four valves
... Concentrates initially on sound "1", noting its intensity and variations, possible duplication and effects of respiration. Sound 1 caused by the closing of the tricuspid and mitral valves. Systole begins with Sound "1" & extends to Sound "2" Then listen to Sound "2" for same characteristics. ...
... Concentrates initially on sound "1", noting its intensity and variations, possible duplication and effects of respiration. Sound 1 caused by the closing of the tricuspid and mitral valves. Systole begins with Sound "1" & extends to Sound "2" Then listen to Sound "2" for same characteristics. ...
CIRCULATION AND BLOOD
... You need to be able to describe the flow of blood around the body through any major organ (e.g. Iliac, jugular/carotid, subclavian, coronary, renal, hepatic). For example: • e.g. path of blood to kidneys: Left ventricle →aorta → renal artery → renal arterioles → capillaries → venules → renal vein → ...
... You need to be able to describe the flow of blood around the body through any major organ (e.g. Iliac, jugular/carotid, subclavian, coronary, renal, hepatic). For example: • e.g. path of blood to kidneys: Left ventricle →aorta → renal artery → renal arterioles → capillaries → venules → renal vein → ...
Starter Qs
... • Describe the action of the SAN on the cardiac muscle cells, including how this stimulates the AVN • Identify SAN and AVN locations in a diagram • State the role of an ECG • Interpret ECG graphs in order to calculate heart rate • State that the heart beat can be regulated by both nervous and hormon ...
... • Describe the action of the SAN on the cardiac muscle cells, including how this stimulates the AVN • Identify SAN and AVN locations in a diagram • State the role of an ECG • Interpret ECG graphs in order to calculate heart rate • State that the heart beat can be regulated by both nervous and hormon ...
143-150 July 15, 1996
... With Chest Pain by Anna N.A. Tosteson, Lee Goldman, I. Steven Udvarhelyi, and Thomas H. Lee ...
... With Chest Pain by Anna N.A. Tosteson, Lee Goldman, I. Steven Udvarhelyi, and Thomas H. Lee ...
Cardiac conducting system - Hamilton Grammar School
... both nervous and hormonal control. The autorhythmic cells of the sinoatrial node (SAN) or pacemaker set the rate at which cardiac muscle cells contract. The timing of cardiac cells contracting is controlled by the impulse from the SAN spreading through the atria and then travelling to the atrioventr ...
... both nervous and hormonal control. The autorhythmic cells of the sinoatrial node (SAN) or pacemaker set the rate at which cardiac muscle cells contract. The timing of cardiac cells contracting is controlled by the impulse from the SAN spreading through the atria and then travelling to the atrioventr ...
Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System
... Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves. Name the functional blood supply ...
... Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves. Name the functional blood supply ...
Coronary circulation
... receptors in the heart D An increased stimulation of β-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart E An increased stimulation of β-2 adrenergic receptors in the heart ...
... receptors in the heart D An increased stimulation of β-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart E An increased stimulation of β-2 adrenergic receptors in the heart ...
Cardiovascular system The heart
... induced water retention increased the workload on the all ready failing heart .thus a vicious cycle of cardiac decomposition in initiated that will lead to death from cardiac failure . ...
... induced water retention increased the workload on the all ready failing heart .thus a vicious cycle of cardiac decomposition in initiated that will lead to death from cardiac failure . ...
Heart Failure: Dx and Management
... Approximately 5 million patients in this country have HF Over 550,000 patients are diagnosed with HF for the first time each year Primary reason for 12 to 15 million office visits and 6.5 million hospital days each year In 2001, nearly 53,000 patients died of HF as a primary cause ...
... Approximately 5 million patients in this country have HF Over 550,000 patients are diagnosed with HF for the first time each year Primary reason for 12 to 15 million office visits and 6.5 million hospital days each year In 2001, nearly 53,000 patients died of HF as a primary cause ...
Study Questions on Cardiovascular System
... 2. Blood vessel called _____________ carry blood away from the heart and ___________ carry blood toward the heart. Which carries oxygenated blood? (8.1, Fig 8.9) 3. Describe the similarities and differences in structure of arteries and veins. How does their structure make them fit for their purpose? ...
... 2. Blood vessel called _____________ carry blood away from the heart and ___________ carry blood toward the heart. Which carries oxygenated blood? (8.1, Fig 8.9) 3. Describe the similarities and differences in structure of arteries and veins. How does their structure make them fit for their purpose? ...
