25% or 1_ green apples 4