Pathophysiology__Cardiac_Study_Guide16
... 28. Explain the series of the ECG waves 29. What does the P wave show? 30. What does the QRS wave show? 31. What does the T wave show? 32. What does an elevated ST wave segment indicate? 33. What is a normal sinus rhythm ? 34. Explain a premature atrial contraction 35. Explain a premature ventricula ...
... 28. Explain the series of the ECG waves 29. What does the P wave show? 30. What does the QRS wave show? 31. What does the T wave show? 32. What does an elevated ST wave segment indicate? 33. What is a normal sinus rhythm ? 34. Explain a premature atrial contraction 35. Explain a premature ventricula ...
280208.ppt
... • Look for the clues needed to develop the question to the physician for clarification of the ...
... • Look for the clues needed to develop the question to the physician for clarification of the ...
Section 7 Problems of Oxygenation: Perfusion NURSING
... Health Promotion. Behaviors to reduce the risk for CAD are ...
... Health Promotion. Behaviors to reduce the risk for CAD are ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... and then transmitting that energy to keep blood moving after the aortic and pulmonary valves close. ...
... and then transmitting that energy to keep blood moving after the aortic and pulmonary valves close. ...
lecture slides
... Do we have more blood than we need? • Veins of the systemic circulation act as a reservoir where blood is allowed to pool under resting conditions. • When more Pressure and C.O. is needed, not only does the heart beat faster and stronger, the veins squeeze on this reservoir to push more blood back ...
... Do we have more blood than we need? • Veins of the systemic circulation act as a reservoir where blood is allowed to pool under resting conditions. • When more Pressure and C.O. is needed, not only does the heart beat faster and stronger, the veins squeeze on this reservoir to push more blood back ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
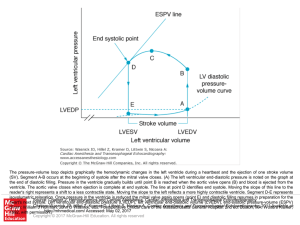
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
lesson 20 arteries and veins
... Veins Veins carry blood back to the heart The muscular layer and layers of elastic fibres in the vein wall are thinner than those in an artery because blood flows along a vein at low pressure The lumen of a vein is wider than that of an artery Valves are present in veins, to prevent the backflow o ...
... Veins Veins carry blood back to the heart The muscular layer and layers of elastic fibres in the vein wall are thinner than those in an artery because blood flows along a vein at low pressure The lumen of a vein is wider than that of an artery Valves are present in veins, to prevent the backflow o ...
2. A condition in which one or both of the cusps of the mitral vlave is
... 23. The AV node extension into the interventricular septum is called the atrioventricular ____. 25. A surgical technique that uses a balloon like structure to increase the diameter of coronary arteries. 26. Abbr. for premature ventricular contractions. 29. The more pointed part of the whole heart is ...
... 23. The AV node extension into the interventricular septum is called the atrioventricular ____. 25. A surgical technique that uses a balloon like structure to increase the diameter of coronary arteries. 26. Abbr. for premature ventricular contractions. 29. The more pointed part of the whole heart is ...
CVS Pathology Lecture Notes (L4)
... Definition a structural abnormality present from birth Incidence 6-10 per 1000 live born, full term birth Functional Classification of congenital Heart Disease 1. without shunt – acyanotic 2. with shunt a. cyanotic – R to L shunt b. potentially cyanotic – L to R shunt Tetralogy of Fallot Right ventr ...
... Definition a structural abnormality present from birth Incidence 6-10 per 1000 live born, full term birth Functional Classification of congenital Heart Disease 1. without shunt – acyanotic 2. with shunt a. cyanotic – R to L shunt b. potentially cyanotic – L to R shunt Tetralogy of Fallot Right ventr ...
Cardiovascular Unit Vocab List 1. Heart: the muscle that makes the
... 6. Ventricles: bottom 2 chambers of the heart; left ventricle and right ventricle 7. Arteries: 8. Blood pressure: a measure of the amount of force that the blood places on the walls of blood vessels, particularly large arteries, as it is pumped through the body. 9. Angina pectoris: chest pain that r ...
... 6. Ventricles: bottom 2 chambers of the heart; left ventricle and right ventricle 7. Arteries: 8. Blood pressure: a measure of the amount of force that the blood places on the walls of blood vessels, particularly large arteries, as it is pumped through the body. 9. Angina pectoris: chest pain that r ...
Abstract_InaHRS2016_Ervan_Zuhri(1)
... fibrillation. Molecular mechanism underlying fever-induced ventricular arrhythmias leading syncope or cardiac arrest in patients with BS are not well understood, but some mechanism were proposed. Fever-induced BS are tought involving the effect of high temperature to reduce sodium current, accelerat ...
... fibrillation. Molecular mechanism underlying fever-induced ventricular arrhythmias leading syncope or cardiac arrest in patients with BS are not well understood, but some mechanism were proposed. Fever-induced BS are tought involving the effect of high temperature to reduce sodium current, accelerat ...
AP Biology Reading/Study Guide (aka Important Stuff to Know
... 22. How does the tracheal system “work” in insects and why is this an advantage to gas exchange? ...
... 22. How does the tracheal system “work” in insects and why is this an advantage to gas exchange? ...
Electrocardiogram
... • Shorter and not as loud as the first • Sound created by blood turbulence • Associated with closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole ...
