Moduels 37, 38, and 39
... (a) Proximity (geographic nearness): Mere exposure effect: repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them) (b) Similarity (c) Familiarity 9. Bystander effect: The tendency for any bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present (Notice incident?Interpret it as e ...
... (a) Proximity (geographic nearness): Mere exposure effect: repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them) (b) Similarity (c) Familiarity 9. Bystander effect: The tendency for any bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present (Notice incident?Interpret it as e ...
Urban sociology, 2 CLV 2008
... Public spaces have their own regulations rules. Micro sociology gives the necessary tools to describe them. Actually its problematic character comes from its lack of definition, precisely – it is never defined once for all – but at the contrary it is always in construction. Free access allows free ...
... Public spaces have their own regulations rules. Micro sociology gives the necessary tools to describe them. Actually its problematic character comes from its lack of definition, precisely – it is never defined once for all – but at the contrary it is always in construction. Free access allows free ...
Sociology - eReportz
... systematically cause people to take their own lives!!! A theory is then born to offer general explanation of suicidal behavior. Theories are attempts to explain events, forces, materials, ideas, or behavior in a comprehensive manner. In sociology, theory explains problems, actions or behavior. ...
... systematically cause people to take their own lives!!! A theory is then born to offer general explanation of suicidal behavior. Theories are attempts to explain events, forces, materials, ideas, or behavior in a comprehensive manner. In sociology, theory explains problems, actions or behavior. ...
Social Psychology
... attempting to persuade you may weaken the effect ◦ Ex: informing the audience that they are going to hear a persuasive speech on a particular topic may weaken the effect and attitudes of the audience ◦ Inoculation Effect: Beginning with a weak argument and moving to a strong one May reject both ar ...
... attempting to persuade you may weaken the effect ◦ Ex: informing the audience that they are going to hear a persuasive speech on a particular topic may weaken the effect and attitudes of the audience ◦ Inoculation Effect: Beginning with a weak argument and moving to a strong one May reject both ar ...
Interactive Powerpoint assignment
... Studies how organisms learn new behaviors or modify existing ones depending on whether events in their environments reward or punish these behaviors ...
... Studies how organisms learn new behaviors or modify existing ones depending on whether events in their environments reward or punish these behaviors ...
Study Guide - Stamford High School
... b. Under what specific conditions will someone’s attitudes actually guide his/her behavior? c. Explain the foot-in-the-door phenomenon, and describe situations where it might have a positive or negative outcome. How does it compare to door-in-the-face? d. Explain cognitive dissonance theory, includi ...
... b. Under what specific conditions will someone’s attitudes actually guide his/her behavior? c. Explain the foot-in-the-door phenomenon, and describe situations where it might have a positive or negative outcome. How does it compare to door-in-the-face? d. Explain cognitive dissonance theory, includi ...
Social Psychology - ISA
... tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal ...
... tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal ...
chapter_16_-_social_psychology
... for accepted and expected behavior – because the price we pay for being different may be severe. ...
... for accepted and expected behavior – because the price we pay for being different may be severe. ...
vlcek_final_exam
... psychologists to remember, in most societies, the different genders will have differentiating responses to social interventions, from the interventions having dissimilar degrees of impact to completely opposing reactions, so adjust interventions accordingly. To put it simply, men and women will ofte ...
... psychologists to remember, in most societies, the different genders will have differentiating responses to social interventions, from the interventions having dissimilar degrees of impact to completely opposing reactions, so adjust interventions accordingly. To put it simply, men and women will ofte ...
Sociology 545 Social Psychology
... “Large geographically diffuse social interaction which can be of both shorter or longer duration, that demonstrates identity orientation, resulting in affective behavior.” ...
... “Large geographically diffuse social interaction which can be of both shorter or longer duration, that demonstrates identity orientation, resulting in affective behavior.” ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) are inconsistent example- when we become aware that our attitudes and our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes ...
... we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) are inconsistent example- when we become aware that our attitudes and our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes ...
AP Psych Rapid Review
... expectations of others influence how we treat them, bringing about the very behavior we expected. ...
... expectations of others influence how we treat them, bringing about the very behavior we expected. ...
Social Entrepreneurship
... Scottish Executive emphasises this role without exploring the definition or usage of the concept Social economy and social enterprise strategies are directed at providing products, services and employment to deprived regions and areas Supposed to assist in producing regional sustainability in ...
