Energy and Energy Sources
... 1. Example – as a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from kinetic to potential and back. 2. If the energy of the swing decreases, then the energy of some other object must increase by an equal amount. 3. Friction converts on the mechanical energy into thermal energy. ...
... 1. Example – as a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from kinetic to potential and back. 2. If the energy of the swing decreases, then the energy of some other object must increase by an equal amount. 3. Friction converts on the mechanical energy into thermal energy. ...
P1 mindmap
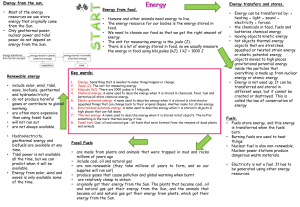
... v – energy sources thatvare naturally Renewable energy Water and wind can be used replenished on a human timescale. to drive turbines directly (no Examples: solar, wind, tidal, hydroelectric, geothermal, steam) biofuel (NOT fossil fuels or nuclear) Solar cells can turn Sun’s Environmental effects ra ...
... v – energy sources thatvare naturally Renewable energy Water and wind can be used replenished on a human timescale. to drive turbines directly (no Examples: solar, wind, tidal, hydroelectric, geothermal, steam) biofuel (NOT fossil fuels or nuclear) Solar cells can turn Sun’s Environmental effects ra ...
Energy - My CCSD
... Heat= the number of molecules Temperature= the motion of molecules Which has more Heat? Which has more Temp? Boiling pot of water vs. Iceberg Ice Sculpture vs. Lit Match ...
... Heat= the number of molecules Temperature= the motion of molecules Which has more Heat? Which has more Temp? Boiling pot of water vs. Iceberg Ice Sculpture vs. Lit Match ...
Science Year 7 Learn Sheet DC4 – Energy
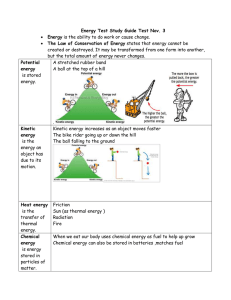
... Chemical energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in chemicals. Food, fuel and batteries all store chemical energy. Elastic potential energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in stretched or squashed things that can change back to their original shapes. Another name f ...
... Chemical energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in chemicals. Food, fuel and batteries all store chemical energy. Elastic potential energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in stretched or squashed things that can change back to their original shapes. Another name f ...
STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... 44. Geologists could use which of the following to compare the age of sedimentary rock layers in Bryce Canyon with sedimentary rock layers in the Grand Canyon? a. radioactive isotopes c. relative dating b. index fossils d. all of the above ...
... 44. Geologists could use which of the following to compare the age of sedimentary rock layers in Bryce Canyon with sedimentary rock layers in the Grand Canyon? a. radioactive isotopes c. relative dating b. index fossils d. all of the above ...
Forms of Energy
... chemical bonds of molecules and compounds (Think: food, batteries and fuels including fossil fuels and wood) 1. Food contains molecules of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates 2. Fossil Fuels were formed from the remains of living things which are made of molecules which contain chemical energy **When ...
... chemical bonds of molecules and compounds (Think: food, batteries and fuels including fossil fuels and wood) 1. Food contains molecules of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates 2. Fossil Fuels were formed from the remains of living things which are made of molecules which contain chemical energy **When ...
Nonrenewable Energy
... which can be turned into electricity and heat • Wind • Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth • Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil • Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam ...
... which can be turned into electricity and heat • Wind • Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth • Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil • Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam ...
Energy Practice
... LT: I can identify and describe the different forms of potential and kinetic energy. _____ LT: I can give/explain examples of energy transformations. _____ Potential and Kinetic Energy Identify each of the following forms of energy as either potential energy (P) or kinetic energy (K). _____ Sound ...
... LT: I can identify and describe the different forms of potential and kinetic energy. _____ LT: I can give/explain examples of energy transformations. _____ Potential and Kinetic Energy Identify each of the following forms of energy as either potential energy (P) or kinetic energy (K). _____ Sound ...
Energy – Where does it come from and why does it produce waste?
... are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and ...
... are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and ...
Chapter 15 –Energy
... Energy cannot be destroyed Energy can be converted from one form to another Both statements 11. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and Force, mass, work 12. Biomass energy is what type of energy stored in living things? Chemical, nuclear, thermal 13. Nonrenewable energy resources do not include Coa ...
... Energy cannot be destroyed Energy can be converted from one form to another Both statements 11. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and Force, mass, work 12. Biomass energy is what type of energy stored in living things? Chemical, nuclear, thermal 13. Nonrenewable energy resources do not include Coa ...
Energy and Electrical Definitions
... Energy is the ability to do work, or cause change. Energy is literally what makes the world and everything in it go. Energy is the magic stuff stored in the battery that makes the flashlight work. The gasoline in a car’s gas tank contains energy. The car’s engine merely converts the gasoline’s energ ...
... Energy is the ability to do work, or cause change. Energy is literally what makes the world and everything in it go. Energy is the magic stuff stored in the battery that makes the flashlight work. The gasoline in a car’s gas tank contains energy. The car’s engine merely converts the gasoline’s energ ...
