104 mid 1 1434-1435
... a)The net electric flux through a closed surface depends on the total charge located outside the surface ( F ...
... a)The net electric flux through a closed surface depends on the total charge located outside the surface ( F ...
Sound Waves & Electromagneic W
... Properties of Electromagnetic Waves All electromagnetic waves: travel at the speed (c) of 3 * 108 ms-1 in free space are transverse obey the laws of reflection and refraction show interference and diffraction effects can be polarized are unaffected by electric and magnetic fields ...
... Properties of Electromagnetic Waves All electromagnetic waves: travel at the speed (c) of 3 * 108 ms-1 in free space are transverse obey the laws of reflection and refraction show interference and diffraction effects can be polarized are unaffected by electric and magnetic fields ...
Advanced lab-class for bachelor students in physics
... of the electron spin and enables direct measurement of the Bohr magneton µB . Therefore, the SternGerlach experiment is a fundamental experiment, which demonstrates the nature of quantum mechanics. Later the experiment was repeated using hydrogen atoms. In our lab course, potassium atoms are used. ...
... of the electron spin and enables direct measurement of the Bohr magneton µB . Therefore, the SternGerlach experiment is a fundamental experiment, which demonstrates the nature of quantum mechanics. Later the experiment was repeated using hydrogen atoms. In our lab course, potassium atoms are used. ...
Psc CH-21 Electric Fields
... 4.5 x 10 N is measured between two particles. One particle has a charge of ...
... 4.5 x 10 N is measured between two particles. One particle has a charge of ...
METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR POWERING A
... induced curvature that causes these conditions. The top’s spin acts as a driving function to amplify Φ (the scalar potential), and thus enhance counter-gravitation between the top & base, at resonance. This spin connection resonance (SCR) is defined in [6] thru [8]. As shown above, it too is needed ...
... induced curvature that causes these conditions. The top’s spin acts as a driving function to amplify Φ (the scalar potential), and thus enhance counter-gravitation between the top & base, at resonance. This spin connection resonance (SCR) is defined in [6] thru [8]. As shown above, it too is needed ...
A Circuit Approach to Teaching Skin Effect
... which can be demonstrated using only circuit analysis and Faraday’s Law. A simple circuit with three equal, parallel resistors, arranged in a plane can be used to illustrate the crowding of current to the outside resistors, to the “skin”. For electrical engineering students with a strong circuits an ...
... which can be demonstrated using only circuit analysis and Faraday’s Law. A simple circuit with three equal, parallel resistors, arranged in a plane can be used to illustrate the crowding of current to the outside resistors, to the “skin”. For electrical engineering students with a strong circuits an ...
PPT - LSU Physics
... • Electric potential: work needed to bring +1C from infinity; units = V = Volt • Electric potential uniquely defined for every point in space -- independent of path! • Electric potential is a scalar -- add contributions from individual point charges • We calculated the electric potential produced by ...
... • Electric potential: work needed to bring +1C from infinity; units = V = Volt • Electric potential uniquely defined for every point in space -- independent of path! • Electric potential is a scalar -- add contributions from individual point charges • We calculated the electric potential produced by ...
16-5 and 16-6 Coulomb`s Law
... Two 40 gram masses each with a charge of 3μC are placed 50cm apart. Compare the gravitational force between the two masses to the electric force between the two masses. (Ignore the force of the earth on the two masses) ...
... Two 40 gram masses each with a charge of 3μC are placed 50cm apart. Compare the gravitational force between the two masses to the electric force between the two masses. (Ignore the force of the earth on the two masses) ...
Magnetic Fields
... Example 29.1 Proton Moving in a Magnetic Field • If the particle had been an electron, do not use the negative sign of the charge in the calculation. We will continue to let the direction of the vector determine the sign of the vectors associated with magnetic fields. • Use the right-hand rule to d ...
... Example 29.1 Proton Moving in a Magnetic Field • If the particle had been an electron, do not use the negative sign of the charge in the calculation. We will continue to let the direction of the vector determine the sign of the vectors associated with magnetic fields. • Use the right-hand rule to d ...
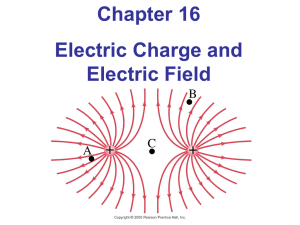
Unit 2 Electric Charge and Electric Field 1. Learn the following
... 2.Read and translate the text: Electric Charge and Electric Field Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or ...
... 2.Read and translate the text: Electric Charge and Electric Field Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or ...
Motional Emf
... two show-work problems (each worth 25 points), giving 100 points total. 2) Closed book and closed notes. 3) Equations and constants will be provided on the midterm 4) Covers the material in Chapters 16, 17, 18, 19, and 20 ...
... two show-work problems (each worth 25 points), giving 100 points total. 2) Closed book and closed notes. 3) Equations and constants will be provided on the midterm 4) Covers the material in Chapters 16, 17, 18, 19, and 20 ...
2. Forces
... • x0 = ±1: These are the local maximum and minimum. If we drop the particle at these points, it stays there for all time. • x0 ∈ (−1, +2): Here the particle is trapped in the dip. It oscillates backwards and forwards between the two points with potential energy V (x0 ). The particle can’t climb to t ...
... • x0 = ±1: These are the local maximum and minimum. If we drop the particle at these points, it stays there for all time. • x0 ∈ (−1, +2): Here the particle is trapped in the dip. It oscillates backwards and forwards between the two points with potential energy V (x0 ). The particle can’t climb to t ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.