Lecture 9 Teams
... collectively achieved less than four times the solo rate. Increases in group size are inversely related to individual performance. ...
... collectively achieved less than four times the solo rate. Increases in group size are inversely related to individual performance. ...
Groups And Formal Organizations
... • Coercion – when groups or individuals are forced to give in to the wishes of other groups or individuals ?? • Conformity – behaving like we are “supposed to” – How important is this in our lives? ...
... • Coercion – when groups or individuals are forced to give in to the wishes of other groups or individuals ?? • Conformity – behaving like we are “supposed to” – How important is this in our lives? ...
Intro_to_Soc_-_Lesson_6_-_Group_Life
... A triad, a three-person social group, is more stable than a dyad because the addition of a third member means that conflicts between two members can be mediated by the third. As groups grow they become more stable at the cost of ...
... A triad, a three-person social group, is more stable than a dyad because the addition of a third member means that conflicts between two members can be mediated by the third. As groups grow they become more stable at the cost of ...
5 Partnership of the pharmaceutical staff
... psychologically attached to it. According to the investment model, commitment is based on one or more of the following factors: high satisfaction, low quality of alternatives, and a high level of investments. Highly committed individuals are more willing to make sacrifices for their relationship, and ...
... psychologically attached to it. According to the investment model, commitment is based on one or more of the following factors: high satisfaction, low quality of alternatives, and a high level of investments. Highly committed individuals are more willing to make sacrifices for their relationship, and ...
Social Psychology
... Raped and stabbed to death in Queens, NY while 38 people watched from their windows. Only one person called the police, after the incident was over. ...
... Raped and stabbed to death in Queens, NY while 38 people watched from their windows. Only one person called the police, after the incident was over. ...
Attitudes
... Putting personal goals ahead of group goals and defining one’s identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group memberships. ...
... Putting personal goals ahead of group goals and defining one’s identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group memberships. ...
Chapter 16
... Putting group goals ahead of personal goals and defining one’s identity in terms of the groups one belongs to. ...
... Putting group goals ahead of personal goals and defining one’s identity in terms of the groups one belongs to. ...
Psy 202 – Lecture 14 (11/15/05)
... 1) We like members of our in-group better and are nicer to them than members of out-groups. sororities - not so highly respected groups especially likely to put down out-group members. 2) out-group homogeneity: perception that members of out-group are all alike-- more similar to each other than the ...
... 1) We like members of our in-group better and are nicer to them than members of out-groups. sororities - not so highly respected groups especially likely to put down out-group members. 2) out-group homogeneity: perception that members of out-group are all alike-- more similar to each other than the ...
Chapter 4
... motivation – The self-evaluation maintenance (SEM) model: people affiliate with individuals who do not outperform them in areas that are very relevant to their self-esteem. ...
... motivation – The self-evaluation maintenance (SEM) model: people affiliate with individuals who do not outperform them in areas that are very relevant to their self-esteem. ...
Chapter 15: Social groups PowerPoint
... • One of the best predictors of a person’s general happiness and life satisfaction is quality and extent of social relationships and group memberships • People who are excluded show brain activity similar to pain! – Social pain hypothesis (see Chapter 14) – Dorsal anterior cingulate is activated whe ...
... • One of the best predictors of a person’s general happiness and life satisfaction is quality and extent of social relationships and group memberships • People who are excluded show brain activity similar to pain! – Social pain hypothesis (see Chapter 14) – Dorsal anterior cingulate is activated whe ...
337_Chapter3_Winter_2008
... interaction patterns is for the worker to be aware that when ever people are together in a group, they are communicating Workers who are aware that group members communicate for many reasons can observe, assess and understand communication and interaction patterns Noise and other distortions inside ...
... interaction patterns is for the worker to be aware that when ever people are together in a group, they are communicating Workers who are aware that group members communicate for many reasons can observe, assess and understand communication and interaction patterns Noise and other distortions inside ...
