Zoonotic Diseases in Pork Production
... A: There are numerous steps to be taken. These include: proper personal protective equipment, careful hand washing, and other steps to avoid contact with infectious agents. Refer to the sample plan on infection control for more detailed information. Q: Are there any groups at higher levels of risk t ...
... A: There are numerous steps to be taken. These include: proper personal protective equipment, careful hand washing, and other steps to avoid contact with infectious agents. Refer to the sample plan on infection control for more detailed information. Q: Are there any groups at higher levels of risk t ...
is often called the kissing disease. The virus that causes mono is
... Infectious mononucleosis (mono) is often called the kissing disease. The virus that causes mono is transmitted through saliva, so you can get it through kissing, but you can also be exposed through a cough or sneeze, or by sharing a glass or food utensil with someone who has mono. Signs and symptoms ...
... Infectious mononucleosis (mono) is often called the kissing disease. The virus that causes mono is transmitted through saliva, so you can get it through kissing, but you can also be exposed through a cough or sneeze, or by sharing a glass or food utensil with someone who has mono. Signs and symptoms ...
2.1 and 2.2 - WordPress.com
... • The trigger to switch between one replication strategy to another depends on the health of the host cell. ...
... • The trigger to switch between one replication strategy to another depends on the health of the host cell. ...
Immunology
... ◦ Antigens-a marker on the surface of cell that identifies it as “self” or “non-self” ◦ Antibody-a substance produced by B lymphocytes in response to the presence of a foreign antigen that will combine with and control the antigen, thus preventing infection ◦ Immunity-a long term condition of protec ...
... ◦ Antigens-a marker on the surface of cell that identifies it as “self” or “non-self” ◦ Antibody-a substance produced by B lymphocytes in response to the presence of a foreign antigen that will combine with and control the antigen, thus preventing infection ◦ Immunity-a long term condition of protec ...
Bovine Respiratory Disease - Veterinary Extension
... mechanisms designed to protect the lungs. This is much more serious and causes more severe signs than does an upper respiratory infection. The causes of BRD are multiple and complex, but the three factors of stress, viral infection, and bacterial infection are almost always involved in cases of seve ...
... mechanisms designed to protect the lungs. This is much more serious and causes more severe signs than does an upper respiratory infection. The causes of BRD are multiple and complex, but the three factors of stress, viral infection, and bacterial infection are almost always involved in cases of seve ...
Streptoccocal Respiratory Infection
... It has ability to colonize and rapidly multiply and spread in its host while resist phagocytosis due to the cell surface T, R, M-proteins.. About 100 serotypes Resistance & Immunity to infection developed by presence of specific M-protein antibodies Respiratory Infection.. Via droplets..Mostly ...
... It has ability to colonize and rapidly multiply and spread in its host while resist phagocytosis due to the cell surface T, R, M-proteins.. About 100 serotypes Resistance & Immunity to infection developed by presence of specific M-protein antibodies Respiratory Infection.. Via droplets..Mostly ...
Copyright Slapped Cheeks - STA HealthCare Communications
... develop, primarily in adults. Vertical transmission of the infection in pregnant women has been linked to hydrops fetalis and spontaneous abortion. In patients with underlying chronic hemolytic anemias such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia or immunodeficiency states such as leukemia, EI infection ...
... develop, primarily in adults. Vertical transmission of the infection in pregnant women has been linked to hydrops fetalis and spontaneous abortion. In patients with underlying chronic hemolytic anemias such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia or immunodeficiency states such as leukemia, EI infection ...
A2/C2 - MDPI
... overlaps with the small surface protein (HBsAg). For this reason, mutations in the RT region could result in alterations in the replication capacity, antigenicity, encapsulation, tolerance against antiviral therapy and virulence of HBV [8–10]. According to the criteria of 8% divergence in the comple ...
... overlaps with the small surface protein (HBsAg). For this reason, mutations in the RT region could result in alterations in the replication capacity, antigenicity, encapsulation, tolerance against antiviral therapy and virulence of HBV [8–10]. According to the criteria of 8% divergence in the comple ...
