Work and Energy
... W = (2.0 kg) (9.8 m/s2) (1.0 m) W = 20 J Now Sally holds the book over her head. What is the work she is now exerting on the book? W = 0 J (no movement = no work) ...
... W = (2.0 kg) (9.8 m/s2) (1.0 m) W = 20 J Now Sally holds the book over her head. What is the work she is now exerting on the book? W = 0 J (no movement = no work) ...
What a Middle School 7th grade science student should know
... Energy can change from one form to another, although in the process some energy is always converted to heat. Some systems transform energy with less loss of heat than others. Electrical energy can be produced from a variety of energy sources and can be transformed into almost any other form of e ...
... Energy can change from one form to another, although in the process some energy is always converted to heat. Some systems transform energy with less loss of heat than others. Electrical energy can be produced from a variety of energy sources and can be transformed into almost any other form of e ...
Torque, Atwood Machines, Angular M.
... Maybe but it isn't easy. That extra distance AWAY from the point of rotation gives you the extra leverage you need. THUS we call this distance the LEVER (EFFORT) ARM (r) . ...
... Maybe but it isn't easy. That extra distance AWAY from the point of rotation gives you the extra leverage you need. THUS we call this distance the LEVER (EFFORT) ARM (r) . ...
Lab Writeup Springs and SHM
... Many forces vary with position. That is, they can grow stronger or weaker as the position of the particle undergoing the force changes. One such example is the force exerted on a mass attached to a spring. As the particle is moved away from the attached spring, the spring will exert more force to re ...
... Many forces vary with position. That is, they can grow stronger or weaker as the position of the particle undergoing the force changes. One such example is the force exerted on a mass attached to a spring. As the particle is moved away from the attached spring, the spring will exert more force to re ...
Lecture 06 - Potential
... the electric field is equal to the energy PER UNIT CHARGE between the points: ...
... the electric field is equal to the energy PER UNIT CHARGE between the points: ...
9.2 The Center of Mass
... where M is the total mass, and ri are the position vectors of the masses mi. Differentiating, where the v vectors are velocity vectors. This leads to ...
... where M is the total mass, and ri are the position vectors of the masses mi. Differentiating, where the v vectors are velocity vectors. This leads to ...
CnErCS2
... Thus, from this view point, ‘wormholes’ and null hyper spaces do not exist in the real world. They should be purged from Physics and forgotten. Their existence for public culture is pregnant with psychological pathologies and trauma. ‘Black holes’ are an illogical construction from GRT. The essence ...
... Thus, from this view point, ‘wormholes’ and null hyper spaces do not exist in the real world. They should be purged from Physics and forgotten. Their existence for public culture is pregnant with psychological pathologies and trauma. ‘Black holes’ are an illogical construction from GRT. The essence ...
Topic 6 and 10 TEST
... the work done per unit mass to move a small mass from infinity to the point. ...
... the work done per unit mass to move a small mass from infinity to the point. ...
80 Newton`s Laws of Motion - Merrillville Community School
... The force of the gases pushes downward at the force of the gases is pushing the same time that the gases push the rocket the rocket up. upwards. It may seem that the third law contradicts the second law. If there are always equal and opposite forces, how can there ever be an unbalanced force? In the ...
... The force of the gases pushes downward at the force of the gases is pushing the same time that the gases push the rocket the rocket up. upwards. It may seem that the third law contradicts the second law. If there are always equal and opposite forces, how can there ever be an unbalanced force? In the ...
Chapter 02 Motion
... 56. A hole is drilled to the center of the earth and a ball is dropped into it. When the ball is at the earth's center, compared with their respective values at the earth's surface, A. its mass and weight are the same. B. its mass and weight are both 0. C. its mass is the same and its weight is 0. D ...
... 56. A hole is drilled to the center of the earth and a ball is dropped into it. When the ball is at the earth's center, compared with their respective values at the earth's surface, A. its mass and weight are the same. B. its mass and weight are both 0. C. its mass is the same and its weight is 0. D ...
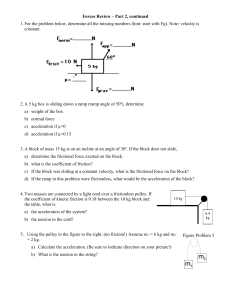
Review Forces Part 2
... a) What is the acceleration of the block? b) What is the distance covered in 10 s, if the initial velocity is 1.5 m/s? 7. A boy on a sled (total mass = 80 kg) is sliding down a snow-covered hill. The slope is at an angle of 15 to the horizontal. Find the boy’s a) acceleration if there is no frictio ...
... a) What is the acceleration of the block? b) What is the distance covered in 10 s, if the initial velocity is 1.5 m/s? 7. A boy on a sled (total mass = 80 kg) is sliding down a snow-covered hill. The slope is at an angle of 15 to the horizontal. Find the boy’s a) acceleration if there is no frictio ...