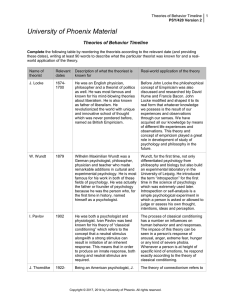
psy420r2_theories_of_behavior_timeline_1
... Social cognitive theory (SCT) is not only applicable in psychology but also in education and communication studies. This extremely useful theory is concerned with the fact that people not only learn the things and innovative behaviors they adapt by only learning or education but also by seeing or ob ...
... Social cognitive theory (SCT) is not only applicable in psychology but also in education and communication studies. This extremely useful theory is concerned with the fact that people not only learn the things and innovative behaviors they adapt by only learning or education but also by seeing or ob ...
Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives
... Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Learning This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observa ...
... Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Learning This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observa ...
Learning
... Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Learning This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observa ...
... Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Learning This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observa ...
Chap012 - Organizational Behavior
... behavioristic, cognitive, and social. • Discuss the principle of reinforcement, with special attention given to the law of effect, positive and negative reinforcers, and punishment. ...
... behavioristic, cognitive, and social. • Discuss the principle of reinforcement, with special attention given to the law of effect, positive and negative reinforcers, and punishment. ...
History and Approaches
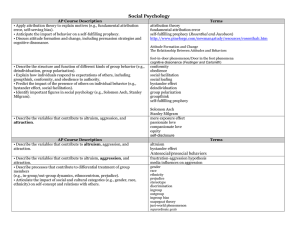
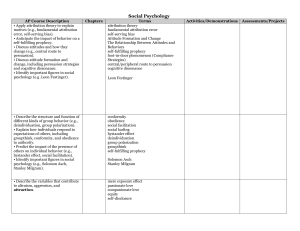
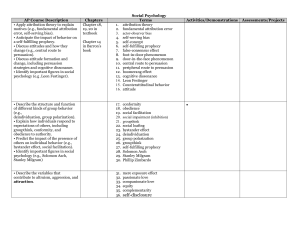
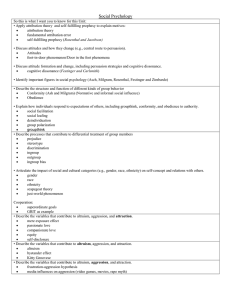
... AP Course Description • Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). • Anticipate the impact of behavior on a self-fulfilling prophecy. • Discuss attitudes and how they change (e.g., central route to persuasion). • Discuss attitude formation a ...
... AP Course Description • Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). • Anticipate the impact of behavior on a self-fulfilling prophecy. • Discuss attitudes and how they change (e.g., central route to persuasion). • Discuss attitude formation a ...
Social Psychology Copy Notes
... overestimate the impact of personal disposition attitude: feelings, often influenced by out own beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events central route to persuasion: occurs when interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoug ...
... overestimate the impact of personal disposition attitude: feelings, often influenced by out own beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events central route to persuasion: occurs when interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoug ...
(1) Introduction 6113
... Ecological Urie Bronfenbrenner Emphasis Super Gestaltism (see Miller introduction), child’s behavior must be situated in the context in which the child operates. ...
... Ecological Urie Bronfenbrenner Emphasis Super Gestaltism (see Miller introduction), child’s behavior must be situated in the context in which the child operates. ...
Learning & Reinforcement - University of Washington
... • Continuous • Intermittent: – Interval • Fixed • Variable ...
... • Continuous • Intermittent: – Interval • Fixed • Variable ...
Distinguish general differences between principles of classical
... Identify key contributors in the psychology of motivation and emotion (e.g., William James, Alfred Kinsey, Abraham Maslow, Stanley Schachter, Hans Selye) Explain the maturation of cognitive abilities (e.g., Piaget’s stages, information processing). Compare and contrast models of moral development ( ...
... Identify key contributors in the psychology of motivation and emotion (e.g., William James, Alfred Kinsey, Abraham Maslow, Stanley Schachter, Hans Selye) Explain the maturation of cognitive abilities (e.g., Piaget’s stages, information processing). Compare and contrast models of moral development ( ...
AP_Ch. 18 Jeopardy Answers
... Zimbardo’s prison study showed the importance of this on our behavior. Cognitive Dissonance Reducing inner tension by changing our attitudes to justify our actions. Alright, Alright! Individualistic Soloman Asch Gain approval / avoid rejection ...
... Zimbardo’s prison study showed the importance of this on our behavior. Cognitive Dissonance Reducing inner tension by changing our attitudes to justify our actions. Alright, Alright! Individualistic Soloman Asch Gain approval / avoid rejection ...
EOY_ Psyhologists to know_ long list
... women and found that they did not score as high on his six stage scale because they focused more on relationships rather than laws and principles. Their reasoning was merely different, not better or worse ...
... women and found that they did not score as high on his six stage scale because they focused more on relationships rather than laws and principles. Their reasoning was merely different, not better or worse ...
Explaining Behavior with Learning Theory – The Behaviorists What
... they learned. With drug abuse the issue of genetics plays a role because there may be a genetic predisposition towards abuse that is contributing to the outcome. Nonetheless, a child whose parents abused drugs can come to the conclusion that they will never touch the stuff, or they may model their b ...
... they learned. With drug abuse the issue of genetics plays a role because there may be a genetic predisposition towards abuse that is contributing to the outcome. Nonetheless, a child whose parents abused drugs can come to the conclusion that they will never touch the stuff, or they may model their b ...
Free-Response Question
... AP Psychology: Social Psychology 1. The enhancement of a group’s prevailing tendencies occurs when people within a group discuss an idea that most of them either favor or oppose. This tendency is called (a) group polarization. (b) deindividuation. (c) the just-world phenomenon. (d) discrimination. ( ...
... AP Psychology: Social Psychology 1. The enhancement of a group’s prevailing tendencies occurs when people within a group discuss an idea that most of them either favor or oppose. This tendency is called (a) group polarization. (b) deindividuation. (c) the just-world phenomenon. (d) discrimination. ( ...
Albert Bandura

Albert Bandura OC (/bænˈdʊərə/; born December 4, 1925) is a psychologist who is the David Starr Jordan Professor Emeritus of Social Science in Psychology at Stanford University. For almost six decades, he has been responsible for contributions to the field of education and to many fields of psychology, including social cognitive theory, therapy and personality psychology, and was also influential in the transition between behaviorism and cognitive psychology. He is known as the originator of social learning theory and the theoretical construct of self-efficacy, and is also responsible for the influential 1961 Bobo doll experiment.Social learning theory is how people learn through observing others. An example of social learning theory would be the students imitating the teacher. Self-efficacy is ""the belief in one’s capabilities to organize and execute the courses of action required to manage prospective situations."" To paraphrase, self-efficiacy is believing in yourself to take action. The Bobo Doll Experiment was how Albert Bandura studied aggression and non-aggression in children.A 2002 survey ranked Bandura as the fourth most-frequently cited psychologist of all time, behind B. F. Skinner, Sigmund Freud, and Jean Piaget, and as the most cited living one. Bandura is widely described as the greatest living psychologist, and as one of the most influential psychologists of all time.In 1974 Bandura was elected to be the Eighty-Second President of the American Psychological Association (APA). He was one of the youngest president-elects in the history of the APA at the age of 48. Bandura served as a member of the APA Board of Scientific Affairs from 1968 to 1970 and is well known as a member of the editorial board of nine psychology journals including the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology from 1963 to 1972. At the age of 82, Bandura was awarded the Grawemeyer Award for psychology.