* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10EC54_MicrowaveAndRadar-Unit4
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Impedance matching wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Microwave transmission wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
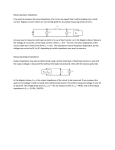
Subject Name: Microwave and Radar- Unit 4 22/8/14 Subject Code: 10EC54 Prepared By: Lakshmi C R, Dharani K G Department: ECE Date: 10.11.14 UNIT 4 Microwave Network Theory Topic Details •Microwave Network Theory •Symmetrical Z and Y parameters for reciprocal networks •S matrix Representation of multi port networks Microwave Network Analysis Solving Maxwell’s equations for microwave networks/transmission line networks is bit hard, with many terms repeating some times. While we removing the repeated terms (by cancellation or taking arbitrary constant), a qualitative term will get – which can be defined by “Voltage and Current” intern. By further reducing the terms with RLC component, the problems looks simple. For such problems, we can apply old network analysis. That’s called “Microwave network analysis”. Keep in mind: where ever the components (especially the z components) are same thought-out circuit, then we can apply MNA. For example – A ferrite device shall change the phase (may not allow in opposite direction), so a suitable parameter should be introduced for such networks Concept of Impedance •The term “Impedance” has been coined by “Oliver Heaviside”. •Impedance can be defined as “complex ratio of Voltage to Current”, this has been used hugely in AC circuits. •For example, pointing vector of one port network •“Port” is a key word to define two-terminal-pair. In Microwave circuits, instead of positive-negative line (pair), the ports have “Incident – Reflected components” or “voltage – current” •In case of “multi-port” problems, the use of matrices is very important. Matrix form shall reduce plenty of complexity So called “Port Parameters” or “Parameter matrix” Impedance and Admittance Matrices Must keep in mind, all port components are taken with respect to a reference line (so during measurement, all components are in-phase), called position z = 0. Network properties 1. Reciprocal property The impedance/admittance matrix is symmetry Z ij Z ji Yij Y ji 2. Lossless property In word, real part of impedance is responsible for loss, so for lossless: Re Z ij 0 3.Matching property Zii Z0 Yii Y0 1 Z0 Show that it’s impossible to construct a three port network with Matched, Reciprocal and Lossless. To begin: