
Improving Mining Quality by Exploiting Local Dependency
... is incomplete or only partially up-to-date. Many queries ask for the minimum/maximum values among all sensor readings. For that, we need a cost-efficient way to infer such extrema while probing the sensors as little as possible. The problem here is related to filling in missing attributes in data cl ...
... is incomplete or only partially up-to-date. Many queries ask for the minimum/maximum values among all sensor readings. For that, we need a cost-efficient way to infer such extrema while probing the sensors as little as possible. The problem here is related to filling in missing attributes in data cl ...
presentation
... For various diseases the most discriminative genes are likely to correspond to a limited set of biological functions or pathways Hypothesis: Focusing to key functional expression patterns could result in improved accuracy as compared to analyzing individual gene expression readings Approach: E ...
... For various diseases the most discriminative genes are likely to correspond to a limited set of biological functions or pathways Hypothesis: Focusing to key functional expression patterns could result in improved accuracy as compared to analyzing individual gene expression readings Approach: E ...
Docs - Orange Data Mining
... The following workflow looks intimidating, but it’s not as complicated as it looks. The question we are trying to answer is: do different classifiers misclassify the same tissue samples? That is, are some specific test instances hard to classify? Are they outliers, or even originally misclassified ti ...
... The following workflow looks intimidating, but it’s not as complicated as it looks. The question we are trying to answer is: do different classifiers misclassify the same tissue samples? That is, are some specific test instances hard to classify? Are they outliers, or even originally misclassified ti ...
Genetic Linkage Analysis
... Model-free linkage methods can be used as a first screen of multiple markers to identify promising linkage relationships. Such promising linkage relationships can subsequently be confirmed by consideration of other markers, by standard model-based analysis, by other methods, or a combination of appr ...
... Model-free linkage methods can be used as a first screen of multiple markers to identify promising linkage relationships. Such promising linkage relationships can subsequently be confirmed by consideration of other markers, by standard model-based analysis, by other methods, or a combination of appr ...
Prediction and Validation of Gene-Disease Associations
... in model species has been explosive, which suggests an alternative way to find candidate genes for human diseases. McGary et al.[16] used this treasure trove of information to find surprising connections between model species phenotypes and human diseases by looking for pairs of human diseases and m ...
... in model species has been explosive, which suggests an alternative way to find candidate genes for human diseases. McGary et al.[16] used this treasure trove of information to find surprising connections between model species phenotypes and human diseases by looking for pairs of human diseases and m ...
Microarray Data Analysis for Detection and Classification of Viral
... methods for the analysis of a limited number of genes at a time [1], But microarray technology can assess thousands of genes or proteins simultaneously. The type of microarray depends on the materials placed on the slide: If the material is DNA, it is called DNA microarray, if the material is RNA, i ...
... methods for the analysis of a limited number of genes at a time [1], But microarray technology can assess thousands of genes or proteins simultaneously. The type of microarray depends on the materials placed on the slide: If the material is DNA, it is called DNA microarray, if the material is RNA, i ...
ppt
... B. The Paint Box & exchangable distributions on Partitions. C. All coalescents are restrictions of “The Coalescent” – a process with entrance boundary infinity. D. Robustness of “The Coalescent”: If offspring distribution is exchangeable and Var(n1) --> s2 & E(n1m) < Mm for all m, then genealogies f ...
... B. The Paint Box & exchangable distributions on Partitions. C. All coalescents are restrictions of “The Coalescent” – a process with entrance boundary infinity. D. Robustness of “The Coalescent”: If offspring distribution is exchangeable and Var(n1) --> s2 & E(n1m) < Mm for all m, then genealogies f ...
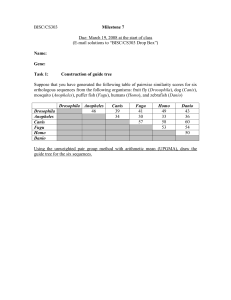
Milestone7
... At the top of the results page, click on the “Start Jalview” button to open an interactive display of the MSA. One of the advantages of a MSA is that it can provide insight into various properties of a family of proteins. When studying your MSA, if you find portions of your sequences that do not ali ...
... At the top of the results page, click on the “Start Jalview” button to open an interactive display of the MSA. One of the advantages of a MSA is that it can provide insight into various properties of a family of proteins. When studying your MSA, if you find portions of your sequences that do not ali ...
