contraception for patients with congenital heart disease
... CONTRACEPTION FOR PATIENTS WITH CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Unplanned pregnancy can be disastrous for patients with congenital heart defects. It is vital that they are given adequate and accurate advice about which forms of contraception are suitable for them. The contraceptive efficacy of each differe ...
... CONTRACEPTION FOR PATIENTS WITH CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Unplanned pregnancy can be disastrous for patients with congenital heart defects. It is vital that they are given adequate and accurate advice about which forms of contraception are suitable for them. The contraceptive efficacy of each differe ...
Notes
... a) may be caused by elevated temp, certain drugs, stress, or heart disease 2) Bradycardia – less than 60 beats per minute a) may be caused by low temp, certain drugs, or parasympathetic activation 3) Fibrillation – uncoordinated or quivering heartbeat a) caused by damage/defect of conduction system ...
... a) may be caused by elevated temp, certain drugs, stress, or heart disease 2) Bradycardia – less than 60 beats per minute a) may be caused by low temp, certain drugs, or parasympathetic activation 3) Fibrillation – uncoordinated or quivering heartbeat a) caused by damage/defect of conduction system ...
The arterial blood supply of the heart is provided by
... The right coronary artery arises from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta and runs forward between the pulmonary trunk and the right auricle. This artery gives rise to an important branch immediately after leaving the ascending aorta. This is the anterior right atrial branch, which give ...
... The right coronary artery arises from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta and runs forward between the pulmonary trunk and the right auricle. This artery gives rise to an important branch immediately after leaving the ascending aorta. This is the anterior right atrial branch, which give ...
Cardiovascular System
... – 2/3rds of the heart lies to the left of the mid-line. – It is about the size of a clenched fist. – Pericardium- Sac of connective tissue that covers and protects the heart. ...
... – 2/3rds of the heart lies to the left of the mid-line. – It is about the size of a clenched fist. – Pericardium- Sac of connective tissue that covers and protects the heart. ...
6.2 – The Blood System
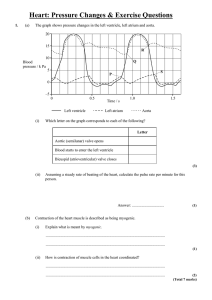
... A. Diastole – not contracting B. Systole – contracting C. As blood enters the atria, the atrioventricular valves are closed. The increase in volume increases pressure. D. Systole of atria pushes open atrioventricular valves and moves blood into ventricles E. Systole of ventricles forces atrioventric ...
... A. Diastole – not contracting B. Systole – contracting C. As blood enters the atria, the atrioventricular valves are closed. The increase in volume increases pressure. D. Systole of atria pushes open atrioventricular valves and moves blood into ventricles E. Systole of ventricles forces atrioventric ...
DIY DIY t Thes love ( Mate • • • • • • Heart Sach tutorial create e
... ne of the largeer heart piecees before procceeding to thee next step. ...
... ne of the largeer heart piecees before procceeding to thee next step. ...
Circulatory System
... Blood vessels that lead blood away from the heart Thick walls but they are very elastic They can expand and contract as the blood is pumped into them and then moves on The arteries nearest your heart are the largest. As they get further and further from the heart, they become smaller and smaller ...
... Blood vessels that lead blood away from the heart Thick walls but they are very elastic They can expand and contract as the blood is pumped into them and then moves on The arteries nearest your heart are the largest. As they get further and further from the heart, they become smaller and smaller ...
S073510970802826X_mmc1
... Patient Population Eligible participants for this study were patients with: 1) acute myocardial infarction (AMI) <48 h, confirmed by ischemic symptoms for at least 30 min with elevated cardiac markers or ST-segment elevation or left bundle branch block. An AMI was suspected when patients were resusc ...
... Patient Population Eligible participants for this study were patients with: 1) acute myocardial infarction (AMI) <48 h, confirmed by ischemic symptoms for at least 30 min with elevated cardiac markers or ST-segment elevation or left bundle branch block. An AMI was suspected when patients were resusc ...
Cardiovascular System Powerpoint
... Stroke Volume (mL/beat) X Heart Rate (beats/min) = Cardiac Output (mL/min) 75 mL/beat X 72 beats/min. = 5400 mL/min. Questions 1. Do athletes have greater or lesser demands for oxygen than non-athletes? 2. Do athletes have greater or lesser resting heart rates than non-athletes? 3. How do you reconc ...
... Stroke Volume (mL/beat) X Heart Rate (beats/min) = Cardiac Output (mL/min) 75 mL/beat X 72 beats/min. = 5400 mL/min. Questions 1. Do athletes have greater or lesser demands for oxygen than non-athletes? 2. Do athletes have greater or lesser resting heart rates than non-athletes? 3. How do you reconc ...
Cardiovascular system
... •Tissue-paper thin but tough, the valves of the human heart open and close to pump 6 quarts of blood a day through 60,000 miles of vessels. •On the right the Tricuspid valve prevents back flow of (deoxygenated blood coming from the right atria into the right ventricle •On the left the mitral (bicusp ...
