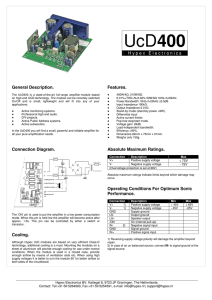
UcD400
... The ‘ON’ pin is used to put the amplifier in a low power consumption mode. When this pin is held low the amplifier will become active after approx. 1.5s. This pin can be controlled by either a switch or transistor. ...
... The ‘ON’ pin is used to put the amplifier in a low power consumption mode. When this pin is held low the amplifier will become active after approx. 1.5s. This pin can be controlled by either a switch or transistor. ...
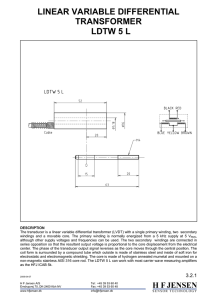
LINEAR VARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMER LDTW 5 L
... although other supply voltages and frequencies can be used. The two secondary windings are connected in series opposition so that the resultant output voltage is proportional to the core displacement from the electrical center. The phase of the transducer output signal reverses as the core moves thr ...
... although other supply voltages and frequencies can be used. The two secondary windings are connected in series opposition so that the resultant output voltage is proportional to the core displacement from the electrical center. The phase of the transducer output signal reverses as the core moves thr ...
Introduction to MOS Transistor
... Goal: to cancel the imaginary admittance with an inductor! An effective output capacitance of 135 fF An effective output resistance of 1/1.107mS=900 Ohms Since we know fo, and Ceff, we can calculate Leff: 15.3 nH ...
... Goal: to cancel the imaginary admittance with an inductor! An effective output capacitance of 135 fF An effective output resistance of 1/1.107mS=900 Ohms Since we know fo, and Ceff, we can calculate Leff: 15.3 nH ...
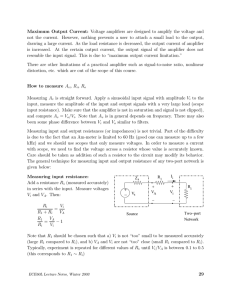
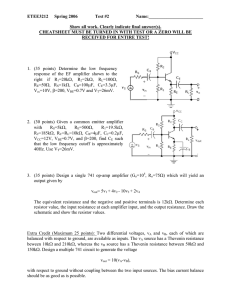
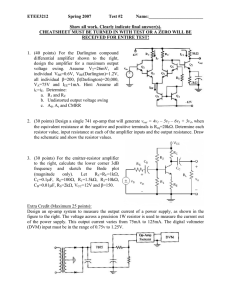
Maximum Output Current: Voltage amplifiers are designed to amplify
... and compute Av = Vo /Vi . Note that Av is in general depends on frequency. There may also been some phase difference between Vi and Vo similar to filters. Measuring input and output resistances (or impedances) is not trivial. Part of the difficulty is due to the fact that an Am-meter is limited to 6 ...
... and compute Av = Vo /Vi . Note that Av is in general depends on frequency. There may also been some phase difference between Vi and Vo similar to filters. Measuring input and output resistances (or impedances) is not trivial. Part of the difficulty is due to the fact that an Am-meter is limited to 6 ...
Problem 2. - ShareStudies.com
... line length in wavelengths () to produce an input impedance, Zin =0 - j36. Repeat for Zin = j100. Determine the length of an open circuit line for Zin = j100 Problem 7. An antenna has an input impedance equal to 25 + j40 and a frequency at 100MHz. The antenna is connected to a 50 coaxial cabl ...
... line length in wavelengths () to produce an input impedance, Zin =0 - j36. Repeat for Zin = j100. Determine the length of an open circuit line for Zin = j100 Problem 7. An antenna has an input impedance equal to 25 + j40 and a frequency at 100MHz. The antenna is connected to a 50 coaxial cabl ...
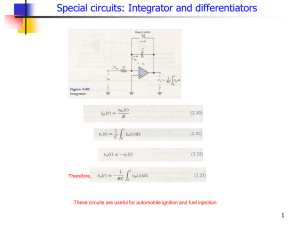
Operational Amplifiers IDEAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
... gain–bandwidth product, output impedance, slew rate, and other specifications 4. Be easily adjusted ...
... gain–bandwidth product, output impedance, slew rate, and other specifications 4. Be easily adjusted ...
ECE 541 – Lecture 4 Wilkonson Power Divider
... ECE 6130 Wilkinson Power Divider Text Section 7.3 How do you design a Wilkinson Power Divider? See for example Chapter 7 Problems 9,10 Wilkinson Power Divider: Matched at all ports Complete isolation between output ports Lossless when output ports are matched. Lossy when they are not (only reflected ...
... ECE 6130 Wilkinson Power Divider Text Section 7.3 How do you design a Wilkinson Power Divider? See for example Chapter 7 Problems 9,10 Wilkinson Power Divider: Matched at all ports Complete isolation between output ports Lossless when output ports are matched. Lossy when they are not (only reflected ...
unit 2 network theorems
... 1. Norton’s equivalent circuit with In, Zn, Zl can be constructed 2. To find Norton’s current, short circuit load 3. To find Norton’s equivalent impedance 4. Who am I ...
... 1. Norton’s equivalent circuit with In, Zn, Zl can be constructed 2. To find Norton’s current, short circuit load 3. To find Norton’s equivalent impedance 4. Who am I ...
CP Worksheet - Charges and Coulomb`s Law
... 1. 8 x 10-4 C of charge pass through a wire every .2 seconds. What is the electrical current through the wire? Formula: 2. A 10 resistor and a 50 resistor are placed in a series circuit, and connected to a 120 v power supply. a. What is the total equivalent resistance of the circuit? Formula: b. ...
... 1. 8 x 10-4 C of charge pass through a wire every .2 seconds. What is the electrical current through the wire? Formula: 2. A 10 resistor and a 50 resistor are placed in a series circuit, and connected to a 120 v power supply. a. What is the total equivalent resistance of the circuit? Formula: b. ...
VOLTAGE STABILITY
... VOLTAGE STABILITY On-line assessment Future power system operation • Power transfers are increased • Environmental reasons restrict the expansion of networks • Better service is required for a reduced cost ...
... VOLTAGE STABILITY On-line assessment Future power system operation • Power transfers are increased • Environmental reasons restrict the expansion of networks • Better service is required for a reduced cost ...
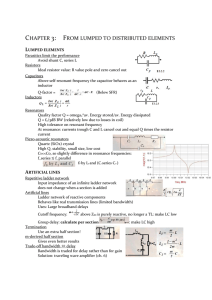
Chapter 3: From lumped to distributed elements
... Bandwidth is traded for delay rather than for gain Solution: traveling wave amplifier (ch. 6) ...
... Bandwidth is traded for delay rather than for gain Solution: traveling wave amplifier (ch. 6) ...
THEORY: AppCAD is an easy-to-use program that provides you with
... A unique feature of AppCAD's Everything S-Parameters is the ability to load up to 3 sets of SnP files and make side-by-side comparisons.This side-by-side comparison feature is exceptionally useful for comparing different devices to assist with design-in decisions, or analyzing the same device under ...
... A unique feature of AppCAD's Everything S-Parameters is the ability to load up to 3 sets of SnP files and make side-by-side comparisons.This side-by-side comparison feature is exceptionally useful for comparing different devices to assist with design-in decisions, or analyzing the same device under ...