Ischemic heart disease
... Because as we said earlier, in 90%of the cases we have a condition where we have atherosclerotic lesions causing fixed supply and this will come to the surface once demands have increased. We want to know, specifically in this situation, what kind of things can increase myocardial oxygen demands (m ...
... Because as we said earlier, in 90%of the cases we have a condition where we have atherosclerotic lesions causing fixed supply and this will come to the surface once demands have increased. We want to know, specifically in this situation, what kind of things can increase myocardial oxygen demands (m ...
Unit 10 Student Guided Notes Heart -Introduction Parts of the Heart
... VENTRICLES Diastole Systole Diastole ...
... VENTRICLES Diastole Systole Diastole ...
Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation
... 1. Identify the two divisions of circulation and track the pathway of the blood through both circulations. 2. Outline the various parts of circulation and identify the differences in structure, function, pressure and velocity of blood in different vessels. 3. Describe the physiological anatomy of th ...
... 1. Identify the two divisions of circulation and track the pathway of the blood through both circulations. 2. Outline the various parts of circulation and identify the differences in structure, function, pressure and velocity of blood in different vessels. 3. Describe the physiological anatomy of th ...
Vericel to Present Data at the American Heart Association`s
... form of abnormal heart rhythm that originate in the ventricles of the heart and are common in patients with heart failure and cardiomyopathy. Previous studies have demonstrated an association between ventricular arrhythmias and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with left ventricu ...
... form of abnormal heart rhythm that originate in the ventricles of the heart and are common in patients with heart failure and cardiomyopathy. Previous studies have demonstrated an association between ventricular arrhythmias and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with left ventricu ...
Assumed Knowledge Or What you should know and don`t!!
... The main aim of the Respiratory System is to bring blood into contact with atmospheric air so that O2 Can be taken in and CO2 can be expelled. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing in and out!) follows a particular pathway; Task 1. Put the following structures in order to show the route of air from the a ...
... The main aim of the Respiratory System is to bring blood into contact with atmospheric air so that O2 Can be taken in and CO2 can be expelled. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing in and out!) follows a particular pathway; Task 1. Put the following structures in order to show the route of air from the a ...
Lab 3 – The Mammalian Cardiovascular System
... As increased muscle activity from exercise caused increased rates of cellular respiration in our subject, there was a greater demand for oxygen (O2) to be replenished and carbon dioxide (CO2) and other wastes to be removed from bodily tissues. The same demand was produced in our subject when they he ...
... As increased muscle activity from exercise caused increased rates of cellular respiration in our subject, there was a greater demand for oxygen (O2) to be replenished and carbon dioxide (CO2) and other wastes to be removed from bodily tissues. The same demand was produced in our subject when they he ...
Physiology: Lecture Study Guide (muscle - Faculty Websites
... 2. What is the right side of the heart responsible for? What does the left side of the heart do? 3. What are intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue? How do they aid cardiac muscle contraction? 4. Describe the roles of the autorhythmic and contractile cells. I. Describe how each is depolarized a ...
... 2. What is the right side of the heart responsible for? What does the left side of the heart do? 3. What are intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue? How do they aid cardiac muscle contraction? 4. Describe the roles of the autorhythmic and contractile cells. I. Describe how each is depolarized a ...
HYPERTENSIVE HEART DISEASE (Hypertensive cardiomyopathy)
... • Individual myocyte hypertrophy increases the distance for oxygen and nutrient diffusion from adjacent capillaries. • In a significant number of patients there is associated coronary atherosclerosis accompanying hypertension which may further lead to ischemia ...
... • Individual myocyte hypertrophy increases the distance for oxygen and nutrient diffusion from adjacent capillaries. • In a significant number of patients there is associated coronary atherosclerosis accompanying hypertension which may further lead to ischemia ...
Questions to hand in - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Observe the toes on your pig. How many toes are on the feet? _____________________ Do they have an odd or even number of toes? _________________________________ ...
... Observe the toes on your pig. How many toes are on the feet? _____________________ Do they have an odd or even number of toes? _________________________________ ...