Anaesthetic Implications in a Child With Glenn`s Shunt Undergoing
... haemodynamically stable and SpO2 maintained between 84-88%. There was no bleeding from the sockets. Tab Warfarin was restarted on Day-2. ...
... haemodynamically stable and SpO2 maintained between 84-88%. There was no bleeding from the sockets. Tab Warfarin was restarted on Day-2. ...
Provider Bills:
... Morbid obesity: BMI greater than 40 Increased risk of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, breast and colon cancer and gallbladder disease ...
... Morbid obesity: BMI greater than 40 Increased risk of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, breast and colon cancer and gallbladder disease ...
Exercise and stable coronary artery disease
... heart's workload, help widen coronary arteries, and relieve and control angina. Nitroglycerin widens the coronary arteries, increasing blood flow to the heart muscle and ...
... heart's workload, help widen coronary arteries, and relieve and control angina. Nitroglycerin widens the coronary arteries, increasing blood flow to the heart muscle and ...
Independent influence of previous myocardial infarction
... The Goal: Processes of cardiac remodelling, especially collagen deposition and following fibrosis, seen both in infarcted and non-infarcted myocardium are important contributors to the development of the impaired left ventricular (LV) function. The objective of this study was to assess the independe ...
... The Goal: Processes of cardiac remodelling, especially collagen deposition and following fibrosis, seen both in infarcted and non-infarcted myocardium are important contributors to the development of the impaired left ventricular (LV) function. The objective of this study was to assess the independe ...
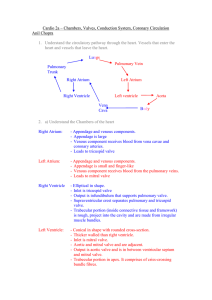
Chambers Valves, Conduction System, Coronary Circulation
... - Appendage and venous components. - Appendage is large - Venous component receives blood from vena cavae and coronary arteries. - Leads to tricuspid valve ...
... - Appendage and venous components. - Appendage is large - Venous component receives blood from vena cavae and coronary arteries. - Leads to tricuspid valve ...
End stage CHF
... • 03/2010: Procedure was long and difficult LV lead could not be placed (RA and RV lead in place) ...
... • 03/2010: Procedure was long and difficult LV lead could not be placed (RA and RV lead in place) ...
the heart - WordPress.com
... valves both prevents black flow of blood into our atria. The Aorta is a major blood vessel that branches off to pump blood to other major arteries in the body. Our pulmonary veins and arteries aid in the pulmonary circuit where our oxygen exchange takes place. ...
... valves both prevents black flow of blood into our atria. The Aorta is a major blood vessel that branches off to pump blood to other major arteries in the body. Our pulmonary veins and arteries aid in the pulmonary circuit where our oxygen exchange takes place. ...
Functional Anatomy of Heart
... • As the heart lies between the sternum and vertebral column, it is possible to compress the sternum and drive blood out of the heart when heart is not pumping effectively. • This external compression of heart is done in CPR [Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation], which is life saving, till proper therapy ...
... • As the heart lies between the sternum and vertebral column, it is possible to compress the sternum and drive blood out of the heart when heart is not pumping effectively. • This external compression of heart is done in CPR [Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation], which is life saving, till proper therapy ...
COMMON USED CARDIAC MEDICATIONS
... What can you tell about Prinzmetal’s angina? How is it different from typical angina? ...
... What can you tell about Prinzmetal’s angina? How is it different from typical angina? ...
Procoralan Ivabradine Prescribing Information Refer to
... Refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) before prescribing. Presentation: Film-coated tablets, 5mg, 7.5mg. Indications: Symptomatic treatment of Chronic stable angina pectoris: in coronary artery disease adults with normal sinus rhythm and heart rate ≥ 70 bpm. Indicated in patients unable ...
... Refer to Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) before prescribing. Presentation: Film-coated tablets, 5mg, 7.5mg. Indications: Symptomatic treatment of Chronic stable angina pectoris: in coronary artery disease adults with normal sinus rhythm and heart rate ≥ 70 bpm. Indicated in patients unable ...
Cardiovascular System notes
... • respond to needs of the cells • low oxygen and nutrients cause sphincter to relax ...
... • respond to needs of the cells • low oxygen and nutrients cause sphincter to relax ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.