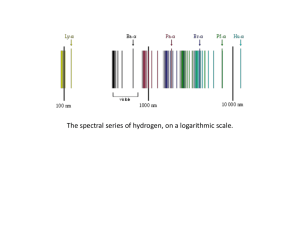
Wave nature of light
... concluded, light must be a wave (recall earlier, only waves interfere, particles do not). • Wave theory supported by Maxwell (light =electromagnetic wave, carrying energy), and Hertz’s demo with sparks from electric circuits • Einstein (1905): light = wave and particle! Dual nature, eg it travels wi ...
... concluded, light must be a wave (recall earlier, only waves interfere, particles do not). • Wave theory supported by Maxwell (light =electromagnetic wave, carrying energy), and Hertz’s demo with sparks from electric circuits • Einstein (1905): light = wave and particle! Dual nature, eg it travels wi ...
5.4 Quantum Devices Energy Levels in a Single Quantum Well
... Since single atoms may also be described as SQWs (for one electron you just have the hydrogen atom type with a Coulomb potential), we must expect that the wave function of the electrons start to overlap as soon as the single SQWs in the MQW structure are close enough. The situation is completely ana ...
... Since single atoms may also be described as SQWs (for one electron you just have the hydrogen atom type with a Coulomb potential), we must expect that the wave function of the electrons start to overlap as soon as the single SQWs in the MQW structure are close enough. The situation is completely ana ...
Document
... Any object (including atoms) can emit or absorb only certain quantities of energy. Energy is quantized; it occurs in fixed quantities, rather than being continuous. Each fixed quantity of energy is called a quantum. An atom changes its energy state by emitting or absorbing one or more quanta of ener ...
... Any object (including atoms) can emit or absorb only certain quantities of energy. Energy is quantized; it occurs in fixed quantities, rather than being continuous. Each fixed quantity of energy is called a quantum. An atom changes its energy state by emitting or absorbing one or more quanta of ener ...
Vocabulary:
... Bohr’s Atomic Model Planetary System Model – Electrons move around the nucleus of an atom, like the planets around the sun. James Maxwell – Proposed that visible light consists of electromagnetic waves. Maxwell Planck – Suggested that atoms and molecules emit energy in discrete quantities, called qu ...
... Bohr’s Atomic Model Planetary System Model – Electrons move around the nucleus of an atom, like the planets around the sun. James Maxwell – Proposed that visible light consists of electromagnetic waves. Maxwell Planck – Suggested that atoms and molecules emit energy in discrete quantities, called qu ...
Rutherford–Bohr model
... existence of excited states in mercury atoms, helping to confirm the quantum theory which predicted that electrons occupied only discrete, quantized energy states. Electrons were accelerated by a voltage toward a positively charged grid in a glass envelope filled with mercury vapor. Past the grid wa ...
... existence of excited states in mercury atoms, helping to confirm the quantum theory which predicted that electrons occupied only discrete, quantized energy states. Electrons were accelerated by a voltage toward a positively charged grid in a glass envelope filled with mercury vapor. Past the grid wa ...
1 - High School Teachers
... 5. thermal expansion 6. use of heat 7. electrostatics 8. electric current 9. electricity and magnetism 10. electric circuits 11. electric power ...
... 5. thermal expansion 6. use of heat 7. electrostatics 8. electric current 9. electricity and magnetism 10. electric circuits 11. electric power ...
Chapter 3 de Broglie`s postulate: wavelike properties of particles
... width of either line, / ? (c) Calculate the uncertainty E in the energy of the excited state of the atom. (d) From the previous results determine, to within an accuracy E , the energy E of the excited state of a sodium atom, relative to its o lowest energy state, that emits a photon whose ...
... width of either line, / ? (c) Calculate the uncertainty E in the energy of the excited state of the atom. (d) From the previous results determine, to within an accuracy E , the energy E of the excited state of a sodium atom, relative to its o lowest energy state, that emits a photon whose ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
... All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
Theoretical Physics T2 Quantum Mechanics
... 1.7.1 Comparison of classical and quantum mechanical results 1.7.2 Interpretation of quantum mechanical results . . . . . . . 1.7.3 Interferometry with C60 −molecules . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 1.7.1 Comparison of classical and quantum mechanical results 1.7.2 Interpretation of quantum mechanical results . . . . . . . 1.7.3 Interferometry with C60 −molecules . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... Energy and frequency are ____________________________ proportional. Einstein later theorized that light behaves as both a wave and a stream of particles called ____________________. This phenomenon is often referred to as the ________ nature of light. ...
... Energy and frequency are ____________________________ proportional. Einstein later theorized that light behaves as both a wave and a stream of particles called ____________________. This phenomenon is often referred to as the ________ nature of light. ...
REVIEW OF WAVE MECHANICS
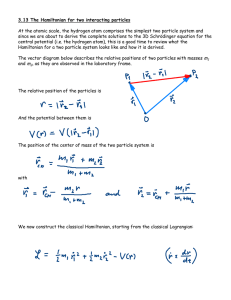
... The wave function oscillates in space when the total energy E > V(r), the local potential energy. However when E < V(r) solutions of the TISE require the wave function to decay or grow exponentially. Clearly if the particle is to remain bound inside its well, its wave function must only decay into t ...
... The wave function oscillates in space when the total energy E > V(r), the local potential energy. However when E < V(r) solutions of the TISE require the wave function to decay or grow exponentially. Clearly if the particle is to remain bound inside its well, its wave function must only decay into t ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... 2. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ...
... 2. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ...
Lecture 1 Where it all Began
... proposed that particles could have wave properties (wave/particle duality). Particles could have an associated wavelength (λ) ...
... proposed that particles could have wave properties (wave/particle duality). Particles could have an associated wavelength (λ) ...