Technical guide - Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index
... consumed in a sub-sector, taking into account the thermodynamic properties of different energy sources. For example switching from a high quality fuel (e.g. electricity) to a low quality fuel (e.g. coal) would result in more energy being used overall to achieve the same outcome.. This is necessary a ...
... consumed in a sub-sector, taking into account the thermodynamic properties of different energy sources. For example switching from a high quality fuel (e.g. electricity) to a low quality fuel (e.g. coal) would result in more energy being used overall to achieve the same outcome.. This is necessary a ...
TOPIC: Energy AIM: What is energy?
... Ethanol = clear, colorless alcohol fuel made from the sugars found in grains, such as corn & wheat, and potato skins & rice. It is renewable because it is made from plants. To make ethanol we use yeast to ferment the sugars and starch in corn. Corn is the main ingredient for ethanol in the US due ...
... Ethanol = clear, colorless alcohol fuel made from the sugars found in grains, such as corn & wheat, and potato skins & rice. It is renewable because it is made from plants. To make ethanol we use yeast to ferment the sugars and starch in corn. Corn is the main ingredient for ethanol in the US due ...
TOPIC: Energy AIM: What is energy?
... • Resources that can’t be replaced by natural processes as quickly as they are used • Takes millions of years for nature to reproduce ...
... • Resources that can’t be replaced by natural processes as quickly as they are used • Takes millions of years for nature to reproduce ...
File - Physics e
... water on a stove, the heat from the burner adds energy to the water, causing the water molecules to move around more rapidly, increasing the water’s thermal energy. Nuclear energy is ______________________________________________________________________ An atom's nucleus can be split apart. When thi ...
... water on a stove, the heat from the burner adds energy to the water, causing the water molecules to move around more rapidly, increasing the water’s thermal energy. Nuclear energy is ______________________________________________________________________ An atom's nucleus can be split apart. When thi ...
Energy Terms and Concepts
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a ...
Chapter: Chapter 14: Energy: Some Basics Multiple Choice 1. Which
... 1. Which of the following terms refers to energy that is stored? a) potential energy b) kinetic energy c) cogeneration d) soft path energy e) first-law efficiency Answer: a 2. Which of the following terms refers to the capture and use of waste heat? a) potential energy b) kinetic energy c) cogenerat ...
... 1. Which of the following terms refers to energy that is stored? a) potential energy b) kinetic energy c) cogeneration d) soft path energy e) first-law efficiency Answer: a 2. Which of the following terms refers to the capture and use of waste heat? a) potential energy b) kinetic energy c) cogenerat ...
Chapter 3 - Bakersfield College
... 3. The potential for a large-scale nuclear accident is present. 4. Discharge of radioactive wastes into the environment from badly run nuclear power plants has occurred. 5. An unsolved disposal problem of radioactive nuclear waste exists. 3-15. The Future A. Nuclear fusion represents a potentially s ...
... 3. The potential for a large-scale nuclear accident is present. 4. Discharge of radioactive wastes into the environment from badly run nuclear power plants has occurred. 5. An unsolved disposal problem of radioactive nuclear waste exists. 3-15. The Future A. Nuclear fusion represents a potentially s ...
Energy Resources
... Fossil fuels are made of hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are energy-rich chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide and water. This process releases energy in the forms of heat and light. Foss ...
... Fossil fuels are made of hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are energy-rich chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide and water. This process releases energy in the forms of heat and light. Foss ...
hw1
... (d) What was the potential and kinetic energy of the 1 kg ball just after being thrown if it travelled 4 meter to the top of the path? (e) What potential and kinetic energy at the top of its path? 6. What are some possible ways to provide energy for society after all the fossil fuels on earth have b ...
... (d) What was the potential and kinetic energy of the 1 kg ball just after being thrown if it travelled 4 meter to the top of the path? (e) What potential and kinetic energy at the top of its path? 6. What are some possible ways to provide energy for society after all the fossil fuels on earth have b ...
Energy of Change
... Sun = Lots of Energy! • The Sun is the source for all energy in our solar system. This is the same for all solar systems in the universe. • The heat, pressure and gravity of the sun causes all energy. • Energy causes change to everything! ...
... Sun = Lots of Energy! • The Sun is the source for all energy in our solar system. This is the same for all solar systems in the universe. • The heat, pressure and gravity of the sun causes all energy. • Energy causes change to everything! ...
Fuel

Fuels are any materials that store potential energy in forms that can be practicably released and used for work or as heat energy. The concept originally applied solely to those materials storing energy in the form of chemical energy that could be released through combustion, but the concept has since been also applied to other sources of heat energy such as nuclear energy (via nuclear fission or nuclear fusion).The heat energy released by many fuels is harnessed into mechanical energy via an engine. Other times the heat itself is valued for warmth, cooking, or industrial processes, as well as the illumination that comes with combustion. Fuels are also used in the cells of organisms in a process known as cellular respiration, where organic molecules are oxidized to release un-usable energy. Hydrocarbons are by far the most common source of fuel used by humans, but other substances, including radioactive metals, are also utilized.Fuels are contrasted with other methods of storing potential energy, such as those that directly release electrical energy (such as batteries and capacitors) or mechanical energy (such as flywheels, springs, compressed air, or water in a reservoir).