Management of Chronic Heart Failure in Adults: Synopsis of the
... No difference exists between selective ß-blockers (ie metoprolol) and nonselective ß-blockers (ie carvedilol) on the combined end point of mortality and hospitalization Combination therapy of ARBs and ACE inhibitors increases risk of hyperkalemia Adding ARB to ACE inhibitor and ß-blocker reduc ...
... No difference exists between selective ß-blockers (ie metoprolol) and nonselective ß-blockers (ie carvedilol) on the combined end point of mortality and hospitalization Combination therapy of ARBs and ACE inhibitors increases risk of hyperkalemia Adding ARB to ACE inhibitor and ß-blocker reduc ...
Aortic Stenosis and Hypertension
... of blood pressure on the indices of AS severity; others could not prove an independent effect. There is controversy as to whether blood pressure does directly affect common indices of AS severity. It is well known that indices of AS severity are flow dependent. Thus, acute changes in blood pressure ...
... of blood pressure on the indices of AS severity; others could not prove an independent effect. There is controversy as to whether blood pressure does directly affect common indices of AS severity. It is well known that indices of AS severity are flow dependent. Thus, acute changes in blood pressure ...
Complete Cardiac Workup, a healthy heart is a happy heart
... with every beat which causes damage to the heart over time. Blood pressure is very easy to measure just like it is in humans. High blood pressure can be the first warning sign of early heart disease. We recommend checking yearly, especially in breeds predisposed to heart disease. ...
... with every beat which causes damage to the heart over time. Blood pressure is very easy to measure just like it is in humans. High blood pressure can be the first warning sign of early heart disease. We recommend checking yearly, especially in breeds predisposed to heart disease. ...
Chassot, et al. — Br J Anaesth 89: 747, 2002
... • Stage 1 & 2 hypertension (<180 / 110 mmHg) – “not an independent risk factor for perioperative CVS complications” – American Heart Association / American College of Cardiology – Howell, et al. — Br J Anaesth 92: 570, 2004 ...
... • Stage 1 & 2 hypertension (<180 / 110 mmHg) – “not an independent risk factor for perioperative CVS complications” – American Heart Association / American College of Cardiology – Howell, et al. — Br J Anaesth 92: 570, 2004 ...
Long term responses of exercise on the cardiovascular system
... Long term responses of exercise on the cardiovascular system ...
... Long term responses of exercise on the cardiovascular system ...
Ischemic stroke
... • based on the history of events and PE. • Can usually identify which artery in the brain is blocked based on symptoms. – For example, weakness or paralysis of the left leg suggests blockage of the artery supplying the area on the right side of the brain that controls the left leg's muscle movements ...
... • based on the history of events and PE. • Can usually identify which artery in the brain is blocked based on symptoms. – For example, weakness or paralysis of the left leg suggests blockage of the artery supplying the area on the right side of the brain that controls the left leg's muscle movements ...
Atrial Fibrillation and Hypertension
... myocardial infarction, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, peripheral vascular disease, cognitive decline and premature death. High blood pressure is the single biggest risk factor for experiencing a stroke; 40% of ischaemic strokes could be prevented by the timely identification and treatment of ...
... myocardial infarction, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, peripheral vascular disease, cognitive decline and premature death. High blood pressure is the single biggest risk factor for experiencing a stroke; 40% of ischaemic strokes could be prevented by the timely identification and treatment of ...
The Body`s Transport System 1
... Cardiovascular System • The overall function of the circulatory system is to transport materials throughout the body toward and away from particular target organs and tissues. • Carries need materials to cells and removes waste from cells. ...
... Cardiovascular System • The overall function of the circulatory system is to transport materials throughout the body toward and away from particular target organs and tissues. • Carries need materials to cells and removes waste from cells. ...
Physiology of the Circulatory System - Milton
... Present a detailed, step-by-step instruction list on how you did the experiment. 6. Results ______/15 This section should include some variation of the Data Sheet where the average blood pressure and the Fitness Data were recorded. You should also include a summary paragraph with a description of th ...
... Present a detailed, step-by-step instruction list on how you did the experiment. 6. Results ______/15 This section should include some variation of the Data Sheet where the average blood pressure and the Fitness Data were recorded. You should also include a summary paragraph with a description of th ...
Anaesthesia for patients with grown up congenital heart disease
... – Chronic cardiac failure – Chronic non cardiac coexisting diseases; diabetes, neurological, airway, renal and liver ...
... – Chronic cardiac failure – Chronic non cardiac coexisting diseases; diabetes, neurological, airway, renal and liver ...
OUTLINE FOR ALTERATIONS IN CARDIAC FUNCTION
... C. Describe the dynamics of congestive heart failure in an infant and a child. D. Complete the study questions for the case study of a 3 mo old child with Down Syndrome with congestive heart failure (CHF). E. Describe the dynamics of pulmonary hypertension and the implications in the child with obst ...
... C. Describe the dynamics of congestive heart failure in an infant and a child. D. Complete the study questions for the case study of a 3 mo old child with Down Syndrome with congestive heart failure (CHF). E. Describe the dynamics of pulmonary hypertension and the implications in the child with obst ...
