BJTAMP-fre1q-lab
... BJT Amplifiers - Complete Model The common emitter amplifier is one of the most widely used amplifier configurations due to its high gain. Other configurations are the common collector and common base amplifiers which respectively have the collector and base of the transistor grounded, or common to ...
... BJT Amplifiers - Complete Model The common emitter amplifier is one of the most widely used amplifier configurations due to its high gain. Other configurations are the common collector and common base amplifiers which respectively have the collector and base of the transistor grounded, or common to ...
K0CQ-CSVHF2010
... I've found evidence to indicate there is a similar menu for the FT-817, but I don't know if the values or the menu entries are exactly the same. It is handy to align the transmitter gain to absolutely prevent spikes and to keep the power minimized for transverter service without needing to go to the ...
... I've found evidence to indicate there is a similar menu for the FT-817, but I don't know if the values or the menu entries are exactly the same. It is handy to align the transmitter gain to absolutely prevent spikes and to keep the power minimized for transverter service without needing to go to the ...
Work, Power, and Machines
... Work • is the transfer of energy that results from applying a force over a distance – if nothing moves, no work was done ...
... Work • is the transfer of energy that results from applying a force over a distance – if nothing moves, no work was done ...
Caspers
... -> forward traveling wave only, no reflected wave. Amplitude of the forward traveling wave in this case is V1=5V; forward power = 25V 2 / 50 0.5W Matching means maximum power transfer from a generator with given source impedance to an external load ...
... -> forward traveling wave only, no reflected wave. Amplitude of the forward traveling wave in this case is V1=5V; forward power = 25V 2 / 50 0.5W Matching means maximum power transfer from a generator with given source impedance to an external load ...
Surge Impedance of Transmission-line Towers: C. A. Jordan`s
... The surge impedance of transmission-line towers is very important in the design of electric transmission lines. The surge impedance has similar effect as a resistance in direct current circuits. Large surge impedance implies large voltage between the terminals determined by Ohm’s law. When designing ...
... The surge impedance of transmission-line towers is very important in the design of electric transmission lines. The surge impedance has similar effect as a resistance in direct current circuits. Large surge impedance implies large voltage between the terminals determined by Ohm’s law. When designing ...
return loss
... The real world The impedances of real-world components are rarely, if ever, equal at every frequency, so impedance mismatches exist pretty much everywhere. This is especially true in our cable networks. Every connector, tap, line passive, amplifier—even the cable itself—represents an impedance misma ...
... The real world The impedances of real-world components are rarely, if ever, equal at every frequency, so impedance mismatches exist pretty much everywhere. This is especially true in our cable networks. Every connector, tap, line passive, amplifier—even the cable itself—represents an impedance misma ...
Design of 3.67 GHz RF Power Amplifier
... ● Programmed to run by maximizing utility of radio frequency spectrum ...
... ● Programmed to run by maximizing utility of radio frequency spectrum ...
work sheet 1 unit-1 two port network theory
... What are all the considerations do have in high frequency parameters. a. b. c. d. ...
... What are all the considerations do have in high frequency parameters. a. b. c. d. ...
op-amp amplifier - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
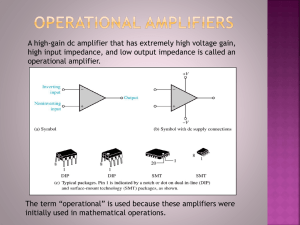
... A high-gain dc amplifier that has extremely high voltage gain, high input impedance, and low output impedance is called an operational amplifier. ...
... A high-gain dc amplifier that has extremely high voltage gain, high input impedance, and low output impedance is called an operational amplifier. ...