Distinguishing coding from non-coding sequences in a prokaryote
... where T P denotes the number of correctly recognized coding sequences, F N the number of coding sequences recognized as non-coding sequences, F P the number of noncoding sequences recognized as coding sequences, and T N the number of correctly recognized non-coding sequences. Then we use the algorit ...
... where T P denotes the number of correctly recognized coding sequences, F N the number of coding sequences recognized as non-coding sequences, F P the number of noncoding sequences recognized as coding sequences, and T N the number of correctly recognized non-coding sequences. Then we use the algorit ...
Unsupervised Gene Selection and Clustering using Simulated
... Feature selection algorithms can be broadly divided into two categories [3, 10]: filters and wrappers. Filters evaluate the relevance of each feature (subset) using the data set alone, while wrappers invoke the learning algorithm to evaluate the quality of each feature (subset). Both approaches, fil ...
... Feature selection algorithms can be broadly divided into two categories [3, 10]: filters and wrappers. Filters evaluate the relevance of each feature (subset) using the data set alone, while wrappers invoke the learning algorithm to evaluate the quality of each feature (subset). Both approaches, fil ...
Facilitating Genetic Analysis: SAS®, the NHLBI and CARe
... CARe investigators also have access to a standardized analysis pipeline for association analysis between genotype and phenotype data. Once an investigator has created a model for a phenotypic trait using the data they requested, they can submit the modeled trait and covariates to the Broad for analy ...
... CARe investigators also have access to a standardized analysis pipeline for association analysis between genotype and phenotype data. Once an investigator has created a model for a phenotypic trait using the data they requested, they can submit the modeled trait and covariates to the Broad for analy ...
BioConductor tutorial
... • A method is a function that performs an action on data (objects). • Methods define how a particular function should behave depending on the class of its arguments. • Methods allow computations to be adapted to particular data types, i.e., classes. • A generic function is a dispatcher, it examines ...
... • A method is a function that performs an action on data (objects). • Methods define how a particular function should behave depending on the class of its arguments. • Methods allow computations to be adapted to particular data types, i.e., classes. • A generic function is a dispatcher, it examines ...
Effective Clustering Algorithms for Gene Expression Data
... K-Means clustering [3], and SOM [9]. Of these K-Means clustering is a very simple and fast efficient one; it was developed by Mac Queen [7]. The K-Means algorithm is effective in producing clusters for many practical applications. But the computational complexity of the original K-Means algorithm is ...
... K-Means clustering [3], and SOM [9]. Of these K-Means clustering is a very simple and fast efficient one; it was developed by Mac Queen [7]. The K-Means algorithm is effective in producing clusters for many practical applications. But the computational complexity of the original K-Means algorithm is ...
Using uniformat and Gene[rate] to analyse data with ambiguities in
... data typings were reported to be not present as a result of pre–processing treatments [11]. To tackle this problem we have been pursuing and applying the alternative approach of adapting population genetics methods to ambiguous data (see references below). To achieve a generalisation of population g ...
... data typings were reported to be not present as a result of pre–processing treatments [11]. To tackle this problem we have been pursuing and applying the alternative approach of adapting population genetics methods to ambiguous data (see references below). To achieve a generalisation of population g ...
Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence... Nagoya, Japan, August 1997
... to be true, the associated uncertainty parameter is in fact the conditional probability that the head is true given that the body is true. Sometimes, more than one set of conditions can cause a predicate to be true. For example, if both a person’s parents have a gene, the first rule will fire twice, ...
... to be true, the associated uncertainty parameter is in fact the conditional probability that the head is true given that the body is true. Sometimes, more than one set of conditions can cause a predicate to be true. For example, if both a person’s parents have a gene, the first rule will fire twice, ...
PowerPoint slides - University of Maryland at College Park
... satisfy the minimum similarity threshold Help users determine the ...
... satisfy the minimum similarity threshold Help users determine the ...
Fuzzy ensemble clustering for DNA microarray data analysis
... improve the accuracy and the reliability of clustering results [2, 3, 4]. In bioinformatics applications, recently proposed methods based on random projections [5] have been also successfully applied to gene expression data analysis [6]. A major problem with these approaches is represented by the bi ...