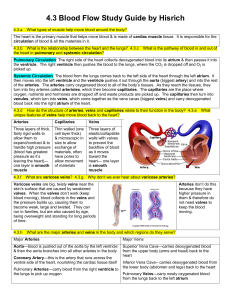
4.3 Blood Flow Study Guide by Hisrich
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
4.3 Blood Flow Study Guide by Hisrich
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
4.3 Blood Flow Study Guide by Hisrich
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
... Systemic Circulation: The blood from the lungs comes back to the left side of the heart through the left atrium. It then moves into the left ventricle and the ventricle pushes it out through the aorta (biggest artery) and into the rest of the arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to all of t ...
Twiddler`s syndrome: a rare cause of implantable cardioverter
... Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. & The Author 2015. For permissions please email: [email protected]. ...
... Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. & The Author 2015. For permissions please email: [email protected]. ...
over view of circulatory system heart and vessels
... Vessels carry the blood through the circuits ...
... Vessels carry the blood through the circuits ...
“Dyspnea” A Cardiologist Perspective
... • Echocardiogram: The echocardiogram showed normal left and right ventricular systolic function. Mild left ventricular hypertrophy with mild diastolic dysfunction. The E:e’ ratio was 9. Diastolic filling pressures were reportedly normal. There was mild left atrial enlargement. Aortic sclerosis, mild ...
... • Echocardiogram: The echocardiogram showed normal left and right ventricular systolic function. Mild left ventricular hypertrophy with mild diastolic dysfunction. The E:e’ ratio was 9. Diastolic filling pressures were reportedly normal. There was mild left atrial enlargement. Aortic sclerosis, mild ...
Cardiovascular Board Review II
... Cardiac markers are often unreliable in patient with cocaineassociated MI Aspirin and b-blockers are indicated A minority of patients with cocaine-associated MI have evidence of underlying coronary artery disease Palpitations and tachycardia are the most commonly associated symptoms The average time ...
... Cardiac markers are often unreliable in patient with cocaineassociated MI Aspirin and b-blockers are indicated A minority of patients with cocaine-associated MI have evidence of underlying coronary artery disease Palpitations and tachycardia are the most commonly associated symptoms The average time ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Synchronous contraction pattern is reflected by homogeneous phase angle distribution of polar map (left) and narrow highly peaked histogram (right). At the 6-month follow-up, no improvement in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class was observed, and LV ejection fraction remained unchange ...
... Synchronous contraction pattern is reflected by homogeneous phase angle distribution of polar map (left) and narrow highly peaked histogram (right). At the 6-month follow-up, no improvement in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class was observed, and LV ejection fraction remained unchange ...
Delivery Plan – unit 2: Practical Engineering and Communication
... Find your heart rate by taking your pulse. What is your resting heart rate? ………………………. ...
... Find your heart rate by taking your pulse. What is your resting heart rate? ………………………. ...
File
... through the pulmonary artery (and round to the lungs) as the left ventricle pumps through the aorta (and round the body) Heart Rate (Pulse) is the number of heartbeats that occurs per minute Stroke Volume is the volume of blood expelled by each ventricle on contraction. The stronger the contraction, ...
... through the pulmonary artery (and round to the lungs) as the left ventricle pumps through the aorta (and round the body) Heart Rate (Pulse) is the number of heartbeats that occurs per minute Stroke Volume is the volume of blood expelled by each ventricle on contraction. The stronger the contraction, ...
CJO~@§l13@j @YJ? ffOO@ OO§t6l.KtfT
... aa well aa Ihelr titles. 'The atria and ventricles are not to be In the middle 01 the page, color the stages 01 blood flow through Ihe related lettars. These stages relate to voltage changes in the ECG Color the ECG and related letters. starting at the left and working to the parts oIlhe ECG are rel ...
... aa well aa Ihelr titles. 'The atria and ventricles are not to be In the middle 01 the page, color the stages 01 blood flow through Ihe related lettars. These stages relate to voltage changes in the ECG Color the ECG and related letters. starting at the left and working to the parts oIlhe ECG are rel ...
Top Ten Things To Know Treatment of Hypertension in Patients With
... antagonists) generally also reduce blood pressure and should be used in this population. 9. It is recommended that patients who have hypertension and HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) receive treatment to control systolic and diastolic hypertension, ventricular rate in the presence of atri ...
... antagonists) generally also reduce blood pressure and should be used in this population. 9. It is recommended that patients who have hypertension and HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) receive treatment to control systolic and diastolic hypertension, ventricular rate in the presence of atri ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.