File
... The systems used by different organisms are a reflection of their requirements and structure – the more complex the organism the more complex the system. - intracellular fluid: the fluid in the cells - extracellular fluid: all other fluid in an organism blood contains both intra and extra cellular ...
... The systems used by different organisms are a reflection of their requirements and structure – the more complex the organism the more complex the system. - intracellular fluid: the fluid in the cells - extracellular fluid: all other fluid in an organism blood contains both intra and extra cellular ...
the quiz questions and answers as a Microsoft Word
... A. After blood flows through the valves, they close, preventing the backflow of blood. B. The ventricles fill with blood. C. The ventricular muscle contracts to force blood out of the chambers of the ventricles. D. None of the above 10. Determining the rate at which oxygen is added to the blood as i ...
... A. After blood flows through the valves, they close, preventing the backflow of blood. B. The ventricles fill with blood. C. The ventricular muscle contracts to force blood out of the chambers of the ventricles. D. None of the above 10. Determining the rate at which oxygen is added to the blood as i ...
Cardiovascular Disease
... • Men have greater incidence but survive more often • Women lower incidence but survival rate is lower • Research has been MALE orientated ...
... • Men have greater incidence but survive more often • Women lower incidence but survival rate is lower • Research has been MALE orientated ...
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
... Fig 6 Reduction in incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) events and stroke in relation to reduction in diastolic blood pressure according to drug dose, number of drugs, pretreatment diastolic blood pressure, and age. *Blood pressure reductions are more uncertain and hence also reductions in d ...
... Fig 6 Reduction in incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) events and stroke in relation to reduction in diastolic blood pressure according to drug dose, number of drugs, pretreatment diastolic blood pressure, and age. *Blood pressure reductions are more uncertain and hence also reductions in d ...
comp3_unit5_lecture1_script
... divided into 3 categories - arteries, capillaries and veins. Arteries are Large thickwalled vessels which can dilate or constrict. Arteries carry blood away from heart. Capillaries are a network of tiny, thin-walled blood vessels. They are the connecting unit between arteries and veins. It is in the ...
... divided into 3 categories - arteries, capillaries and veins. Arteries are Large thickwalled vessels which can dilate or constrict. Arteries carry blood away from heart. Capillaries are a network of tiny, thin-walled blood vessels. They are the connecting unit between arteries and veins. It is in the ...
Heart and Blood Vessels - Lerner Research Institute
... blockage in the arteries carrying blood to the brain; if oxygen carried by blood cannot get to the brain, the result is brain damage and often other physical harm. Carotid stenosis – a blockage caused by plaque build-up in the carotid arteries on either side of the neck – is a significant but treata ...
... blockage in the arteries carrying blood to the brain; if oxygen carried by blood cannot get to the brain, the result is brain damage and often other physical harm. Carotid stenosis – a blockage caused by plaque build-up in the carotid arteries on either side of the neck – is a significant but treata ...
Treatment - American College of Cardiology Puerto Rico Chapter
... PHYSICIANS' HEALTH STUDY The trial's Data and Safety Monitoring Board stopped the aspirin arm of the PHS several years ahead of schedule because it was clear that aspirin had a significant effect on the risk of a first myocardial infarction. As reported in the July 20, 1989 New England Journal of M ...
... PHYSICIANS' HEALTH STUDY The trial's Data and Safety Monitoring Board stopped the aspirin arm of the PHS several years ahead of schedule because it was clear that aspirin had a significant effect on the risk of a first myocardial infarction. As reported in the July 20, 1989 New England Journal of M ...
warm ups! trimester 2
... 1. What are the main structures of the circulatory system? 2. How many chambers are found in the heart? ...
... 1. What are the main structures of the circulatory system? 2. How many chambers are found in the heart? ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapters 10, 11, 12 Review
... 10. What do the words systole and diastole mean? If a person were to say atrial systole and ventricular systole what are they saying? ...
... 10. What do the words systole and diastole mean? If a person were to say atrial systole and ventricular systole what are they saying? ...
Circulatory System - River Vale Schools
... system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body. It usually beats from 60 to 100 times per minute, but can go much faster when necessary. It beats about 100,000 times a day, more than 30 million times per year, and about 2.5 billion times in a 70-year lif ...
... system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body. It usually beats from 60 to 100 times per minute, but can go much faster when necessary. It beats about 100,000 times a day, more than 30 million times per year, and about 2.5 billion times in a 70-year lif ...
HbA1c - Faculty
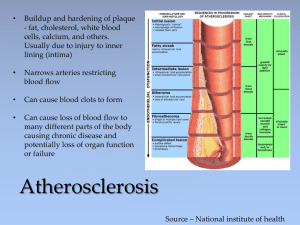
... Buildup and hardening of plaque - fat, cholesterol, white blood cells, calcium, and others. Usually due to injury to inner lining (intima) ...
... Buildup and hardening of plaque - fat, cholesterol, white blood cells, calcium, and others. Usually due to injury to inner lining (intima) ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.