Circular Motion and Gravity
... • Tangential speed depends on the distance from the object to the center of the circular path. • When the tangential speed is constant, the motion is described as uniform circular motion. ...
... • Tangential speed depends on the distance from the object to the center of the circular path. • When the tangential speed is constant, the motion is described as uniform circular motion. ...
Sample Paper
... (c) a body having zero velocity but non-zero acceleration, (d) a body having constant velocity but non-zero acceleration ...
... (c) a body having zero velocity but non-zero acceleration, (d) a body having constant velocity but non-zero acceleration ...
rotational kinetic energy
... L is a constant for the system (as motion of sun is negligible). L is constant for planet. So K is ...
... L is a constant for the system (as motion of sun is negligible). L is constant for planet. So K is ...
Abstract: What could the force of kinetic friction depend on? Theory
... Click and drag to get the region of interest and use the STAT button to get the mean. You don’t need to print out any LoggerPro graphs. Record your kinetic friction data in the following table in Excel! Do at least 7 trials, with 7 different added masses. Choose a good range of added masses! Go up b ...
... Click and drag to get the region of interest and use the STAT button to get the mean. You don’t need to print out any LoggerPro graphs. Record your kinetic friction data in the following table in Excel! Do at least 7 trials, with 7 different added masses. Choose a good range of added masses! Go up b ...
Placing Charges Conceptual Question
... The two forces acting on charge 2 correspond to the forces exerted on it by charge 1 and charge 3. This means that one of these forces must pair with a force on charge 1 of equal magnitude and opposite direction and the other must pair with a force on charge 3 of equal magnitude and opposite directi ...
... The two forces acting on charge 2 correspond to the forces exerted on it by charge 1 and charge 3. This means that one of these forces must pair with a force on charge 1 of equal magnitude and opposite direction and the other must pair with a force on charge 3 of equal magnitude and opposite directi ...
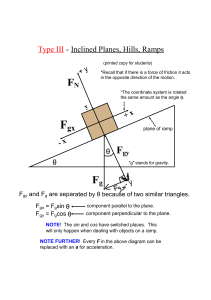
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... *Recall that if there is a force of friction it acts in the opposite direction of the motion. *The coordinate system is rotated the same amount as the angle θ. ...
... *Recall that if there is a force of friction it acts in the opposite direction of the motion. *The coordinate system is rotated the same amount as the angle θ. ...
Lecture 7: Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... • An object can have a centripetal acceleration only if some external force acts on it. • An example is a ball whirling in a circle at the end of a string. In this case the tension in the string is the force that creates the centripetal force. Net centripetal force Fc is the sum of the radial compon ...
... • An object can have a centripetal acceleration only if some external force acts on it. • An example is a ball whirling in a circle at the end of a string. In this case the tension in the string is the force that creates the centripetal force. Net centripetal force Fc is the sum of the radial compon ...
Kinematics Multiples
... Although the speed varies linearly with time, KE is the square of the speed, so it should be a parabola, which rules out graph B. In graph D the PE is decreasing quickly at first and then more slowly while in graph A the PE is decreasing slowly then quickly. Since the ball speeds up as it approaches ...
... Although the speed varies linearly with time, KE is the square of the speed, so it should be a parabola, which rules out graph B. In graph D the PE is decreasing quickly at first and then more slowly while in graph A the PE is decreasing slowly then quickly. Since the ball speeds up as it approaches ...
Roller Coaster Fun!
... Potential energy - energy that is stored for later use. Law of Conservation of Energy - Energy can change from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed. When you ride a roller coaster a motor does the work to get you up the first hill. As the coaster is being pulled up the hill by the ...
... Potential energy - energy that is stored for later use. Law of Conservation of Energy - Energy can change from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed. When you ride a roller coaster a motor does the work to get you up the first hill. As the coaster is being pulled up the hill by the ...
clicking here
... (c) a body having zero velocity but non-zero acceleration, (d) a body having constant velocity but non-zero acceleration ...
... (c) a body having zero velocity but non-zero acceleration, (d) a body having constant velocity but non-zero acceleration ...
Conservation of Mechanical Energy Lab Name Materials: Computer
... 1. How much of the total Energy is Potential Energy at Position One? 2. At position 2, how much of the Potential Energy from Position 1 was transferred to Kinetic Energy? 3. At Positions 3 and 4, the roller coaster car was at a height between position 1 and 2. How did the Kinetic Energy at position ...
... 1. How much of the total Energy is Potential Energy at Position One? 2. At position 2, how much of the Potential Energy from Position 1 was transferred to Kinetic Energy? 3. At Positions 3 and 4, the roller coaster car was at a height between position 1 and 2. How did the Kinetic Energy at position ...
Winter 11 (Grigg)
... 5. For this problem you are working with a spring with spring constant 49 N/m. Assume there is no damping. (a) (10 points) An object of unknown mass hangs from the spring. It is pulled 25 cm down from equilibrium and set in motion with an upward velocity of 1 m/s. You measure the amplitude of the re ...
... 5. For this problem you are working with a spring with spring constant 49 N/m. Assume there is no damping. (a) (10 points) An object of unknown mass hangs from the spring. It is pulled 25 cm down from equilibrium and set in motion with an upward velocity of 1 m/s. You measure the amplitude of the re ...