Design, Modeling and Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices
... • Equivalent this extra electrostatic field to a field generated by another (equivalent) single charge; • Sum up the electrostatic fields generated by the two charges; • Using the linear superposition theory, we can treat the dielectric media (with many dipoles) in any electrostatic field (formed by ...
... • Equivalent this extra electrostatic field to a field generated by another (equivalent) single charge; • Sum up the electrostatic fields generated by the two charges; • Using the linear superposition theory, we can treat the dielectric media (with many dipoles) in any electrostatic field (formed by ...
HOTS(Unsolved)Questions Electrostatics
... acting on the same particle. 3. The plates of a parallel plate system are charged upto 100V. A 4mm thickness dielectric slab is inserted between the plates. Then to maintain the same potential difference, the distance between the systems plates is increased by 2mm. find the dielectric constant. 4. A ...
... acting on the same particle. 3. The plates of a parallel plate system are charged upto 100V. A 4mm thickness dielectric slab is inserted between the plates. Then to maintain the same potential difference, the distance between the systems plates is increased by 2mm. find the dielectric constant. 4. A ...
Orbitals
... The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any attempt to define the path of the electron is incorrect. ...
... The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any attempt to define the path of the electron is incorrect. ...
QHE theoretical background
... kind of accuracy is unusually good, and implies that there must be some kind of deeper significance to the underlying physics. When Klitzing first published his data, condensed matter physicists immediately began working to develop a more fundamental theory to explain this accuracy. One clue to the ...
... kind of accuracy is unusually good, and implies that there must be some kind of deeper significance to the underlying physics. When Klitzing first published his data, condensed matter physicists immediately began working to develop a more fundamental theory to explain this accuracy. One clue to the ...
Mathematical model of a multi-parameter oscillator based on a core
... Over the years linear motors have been taking on bigger and bigger shares in the market for precise positioning systems. They provide a dynamically superior although costly alternative to standard drives such as feed screw conveyors. For a motor to correctly project a desired motion profile a specif ...
... Over the years linear motors have been taking on bigger and bigger shares in the market for precise positioning systems. They provide a dynamically superior although costly alternative to standard drives such as feed screw conveyors. For a motor to correctly project a desired motion profile a specif ...
Modern Physics
... • Max Planck 1900 & Albert Einstein 1905: Planck provided the basic ideas led to the quantum theory & Einstein formulated his special theory of relativity • These developments led to understand the nature, behavior, structure and properties of many materials ...
... • Max Planck 1900 & Albert Einstein 1905: Planck provided the basic ideas led to the quantum theory & Einstein formulated his special theory of relativity • These developments led to understand the nature, behavior, structure and properties of many materials ...
AP Physics – Newton`s Laws – Force and Motion Types of Forces
... 1. Identify the system to be analyzed. This may be only a part of a more complicated system. This is really the most important step. 2. Select a reference frame or coordinate system, stationary or moving, but not accelerating, within which to analyze your system. 3. Identify all forces acting on the ...
... 1. Identify the system to be analyzed. This may be only a part of a more complicated system. This is really the most important step. 2. Select a reference frame or coordinate system, stationary or moving, but not accelerating, within which to analyze your system. 3. Identify all forces acting on the ...
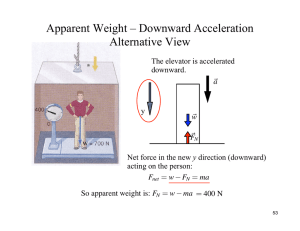
Apparent Weight – Downward Acceleration Alternative View
... high speed of sliding may cause heating and a change in the properties of the surfaces. ...
... high speed of sliding may cause heating and a change in the properties of the surfaces. ...
Magnetic Resonance TOPIC 3
... Permanents magnets have the advantage that their magnetic field does not extend as far away from the magnet (fringe field) as do the other magnetic field of other types. ...
... Permanents magnets have the advantage that their magnetic field does not extend as far away from the magnet (fringe field) as do the other magnetic field of other types. ...
Modeling the Dynamic Solar Atmosphere:
... (2) A robust method of determining the electric field consistent with both the observed evolution of the photospheric field and Faraday’s Law (3) An MHD code (or set of coupled codes) capable of modeling a region encompassing the photosphere (where relatively reliable measurements of the magnetic fi ...
... (2) A robust method of determining the electric field consistent with both the observed evolution of the photospheric field and Faraday’s Law (3) An MHD code (or set of coupled codes) capable of modeling a region encompassing the photosphere (where relatively reliable measurements of the magnetic fi ...
Magnetism
... Does every magnet necessarily have a north and a south pole? Answer: Yes, just as every coin has two sides, a “head” and a “tail.” ...
... Does every magnet necessarily have a north and a south pole? Answer: Yes, just as every coin has two sides, a “head” and a “tail.” ...
Ch16_2008
... their atoms • Removing electrons from a material makes it positive • In solids, it is always the free electrons that move • Electrical charge on the plastic rod induces a separation of charge in scraps of paper and thus attracts them. ...
... their atoms • Removing electrons from a material makes it positive • In solids, it is always the free electrons that move • Electrical charge on the plastic rod induces a separation of charge in scraps of paper and thus attracts them. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.