... •Tissue-paper thin but tough, the valves of the human heart open and close to pump 6 quarts of blood a day through 60,000 miles of vessels. •On the right the Tricuspid valve prevents back flow of (deoxygenated blood coming from the right atria into the right ventricle •On the left the mitral (bicusp ...
Familial Arrhythmia
... dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C), and Brugada syndrome (BrS). While their clinical presentations are generally similar and may include syncope, palpitations, dizziness, dyspnea, stroke, and/or SCD,1 each of these disorders has a different etiology and prognosis. Age of onset varies by condition and ...
... dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C), and Brugada syndrome (BrS). While their clinical presentations are generally similar and may include syncope, palpitations, dizziness, dyspnea, stroke, and/or SCD,1 each of these disorders has a different etiology and prognosis. Age of onset varies by condition and ...
Chp.6 Circulatory System 1
... blood is then oxygen rich – Oxygen-rich blood returns to heart, entering the left atrium – From left atrium, blood flows through the mitral valve into left ventricle – Blood then leaves left ventricle and travels to ...
... blood is then oxygen rich – Oxygen-rich blood returns to heart, entering the left atrium – From left atrium, blood flows through the mitral valve into left ventricle – Blood then leaves left ventricle and travels to ...
Present and Future trends in Paediatric Cardiology Dr Oliver
... Cardiac catheter interventional techniques have secured a firm and growing place in the treatment of so called simple lesions such as patent ductus arteriosus, atrial and ventricular septal defects, and pulmonary or aortic valve stenosis. But, increasingly, catheter techniques are being used and dev ...
... Cardiac catheter interventional techniques have secured a firm and growing place in the treatment of so called simple lesions such as patent ductus arteriosus, atrial and ventricular septal defects, and pulmonary or aortic valve stenosis. But, increasingly, catheter techniques are being used and dev ...
Heart
... The heart is a hollow, cone shaped organ with cardiac muscle forming its walls. There are three layers which form the walls of the muscle: endocardium, myocardium and pericardium. The heart is approximately 10 cm long and is situated in the thoracic cavity, behind the sternum, lying to the left side ...
... The heart is a hollow, cone shaped organ with cardiac muscle forming its walls. There are three layers which form the walls of the muscle: endocardium, myocardium and pericardium. The heart is approximately 10 cm long and is situated in the thoracic cavity, behind the sternum, lying to the left side ...
Cardiac Cycle
... Chambers of the Heart The human heart is divided by a series of partitions, called septa, into four chambers, which segregate the blood at different stages in the pumping cycle. The lower two are ventricles, thickwalled pumping chambers that receive blood from the upper chambers and drive it into th ...
... Chambers of the Heart The human heart is divided by a series of partitions, called septa, into four chambers, which segregate the blood at different stages in the pumping cycle. The lower two are ventricles, thickwalled pumping chambers that receive blood from the upper chambers and drive it into th ...
Document
... B. goes to lungs exchanges CO2 &O2 C. Oxygenated blood comes back to heart to Lt. atrium into Lt. ventricle D. Goes out aorta to all parts of the body fig. 18.5; page 668 III. Layers of Heart A. Pericardium – Double walled sac around heart - Fibrous & serous pericardiums 1. Fibrous pericardium – tou ...
... B. goes to lungs exchanges CO2 &O2 C. Oxygenated blood comes back to heart to Lt. atrium into Lt. ventricle D. Goes out aorta to all parts of the body fig. 18.5; page 668 III. Layers of Heart A. Pericardium – Double walled sac around heart - Fibrous & serous pericardiums 1. Fibrous pericardium – tou ...
Chapter 37
... obstruction of blood flow form the LV to the aorta during systole Common causes include congenital, rheumatic heart disease and senile or ...
... obstruction of blood flow form the LV to the aorta during systole Common causes include congenital, rheumatic heart disease and senile or ...
What To Expect: Circulatory System Main Idea: This system is also
... Main Idea: This system is also known as the body’s ________________________________. Goals: 1. I CAN define cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, arteries, capillaries and veins, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, septum, aorta. 2. I CAN list the functions of the circulatory s ...
... Main Idea: This system is also known as the body’s ________________________________. Goals: 1. I CAN define cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, arteries, capillaries and veins, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, septum, aorta. 2. I CAN list the functions of the circulatory s ...
Transposition of the Great Arteries, L-Type
... In cases where the heart's pacemaker is not functioning properly because of the abnormal conduction pathways, an artificial pacemaker may be inserted. The most common postoperative difficulties involve heart block (the atria and ventricles do not pump in the proper sequence with each other), which m ...
... In cases where the heart's pacemaker is not functioning properly because of the abnormal conduction pathways, an artificial pacemaker may be inserted. The most common postoperative difficulties involve heart block (the atria and ventricles do not pump in the proper sequence with each other), which m ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.