Video Transcript - Rose
... We’re looking for the equivalent impedance between terminals G and H. The circuit, however, is given with all of its elements specified in terms of admittance. We’ll first convert those to impedance, then work the problem entirely in terms of impedance. Recall that impedance is the reciprocal of adm ...
... We’re looking for the equivalent impedance between terminals G and H. The circuit, however, is given with all of its elements specified in terms of admittance. We’ll first convert those to impedance, then work the problem entirely in terms of impedance. Recall that impedance is the reciprocal of adm ...
HW 4 6340
... lossless transmission line of length p, with a parallel inductance Lv in the middle and series capacitors 2Cg at the ends to model the gaps. A conductance 2Gg is placed in parallel with the capacitors to model radiation from the gaps. The resistance Rv models the resistance of the vertical post (via ...
... lossless transmission line of length p, with a parallel inductance Lv in the middle and series capacitors 2Cg at the ends to model the gaps. A conductance 2Gg is placed in parallel with the capacitors to model radiation from the gaps. The resistance Rv models the resistance of the vertical post (via ...
Open circuit test
... The secondary of the transformer is left open-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary. If the applied voltag ...
... The secondary of the transformer is left open-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary. If the applied voltag ...
EL6413 Catalog Description
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
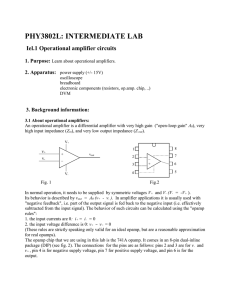
MOSFET Amplifier Input/Output Impedances
... into the impedances looking into the input and output of such an amplifier. The amplifier case in study will be the common-source configuration. Here the techniques of properly biasing a MOSFET amplifier and setting up AC amplification will be used as well as new methods of experimentally measuring ...
... into the impedances looking into the input and output of such an amplifier. The amplifier case in study will be the common-source configuration. Here the techniques of properly biasing a MOSFET amplifier and setting up AC amplification will be used as well as new methods of experimentally measuring ...
The voltage and current induced in the second coil depend on the
... 100 kΩ resistor are chosen to provide a 1 MΩ load to the source, the impedance seen by the analog multiplexer input is about 90 kΩ, still too high for the multiplexed reading to be accurate. • When the values are both downsized by a factor of 100 so the output ...
... 100 kΩ resistor are chosen to provide a 1 MΩ load to the source, the impedance seen by the analog multiplexer input is about 90 kΩ, still too high for the multiplexed reading to be accurate. • When the values are both downsized by a factor of 100 so the output ...
Geen diatitel
... Figure 3.9 A three-mode integrator With S1 open and S2 closed, the dc circuit behaves as an inverting amplifier. Thus o = ic and o can be set to any desired initial conduction. With S1 closed and S2 open, the circuit integrates. With both switches open, the circuit holds o constant, making possi ...
... Figure 3.9 A three-mode integrator With S1 open and S2 closed, the dc circuit behaves as an inverting amplifier. Thus o = ic and o can be set to any desired initial conduction. With S1 closed and S2 open, the circuit integrates. With both switches open, the circuit holds o constant, making possi ...
Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Phys 3610/6610 Lab 18 Student: TA:
... Use a 0 to 5 V, 1 kHz square wave as input for your circuit in this lab. Task 1: Using a npn-transistor, a simple transistor switch can be constructed as in : +5V ...
... Use a 0 to 5 V, 1 kHz square wave as input for your circuit in this lab. Task 1: Using a npn-transistor, a simple transistor switch can be constructed as in : +5V ...
SSPA 9.5-10.5-25 DS_SSPA 9.5-10.5-25 DS.qxd
... is 5.5 dB typical at 25ºC. Input VSWR is 2.0:1 maximum. Output VSWR is 2.0:1 maximum. This unit is equipped with Aethercomm's proprietary DC switching circuitry that enables and disables the DC-DC circuitry in 500/600 nSec typical on this unit. Standard features include reverse polarity protection, ...
... is 5.5 dB typical at 25ºC. Input VSWR is 2.0:1 maximum. Output VSWR is 2.0:1 maximum. This unit is equipped with Aethercomm's proprietary DC switching circuitry that enables and disables the DC-DC circuitry in 500/600 nSec typical on this unit. Standard features include reverse polarity protection, ...
EET-225 Homework #1
... sentences when answering all questions. Where a problem involves a circuit, you must redraw the circuit as part of the solution, showing all indicated voltages and currents on the circuit diagram. Box or underline all final answers and show all work (see syllabus for example of homework standards). ...