... • Shorter and not as loud as the first • Sound created by blood turbulence • Associated with closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole ...
Cardiac pathologies
... meet the needs of the body. This allows fluid buildup in lungs and extremities. • It can be right or left sided each have different signs and symptoms ...
... meet the needs of the body. This allows fluid buildup in lungs and extremities. • It can be right or left sided each have different signs and symptoms ...
Properties of Cardiac Muscle
... from one cell to another--facilitated by the presence of gap junctions that transmit electrical currents From SAN→ atrial muscle & atrioventricular node (AVN) From AVN (slowest) → atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) →left & right bundles →purkinje fibres (fastest) ...
... from one cell to another--facilitated by the presence of gap junctions that transmit electrical currents From SAN→ atrial muscle & atrioventricular node (AVN) From AVN (slowest) → atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) →left & right bundles →purkinje fibres (fastest) ...
EFFECTIVE NECK- CUTTING OF POULTRY
... sides of the throat, just below the jaw bone, is called a ventral neck cut (VNC) and is a reliable method of severing both common carotid arteries and both external jugular veins, in all species. A VNC bleeds birds rapidly, thereby benefiting bird welfare and meat quality. ...
... sides of the throat, just below the jaw bone, is called a ventral neck cut (VNC) and is a reliable method of severing both common carotid arteries and both external jugular veins, in all species. A VNC bleeds birds rapidly, thereby benefiting bird welfare and meat quality. ...
Backgrounder - Bayer Investor Relations
... chest or other location. This can happen if the vein is damaged or if the flow of blood slows down or stops, and can result in two serious complications. Chronic pain and swelling can result if the thrombus blocks the flow of blood through the vein, leading to damage to the blood vessels, and affect ...
... chest or other location. This can happen if the vein is damaged or if the flow of blood slows down or stops, and can result in two serious complications. Chronic pain and swelling can result if the thrombus blocks the flow of blood through the vein, leading to damage to the blood vessels, and affect ...
The heart has four main chambers: the left ______, the left
... The receptors that measure blood pressure are called baroreceptors, and are situated in the aorta and the carotid sinus. These receptors monitor pressure of blood leaving the heart and entering the brain respectively. Signals from these receptors pass into the brainstem centre that controls blood pr ...
... The receptors that measure blood pressure are called baroreceptors, and are situated in the aorta and the carotid sinus. These receptors monitor pressure of blood leaving the heart and entering the brain respectively. Signals from these receptors pass into the brainstem centre that controls blood pr ...
The Circulatory System
... superior & inferior vena cava to the right atrium. • The right atrium pumps blood through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. • The muscles of the right ventricle contract and force the blood into the pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs. • In the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses out an ...
... superior & inferior vena cava to the right atrium. • The right atrium pumps blood through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. • The muscles of the right ventricle contract and force the blood into the pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs. • In the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses out an ...
File
... Name the coverings of the heart. Describe the structure and function of each of the three layers of the heart wall. Describe the structure and functions of the four heart chambers. Name each chamber and provide the name and general route of its associated great vessel(s). ...
... Name the coverings of the heart. Describe the structure and function of each of the three layers of the heart wall. Describe the structure and functions of the four heart chambers. Name each chamber and provide the name and general route of its associated great vessel(s). ...
BHF Factfile: Coronary Heart Disease and Air Travel
... Coronary heart disease and flying The coronary syndromes span an occasional episode of chest pain, frequent angina, unstable angina and myocardial infarction. Symptoms may be absent either on or off treatment and breathlessness may represent an “angina equivalent”, or, be due to significant left ven ...
... Coronary heart disease and flying The coronary syndromes span an occasional episode of chest pain, frequent angina, unstable angina and myocardial infarction. Symptoms may be absent either on or off treatment and breathlessness may represent an “angina equivalent”, or, be due to significant left ven ...
Know your heart:
... through the aortic valve to the aorta and then to the rest of the body. Blood returns from the body to the heart by vessels called the superior and inferior vena cava. It then enters the right atrium and passes through the tricuspid valve. Once through the tricuspid valve the blood goes into the rig ...
... through the aortic valve to the aorta and then to the rest of the body. Blood returns from the body to the heart by vessels called the superior and inferior vena cava. It then enters the right atrium and passes through the tricuspid valve. Once through the tricuspid valve the blood goes into the rig ...
CPR Lesson2 Circulatory Emergencies
... The heart has stopped beating or is in Ventricular Fibrillation (heart is jiggling like a bowl of jello) What are the Signs & Signals of a Heart Attack? (5 P’s) Pain: Severe to mild pain in the chest (angina), spreading up neck, jaw, shoulders and arms ...
... The heart has stopped beating or is in Ventricular Fibrillation (heart is jiggling like a bowl of jello) What are the Signs & Signals of a Heart Attack? (5 P’s) Pain: Severe to mild pain in the chest (angina), spreading up neck, jaw, shoulders and arms ...
S073510970802826X_mmc1
... ventricular end diastolic pressure >20 mm Hg. The onset of shock had to be within 24 h. Exclusion criteria were specified as: age <18 years; prolonged resuscitation (>30 ...
... ventricular end diastolic pressure >20 mm Hg. The onset of shock had to be within 24 h. Exclusion criteria were specified as: age <18 years; prolonged resuscitation (>30 ...