500 Questions chapter 13 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... 487. One reason why many groups have some form of initiation rites and rituals is to have: (A) Group norms (B) Deindividuation (C) Group cohesion (D) Task-oriented groups (E) Socially oriented groups 488. The Lapierre experiment proved that: (A) People’s behavior usually corresponds with their attit ...
... 487. One reason why many groups have some form of initiation rites and rituals is to have: (A) Group norms (B) Deindividuation (C) Group cohesion (D) Task-oriented groups (E) Socially oriented groups 488. The Lapierre experiment proved that: (A) People’s behavior usually corresponds with their attit ...
HRM 601 Organizational Behavior
... – Social groups: people who enjoy each other’s company (chat groups) – Interest groups: groups that develop informally around a common interest (news groups, listserv members) ...
... – Social groups: people who enjoy each other’s company (chat groups) – Interest groups: groups that develop informally around a common interest (news groups, listserv members) ...
What is a group?
... What is a group? • Although groups vary enormously and can be defined in many different ways, some general distinctions can be made. One important distinction is between similarity-based categorical groups (common-identity groups), and interaction-based dynamic groups (common bond groups). • Anothe ...
... What is a group? • Although groups vary enormously and can be defined in many different ways, some general distinctions can be made. One important distinction is between similarity-based categorical groups (common-identity groups), and interaction-based dynamic groups (common bond groups). • Anothe ...
1 Power Point Group Comm Intro
... A small group is: At least 3, but not more than 15 people, Who interact and communicate with one another; Who share a common purpose or goal; Who have group norms and values; Who feel a sense of belonging; and Who exert influence on each other. ...
... A small group is: At least 3, but not more than 15 people, Who interact and communicate with one another; Who share a common purpose or goal; Who have group norms and values; Who feel a sense of belonging; and Who exert influence on each other. ...
Formation
... affiliation tend to join more groups and spend more time in them; however, they often fear rejection ...
... affiliation tend to join more groups and spend more time in them; however, they often fear rejection ...
(1) differentiate between formal and informal groups
... We mean a set of expected behavior patterns that are attributes to someone occupying a given position in a social unit. ...
... We mean a set of expected behavior patterns that are attributes to someone occupying a given position in a social unit. ...
Society, Social Roles and Institutions
... Each of these structures has a function, e.g. to provide social cohesion, to resolve conflict, to ensure the reproduction of the group, to provide nutrition, to provide meaning, etc. Malinowski: British social anthropologist who stressed the universal and often basic needs that diverse institutions ...
... Each of these structures has a function, e.g. to provide social cohesion, to resolve conflict, to ensure the reproduction of the group, to provide nutrition, to provide meaning, etc. Malinowski: British social anthropologist who stressed the universal and often basic needs that diverse institutions ...
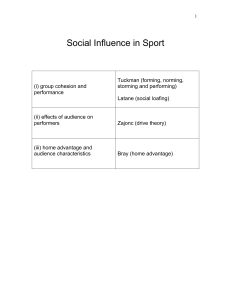
f) Social influence in sport
... There have been many studies looking at the link between group cohesion and performance but one of the interesting results is the finding that individuals often under-perform when in groups. Latane et al. used the phrase social loafing to describe the reduced effort that the individual exerts when w ...
... There have been many studies looking at the link between group cohesion and performance but one of the interesting results is the finding that individuals often under-perform when in groups. Latane et al. used the phrase social loafing to describe the reduced effort that the individual exerts when w ...
Teams-- Hackman
... the shared capacity to take others’ behavior into account during team interactions. – Collective efficacy– the shared belief on the team’s collective ability. ...
... the shared capacity to take others’ behavior into account during team interactions. – Collective efficacy– the shared belief on the team’s collective ability. ...
Cohesion and Teamwork
... exhibit and the relationships they establish with their groups. Ex) clear, consistent communication from captains regarding team goals, tasks, and roles, compatibility between the leader and group members. ...
... exhibit and the relationships they establish with their groups. Ex) clear, consistent communication from captains regarding team goals, tasks, and roles, compatibility between the leader and group members. ...