Shor Handout Updated (click here to download) File
... • Hospital transmission mostly hands, some airborne • Evidence of airborne spread in burn units, positive-pressure ventilation 1940’s-50’s • Some evidence for hospital design, single-bed isolation in prevention of transmission • Difficult to eradicate since many asymptomatic carriers, may be coloniz ...
... • Hospital transmission mostly hands, some airborne • Evidence of airborne spread in burn units, positive-pressure ventilation 1940’s-50’s • Some evidence for hospital design, single-bed isolation in prevention of transmission • Difficult to eradicate since many asymptomatic carriers, may be coloniz ...
Outbreak of Laryngotrachetis in Privet Commercial - An
... intranuclear inclusion bodies from the tracheal epithleal cell's of both infected chickens and experimentally infected cocks , identification using neutralization test with reference anti ILT serum and detection infection level of antibodies titer by ELISA where it showed a titer > 24999 .Some recov ...
... intranuclear inclusion bodies from the tracheal epithleal cell's of both infected chickens and experimentally infected cocks , identification using neutralization test with reference anti ILT serum and detection infection level of antibodies titer by ELISA where it showed a titer > 24999 .Some recov ...
IFN-induced response
... tissue can be cited as examples, e.g. in Hepatitis C virus infection, autoantibodies are found that cross-react between GOR, a normally sequestered host nuclear antigen, and the HCV core peptide, where sequence homology between the two epitopes has been confirmed. Such antibodies are found in up to ...
... tissue can be cited as examples, e.g. in Hepatitis C virus infection, autoantibodies are found that cross-react between GOR, a normally sequestered host nuclear antigen, and the HCV core peptide, where sequence homology between the two epitopes has been confirmed. Such antibodies are found in up to ...
Recommended Vaccination Schedule Vaccination and Worming
... Lyme Disease – LYME: a tickborn disease producing fever, lameness, lethargy, seizures. ...
... Lyme Disease – LYME: a tickborn disease producing fever, lameness, lethargy, seizures. ...
Hepatitis B Vaccination and Post-Vaccination Serology Results
... Pediatric provider: Please complete this form each time the child named below receives a hepatitis B vaccination and post-vaccination serology and fax to the number below. Public Health Agency: _________________________________________ Case Coordinator: ____________________________________________ P ...
... Pediatric provider: Please complete this form each time the child named below receives a hepatitis B vaccination and post-vaccination serology and fax to the number below. Public Health Agency: _________________________________________ Case Coordinator: ____________________________________________ P ...
Communicable Diseases
... Children need five DTaP vaccines: The first three doses are given at 2, 4, and 6 months. The fourth one is given between 15 and 18 months, and the last one is given at 4–6 years. ...
... Children need five DTaP vaccines: The first three doses are given at 2, 4, and 6 months. The fourth one is given between 15 and 18 months, and the last one is given at 4–6 years. ...
Answer (each 1 mark)
... 2- Detection of hepatitis markers i.e. antigens and antibodies in blood: Antigens (1.5 marks): HBsAg: Detected before the symptoms develop it begins to circulate in the blood during the incubation period and during active disease, it may remain for months or years in carriers and is later accompanie ...
... 2- Detection of hepatitis markers i.e. antigens and antibodies in blood: Antigens (1.5 marks): HBsAg: Detected before the symptoms develop it begins to circulate in the blood during the incubation period and during active disease, it may remain for months or years in carriers and is later accompanie ...
Document
... • Vehicle transmission: transmission by an inanimate reservoir (food, water, air) • Vector transmission: Animals transmit pathogens ─ Often arthropods (fleas, ticks, mosquitoes) ─ Arthropods can carry pathogens on their feet ...
... • Vehicle transmission: transmission by an inanimate reservoir (food, water, air) • Vector transmission: Animals transmit pathogens ─ Often arthropods (fleas, ticks, mosquitoes) ─ Arthropods can carry pathogens on their feet ...
Video: Understanding Viruses - Hutchison
... Viruses can reproduce themselves only if they enter and control a host cell. Viruses contain either DNA or RNA. b)What characteristics distinguish them from living organisms? Viruses do not have their own reproductive machinery. They need to control a host cell to reproduce themselves. They do not c ...
... Viruses can reproduce themselves only if they enter and control a host cell. Viruses contain either DNA or RNA. b)What characteristics distinguish them from living organisms? Viruses do not have their own reproductive machinery. They need to control a host cell to reproduce themselves. They do not c ...
Fowl pox in Chickens and Turkeys Fowlpox is a slow
... has been used effectively to differentiate field and vaccine strains of fowlpox virus . Recently, 2monoclonal antibodies that recognize different fowlpox virus antigens have been developed. These monoclonal antibodies can be used for strain differentiation by immunoblotting . The complete sequence o ...
... has been used effectively to differentiate field and vaccine strains of fowlpox virus . Recently, 2monoclonal antibodies that recognize different fowlpox virus antigens have been developed. These monoclonal antibodies can be used for strain differentiation by immunoblotting . The complete sequence o ...
3. Chain of Infection
... • Susceptible Host. The future host is the person who is next exposed to the pathogen. The microorganism may spread to another person but does not develop into an infection if the person’s immune system can fight it off. They may however become a ‘carrier’ without symptoms, able to then be the next ...
... • Susceptible Host. The future host is the person who is next exposed to the pathogen. The microorganism may spread to another person but does not develop into an infection if the person’s immune system can fight it off. They may however become a ‘carrier’ without symptoms, able to then be the next ...