... Scottish Executive emphasises this role without exploring the definition or usage of the concept Social economy and social enterprise strategies are directed at providing products, services and employment to deprived regions and areas Supposed to assist in producing regional sustainability in ...
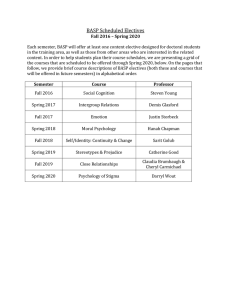
Fall 2016 - Spring 2020 - Basic and Applied Social Psychology
... psychological and situational factors related to social cognition, group power, prejudice, prejudice-reduction, collective action, and social change. ...
... psychological and situational factors related to social cognition, group power, prejudice, prejudice-reduction, collective action, and social change. ...
Informal and Formal Social Control
... giving little conscious thought to whether we will be sanctioned if we fail to conform. Socialization develops our self-control so well that we don’t need further pressure to obey social norms. ...
... giving little conscious thought to whether we will be sanctioned if we fail to conform. Socialization develops our self-control so well that we don’t need further pressure to obey social norms. ...
PSY 327.001: Cognitive Social Psychology Spring 2013 Course Overview
... Course Overview This class will provide a broad introduction to the basic principles of social psychology with an emphasis on the cognitive aspects of interpersonal influence. Throughout this course, you will study cognitive processes – such as perception, memory, and decision-making – while looking ...
... Course Overview This class will provide a broad introduction to the basic principles of social psychology with an emphasis on the cognitive aspects of interpersonal influence. Throughout this course, you will study cognitive processes – such as perception, memory, and decision-making – while looking ...
SOCIAL WORK`S MULTIDIMENSIONAL PERSPECTIVE Eight Main
... their interest over others. Conflict is inevitable when there is a difference in power. Social change is driven by conflict. ...
... their interest over others. Conflict is inevitable when there is a difference in power. Social change is driven by conflict. ...
CHAPTER 6, GROUPS AND ORGANIZATIONS
... other social units. Networks based on race, class, and gender form with particular readiness, especially job networks. ...
... other social units. Networks based on race, class, and gender form with particular readiness, especially job networks. ...
Social Psychology: Attitudes, Group Influences, Social Relations
... Ingroup: “Us”---people who one shares a common identity. Outgroup: “Them”---those perceived as different or apart of one’s ingroup. Ingroup bias: the tendency to favor one’s own group. Scapegoat theory: the theory that prejudice an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame ...
... Ingroup: “Us”---people who one shares a common identity. Outgroup: “Them”---those perceived as different or apart of one’s ingroup. Ingroup bias: the tendency to favor one’s own group. Scapegoat theory: the theory that prejudice an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame ...
Social Psychology: Attitudes, Group Influences, Social Relations
... Ingroup: “Us”---people who one shares a common identity. Outgroup: “Them”---those perceived as different or apart of one’s ingroup. Ingroup bias: the tendency to favor one’s own group. Scapegoat theory: the theory that prejudice an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame ...
... Ingroup: “Us”---people who one shares a common identity. Outgroup: “Them”---those perceived as different or apart of one’s ingroup. Ingroup bias: the tendency to favor one’s own group. Scapegoat theory: the theory that prejudice an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame ...
Social Darwinism - Willingboro School
... Social Darwinism was an intellectual and social movement that gained popularity in the United States and Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It appropriated principles of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution to explain and justify the existing social order. The movement championed unbr ...
... Social Darwinism was an intellectual and social movement that gained popularity in the United States and Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It appropriated principles of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution to explain and justify the existing social order. The movement championed unbr ...
Richard J. Gerrig, Ph.D. and Philip Zimbardo, Ph.D.
... • Conflict experienced after making decision, taking action, or being exposed to information that is contrary to prior beliefs, feelings, or ...
... • Conflict experienced after making decision, taking action, or being exposed to information that is contrary to prior beliefs, feelings, or ...
Talcott Parsons: Toward a General Theory of Action
... theory, perhaps its most fatal flaw, is that it is unverifiable. Even supporters of the general theory of social action have been unable to test it in a satisfactory way. It does not readily offer itself for empirical analysis as good theories do. Which raises the question of if it can even really b ...
... theory, perhaps its most fatal flaw, is that it is unverifiable. Even supporters of the general theory of social action have been unable to test it in a satisfactory way. It does not readily offer itself for empirical analysis as good theories do. Which raises the question of if it can even really b ...