Gravity, Not Mass Increases with Velocity
... becomes harder to change the objects motion—acceleration, deceleration and deviation from its course. According to the main stream relativistic theory, this is due to the increase of the relativistic mass of the object. That requires more than one interpretation of what mass means. One is that mass ...
... becomes harder to change the objects motion—acceleration, deceleration and deviation from its course. According to the main stream relativistic theory, this is due to the increase of the relativistic mass of the object. That requires more than one interpretation of what mass means. One is that mass ...
Chris Khan 2008 Physics Chapter 9 Linear momentum is defined as
... 15.7 m/s. Jumping for joy, a 72-kg balla jumps upward with a speed of 2.1 m/s. What is the impulse experienced by him? Before he jumps, the floor exerts a force of mg on the contestant. What additional average upward force does the floor exert if the contestant pushes down on it for 0.36s during the ...
... 15.7 m/s. Jumping for joy, a 72-kg balla jumps upward with a speed of 2.1 m/s. What is the impulse experienced by him? Before he jumps, the floor exerts a force of mg on the contestant. What additional average upward force does the floor exert if the contestant pushes down on it for 0.36s during the ...
Kinematics Problems, Page 1 Formula: Δx = ½(vf + vi) Δt “LITTLE
... 1) (Solve for Δx) From rest, a ball rolls down a hill, experiencing constant acceleration. After 12 seconds its velocity is 6.0 m/s. How far did it roll? 2) (Solve for Δx) A theme park ride, with an initial velocity of 24m/s starts up a steep ramp. After 4.0 seconds it comes to a stop. How long is t ...
... 1) (Solve for Δx) From rest, a ball rolls down a hill, experiencing constant acceleration. After 12 seconds its velocity is 6.0 m/s. How far did it roll? 2) (Solve for Δx) A theme park ride, with an initial velocity of 24m/s starts up a steep ramp. After 4.0 seconds it comes to a stop. How long is t ...
V 1
... • For any conservative force F we can define a potential energy function U in the following way: W = ...
... • For any conservative force F we can define a potential energy function U in the following way: W = ...
Lec 3
... There is a greater force of air resistance on the falling elephant, which “plows through” more air than the feather in getting to the ground. The elephant encounters several newtons of air resistance, which compared to its huge weight has practically no effect on its rate of fall. Only a small fract ...
... There is a greater force of air resistance on the falling elephant, which “plows through” more air than the feather in getting to the ground. The elephant encounters several newtons of air resistance, which compared to its huge weight has practically no effect on its rate of fall. Only a small fract ...
Chapter 7 Solutions
... IDENTIFY: Initially the ball has all kinetic energy, but at its highest point it has kinetic energy and potential energy. Since it is thrown upward at an angle, its kinetic energy is not zero at its highest point. SET UP: Apply conservation of energy: Kf Uf Ki Ui . Let yi 0, so yf h, the m ...
... IDENTIFY: Initially the ball has all kinetic energy, but at its highest point it has kinetic energy and potential energy. Since it is thrown upward at an angle, its kinetic energy is not zero at its highest point. SET UP: Apply conservation of energy: Kf Uf Ki Ui . Let yi 0, so yf h, the m ...
Lecture 1
... Primary dimensions: In fluid mechanics there are only four primary dimensions from which all other dimensions can be derived. These are mass, length, time and temperature. Qualitative: Identify the nature, or type, of the characteristics (such as length, time, stress, and ...
... Primary dimensions: In fluid mechanics there are only four primary dimensions from which all other dimensions can be derived. These are mass, length, time and temperature. Qualitative: Identify the nature, or type, of the characteristics (such as length, time, stress, and ...
NASA Explorer Schools - NSTA Learning Center
... Calculated by: F = ma (F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration) ...
... Calculated by: F = ma (F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration) ...
AAAAA
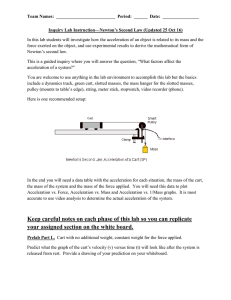
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
Lesson 1 – Stationary Point Charges and Their Forces
... If we try to take this idea quite literally, we immediately come up with a host of objections: • How does the real particle find the energy necessary to continuously produce virtual particles, and yet not lose energy of its own? • If nothing absorbs the virtual particle, then does only the one real ...
... If we try to take this idea quite literally, we immediately come up with a host of objections: • How does the real particle find the energy necessary to continuously produce virtual particles, and yet not lose energy of its own? • If nothing absorbs the virtual particle, then does only the one real ...
Chapter 13: Work and Machines
... • Is applying a force to an object to move it through a distance • W= distance x force • Units is joules (d-meters, f-newtons) • Just holding a box is not work • Picking up a box you are doing work • When work is done energy is added to it • When throwing a ball your work is equal to the kinetic ene ...
... • Is applying a force to an object to move it through a distance • W= distance x force • Units is joules (d-meters, f-newtons) • Just holding a box is not work • Picking up a box you are doing work • When work is done energy is added to it • When throwing a ball your work is equal to the kinetic ene ...
P5 Key facts sheets: RAG - North Leamington School
... Relative speed depends on the direction of movement (in context of two cars travelling on a ...
... Relative speed depends on the direction of movement (in context of two cars travelling on a ...