Chapter 17 Human Health and Environmental Risks
... Infectious diseases- those caused b y infectious agents, known as pathogens. ...
... Infectious diseases- those caused b y infectious agents, known as pathogens. ...
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver. Causes include viruses
... hepatitis from any cause, are profound loss of appetite, aversion to smoking among smokers, dark urine, yellowing of the eyes and skin and abdominal discomfort. Physical findings are ...
... hepatitis from any cause, are profound loss of appetite, aversion to smoking among smokers, dark urine, yellowing of the eyes and skin and abdominal discomfort. Physical findings are ...
Innate immune responses in hepatitis B virus (HBV
... Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection has a low rate of chronicity compared to HCV infection, but chronic liver inflammation can evolve to life threatening complications. Experimental data from HBV infected chimpanzees and HBV transgenic mice have indicated that cytotoxic T cells are the main cell type ...
... Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection has a low rate of chronicity compared to HCV infection, but chronic liver inflammation can evolve to life threatening complications. Experimental data from HBV infected chimpanzees and HBV transgenic mice have indicated that cytotoxic T cells are the main cell type ...
PPT WEEK 2 P 3
... •CANNOT grow in food, but once eaten, they grow inside a person’s intestines •How to prevent? •Example –Hepatitis A ...
... •CANNOT grow in food, but once eaten, they grow inside a person’s intestines •How to prevent? •Example –Hepatitis A ...
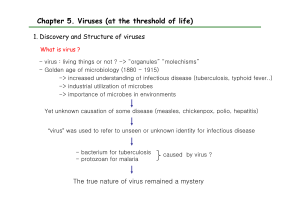
Chapter 5. Viruses (at the threshold of life)
... -> diluted filtered juice -> still infectious -> called contagious living fluid - 1930s, Wendell M. Stanley : crystalization of tobacco mosaic virus ...
... -> diluted filtered juice -> still infectious -> called contagious living fluid - 1930s, Wendell M. Stanley : crystalization of tobacco mosaic virus ...
Slajd 1
... An infectious disease caused by mycobacteria of tuberculosis complex (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M.bovis, M.africanum) and characterised by the formation of granulomas in infected tissues and by cell - mediated hypersensitivity. Most commonly a disease of the lungs but infections may occur at many ...
... An infectious disease caused by mycobacteria of tuberculosis complex (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M.bovis, M.africanum) and characterised by the formation of granulomas in infected tissues and by cell - mediated hypersensitivity. Most commonly a disease of the lungs but infections may occur at many ...
LECTUER-6 INFECTIOUS DISEASES Week No: 5 L. Dr. Yahia I
... Bovine Virus Diarrhoea (BVD) and Mucosal Disease (MD) are caused by a the viruses are classified in the virus family Flaviviridae and are members of the genus pestivirus. Pestiviruses are nonsegmented, single, sense stranded RNA viruses, there are two biotypes designated depending on their effect on ...
... Bovine Virus Diarrhoea (BVD) and Mucosal Disease (MD) are caused by a the viruses are classified in the virus family Flaviviridae and are members of the genus pestivirus. Pestiviruses are nonsegmented, single, sense stranded RNA viruses, there are two biotypes designated depending on their effect on ...
Herpes Simplex: Initial and Recurrent Infections
... pletely the first time they occur. Typically, another outat the same site, and the physician initiated antiviral therbreak can appear weeks or months later at the same site, apy. A culture was positive for HSV-1. but it almost always is less severe and of shorter duration than the initial outbreak. ...
... pletely the first time they occur. Typically, another outat the same site, and the physician initiated antiviral therbreak can appear weeks or months later at the same site, apy. A culture was positive for HSV-1. but it almost always is less severe and of shorter duration than the initial outbreak. ...
assessing changes in the leucogram
... Eosinophils have many general roles in host defence and eosinophilia is often seen as a non-specific component of a systemic inflammatory reaction. Eosinophils are attracted by mast cell degranulation and have therefore been associated with antigen-antibody interactions in tissues rich in mast cells ...
... Eosinophils have many general roles in host defence and eosinophilia is often seen as a non-specific component of a systemic inflammatory reaction. Eosinophils are attracted by mast cell degranulation and have therefore been associated with antigen-antibody interactions in tissues rich in mast cells ...
1 Barley Yellow Dwarf Papaya Ringspot Virus Tobacco Mosaic Virus
... Very small genome - 104-105 nucleotides – this typically codes for 4-7 proteins Viruses contain a single type of nucleic acid, either RNA (most plant viruses) or DNA When completely assembled (the virion), the nucleic acid is protected by a protein coat (the capsid) consisting of individual ...
... Very small genome - 104-105 nucleotides – this typically codes for 4-7 proteins Viruses contain a single type of nucleic acid, either RNA (most plant viruses) or DNA When completely assembled (the virion), the nucleic acid is protected by a protein coat (the capsid) consisting of individual ...
Pathogens that cause disease
... • Viruses are non-living and can infect all types of organisms. • They are obligate intracellular parasites, meaning they cannot replicate outside of cells. • A single virus particle (virion) is composed of genetic material either DNA or RNA, enclosed in a protein coat known as a capsid • Viruses do ...
... • Viruses are non-living and can infect all types of organisms. • They are obligate intracellular parasites, meaning they cannot replicate outside of cells. • A single virus particle (virion) is composed of genetic material either DNA or RNA, enclosed in a protein coat known as a capsid • Viruses do ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.