... improve the accuracy and the reliability of clustering results [2, 3, 4]. In bioinformatics applications, recently proposed methods based on random projections [5] have been also successfully applied to gene expression data analysis [6]. A major problem with these approaches is represented by the bi ...
Fachhochschule Wiesbaden Lectures on Life Sciences Automation
... Alamos National Laboratory: Solve a globalized diagnosis problem for infectious diseases with SOA technology. z (Jan. 11, 2008) Robotics and laboratory automation – Reinhold Schäfer, FHW (Thermo Scientific?) z (Jan. 16, 2008, 14:30 MEZ) In Vivo Automation – Edward J. Kuspiel, Jim Myslik, BMS: Review ...
... Alamos National Laboratory: Solve a globalized diagnosis problem for infectious diseases with SOA technology. z (Jan. 11, 2008) Robotics and laboratory automation – Reinhold Schäfer, FHW (Thermo Scientific?) z (Jan. 16, 2008, 14:30 MEZ) In Vivo Automation – Edward J. Kuspiel, Jim Myslik, BMS: Review ...
AN ALGORITHM FOR MISSING VALUE ESTIMATION FOR DNA
... structure of the data to impute the missing values. KNNimpute uses the weighted averages of the K-nearest uncorrupted neighbors. LLS has two versions to find similar genes whose expressions are not corrupted: the L2 -norm and the Pearson’s correlation coefficients. After a group of similar genes C a ...
... structure of the data to impute the missing values. KNNimpute uses the weighted averages of the K-nearest uncorrupted neighbors. LLS has two versions to find similar genes whose expressions are not corrupted: the L2 -norm and the Pearson’s correlation coefficients. After a group of similar genes C a ...
Supplementary Information (doc 190K)
... same tube as the blood count. Analysis is simple and fast, although it requires a specific instrument. Zinc protoporphyrin is elevated in iron deficiency, but may be falsely high in lead intoxication or if the bilirubin levels are raised. Some studies have shown increased levels in thalassaemia carr ...
... same tube as the blood count. Analysis is simple and fast, although it requires a specific instrument. Zinc protoporphyrin is elevated in iron deficiency, but may be falsely high in lead intoxication or if the bilirubin levels are raised. Some studies have shown increased levels in thalassaemia carr ...
lecture9 - Stanford AI Lab
... Measure levels of RNA expression using probes with partial homology ...
... Measure levels of RNA expression using probes with partial homology ...
Comparison of Target-Capture and Restriction
... ultraconserved elements (UCEs), are emerging as two of the most popular methods for phylogenomics using reducedrepresentation genomic data sets. These two methods were designed to target different evolutionary timescales: RAD-seq was designed for population-genomic level questions and UCEs for deepe ...
... ultraconserved elements (UCEs), are emerging as two of the most popular methods for phylogenomics using reducedrepresentation genomic data sets. These two methods were designed to target different evolutionary timescales: RAD-seq was designed for population-genomic level questions and UCEs for deepe ...
Genetic Algorithms for Evolving Deep Neural Networks
... yielded a smaller reconstruction error, as well as a sparser network. In order to compare the classification accuracy of the two methods, we ran 10,000 new test samples through the two trained networks and recorded the 50 output values for each sample. Recall that in this test phase the weights of th ...
... yielded a smaller reconstruction error, as well as a sparser network. In order to compare the classification accuracy of the two methods, we ran 10,000 new test samples through the two trained networks and recorded the 50 output values for each sample. Recall that in this test phase the weights of th ...
Concepts of Biology - Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
... point where a split occurs in a tree, called a branch point, represents where a single lineage evolved into distinct new ones. Many phylogenetic trees have a single branch point at the base representing a common ancestor of all the branches in the tree. Scientists call such trees rooted, which means ...
... point where a split occurs in a tree, called a branch point, represents where a single lineage evolved into distinct new ones. Many phylogenetic trees have a single branch point at the base representing a common ancestor of all the branches in the tree. Scientists call such trees rooted, which means ...












![Using uniformat and Gene[rate] to analyse data with ambiguities in](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003111231_1-701ba56eac6c2ce171209330d44b2e19-300x300.png)