... sentences when answering all questions. Where a problem involves a circuit, you must redraw the circuit as part of the solution, showing all indicated voltages and currents on the circuit diagram. Box or underline all final answers and show all work (see syllabus for example of homework standards). ...
Chapter10
... - The network function is more easily obtained from impedance analysis than from differential equations. - Both forced response and natural response can be determined. - Poles and zeros: poles are roots of the denominator, zeros are roots of the numerator. - Gain factor corresponds to the dc gain. ...
... - The network function is more easily obtained from impedance analysis than from differential equations. - Both forced response and natural response can be determined. - Poles and zeros: poles are roots of the denominator, zeros are roots of the numerator. - Gain factor corresponds to the dc gain. ...
Thevenin and Norton equivalents
... For any combination of simple voltages and linear resistors, you can find an equivalent circuit composed of a single voltage source and a single equivalent resistor, that will produce the same current (and voltage) through RL. (AND Vth and Rth are independent. of RL.) ...
... For any combination of simple voltages and linear resistors, you can find an equivalent circuit composed of a single voltage source and a single equivalent resistor, that will produce the same current (and voltage) through RL. (AND Vth and Rth are independent. of RL.) ...
FINAL00sp
... 3) (40pts) Design a two-stage Miller-compensated CMOS opamp to be used in a unity gain feedback system with the following specifications: The output load consists of a 10k resistance in parallel with a 10pF capacitance. The phase margin should be 45 degrees. The 3dB frequency of the closed l ...
... 3) (40pts) Design a two-stage Miller-compensated CMOS opamp to be used in a unity gain feedback system with the following specifications: The output load consists of a 10k resistance in parallel with a 10pF capacitance. The phase margin should be 45 degrees. The 3dB frequency of the closed l ...
Instrumentation Amp
... suggested that the common-mode input voltage be 100 times greater than the differential input voltage. Hint: A convenient way to measure CMRR is to measure SNR (signal to noise - or interference - ratio) at both the input and the output. CMRR = SNRout / SNRin . SNR can be measured with both a spectr ...
... suggested that the common-mode input voltage be 100 times greater than the differential input voltage. Hint: A convenient way to measure CMRR is to measure SNR (signal to noise - or interference - ratio) at both the input and the output. CMRR = SNRout / SNRin . SNR can be measured with both a spectr ...
Description: waveform and time duration
... the die surface is lower than that one between electromagnetic (RF) incident field and PCB tracks connected to the input ports of an IC. In such a noisy environment, there are two types of failures induced by conducted RF interference on ICs [1]: a) Static failures: occur in the presence of conducte ...
... the die surface is lower than that one between electromagnetic (RF) incident field and PCB tracks connected to the input ports of an IC. In such a noisy environment, there are two types of failures induced by conducted RF interference on ICs [1]: a) Static failures: occur in the presence of conducte ...
Negative Input (–4.5V to –80V) Synchronous
... features innovative EN/FBIN pin circuitry for slowly varying input signals and an adjustable undervoltage lockout function. This pin is also used for input voltage regulation to avoid collapsing a high impedance supply. The fixed operating frequency is selectable from 100kHz to 750kHz and can be syn ...
... features innovative EN/FBIN pin circuitry for slowly varying input signals and an adjustable undervoltage lockout function. This pin is also used for input voltage regulation to avoid collapsing a high impedance supply. The fixed operating frequency is selectable from 100kHz to 750kHz and can be syn ...
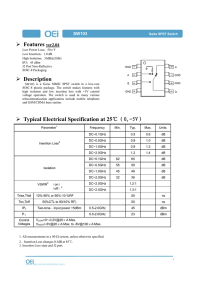
Features ver2.04 Description Typical Electrical
... SW103 is a GaAs MMIC SPST switch in a low-cost SOIC-8 plastic package. The switch makes features with high isolation and low insertion loss with +5V control voltage operation. The switch is used in many various telecommunication applications include mobile telephone and GSM/CDMA base station. ...
... SW103 is a GaAs MMIC SPST switch in a low-cost SOIC-8 plastic package. The switch makes features with high isolation and low insertion loss with +5V control voltage operation. The switch is used in many various telecommunication applications include mobile telephone and GSM/CDMA base station. ...
experiment 1
... - The forward or incident power applied to the line combines with the reflected power to produce a pattern of voltage and current variations along the line known as standing waves. - If the load impedance matches the line impedance, there are no standing waves. - A measure of the mismatch between li ...
... - The forward or incident power applied to the line combines with the reflected power to produce a pattern of voltage and current variations along the line known as standing waves. - If the load impedance matches the line impedance, there are no standing waves. - A measure of the mismatch between li ...