Factsheet Ebola virus disease and close contacts
... Ebola virus then spreads from person to person via contact with the blood, secretions, or other bodily fluids of infected people, and contact with environments contaminated with such fluid, including in healthcare settings. Transmission through sexual contact may occur up to three months after clini ...
... Ebola virus then spreads from person to person via contact with the blood, secretions, or other bodily fluids of infected people, and contact with environments contaminated with such fluid, including in healthcare settings. Transmission through sexual contact may occur up to three months after clini ...
Replication Kinetic of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus in
... early and late genes are subsequently transcribed. Viral capsid assembly and progeny DNA encapsidation takes place in the nucleus. The produced extracellular virions are in infected cells (5, 6). The latent or nonproductive infection is established by expression of latency-associated transcript (LAT ...
... early and late genes are subsequently transcribed. Viral capsid assembly and progeny DNA encapsidation takes place in the nucleus. The produced extracellular virions are in infected cells (5, 6). The latent or nonproductive infection is established by expression of latency-associated transcript (LAT ...
Salon Ecology
... • Bacilli and Spirilla have flagella (cilia) – Hair-like projections which extend from the sides of the cell. ...
... • Bacilli and Spirilla have flagella (cilia) – Hair-like projections which extend from the sides of the cell. ...
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) - Colorado Health and Environmental Data
... Until Robert Koch's discovery of the TB bacteria in 1882, many scientists believed that TB was hereditary and could not be prevented Koch’s discovery brought hopes for a cure but also bred fear of contagion A person with TB was frequently labeled an outcast ...
... Until Robert Koch's discovery of the TB bacteria in 1882, many scientists believed that TB was hereditary and could not be prevented Koch’s discovery brought hopes for a cure but also bred fear of contagion A person with TB was frequently labeled an outcast ...
Hepatitis B Guidelines - Yukon Health and Social Services
... infectious blood and body fluids. It is most commonly acquired through sexual contact, injection drug use, and perinatal exposure from mother to infant. When infection occurs as an adult, about 5 per cent will become chronically infected, while about 90 per cent of infants infected at birth will dev ...
... infectious blood and body fluids. It is most commonly acquired through sexual contact, injection drug use, and perinatal exposure from mother to infant. When infection occurs as an adult, about 5 per cent will become chronically infected, while about 90 per cent of infants infected at birth will dev ...
Clinical Pathology Conference
... Differences in clinical presentation of HBV MN between children and adults Bhimma, R. Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Nephropathy. Am J Nephro. 24(2). 2004. ...
... Differences in clinical presentation of HBV MN between children and adults Bhimma, R. Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Nephropathy. Am J Nephro. 24(2). 2004. ...
ENGLISH 3050 PROJECT 1 Post Viral Cerebellar
... Post Viral Cerebellar Ataxia is caused by damage to or problems with the cerebellum. It is most common in children, especially those younger than age 3 and usually occurs several weeks following a viral infection. Viral infections that may cause Post Viral Cerebellar Ataxia include the following; C ...
... Post Viral Cerebellar Ataxia is caused by damage to or problems with the cerebellum. It is most common in children, especially those younger than age 3 and usually occurs several weeks following a viral infection. Viral infections that may cause Post Viral Cerebellar Ataxia include the following; C ...
Skin Infections I
... o Allows you to determine the MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) of a particular antimicrobial against S.aureus o Once you determine MIC, can determine if that drug is a therapeutic option (ie. does MIC fall into proper dosing range) ...
... o Allows you to determine the MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) of a particular antimicrobial against S.aureus o Once you determine MIC, can determine if that drug is a therapeutic option (ie. does MIC fall into proper dosing range) ...
SEPRL Avian Influenza Research Team David L. Suarez Vaccine
... partners that livestock have not been exposed to infectious virus i.e. differentiate vaccinated only and vaccinated and then infected poultry • Can also be used as surveillance tool for low virulence AIV to determine incidence of infection when vaccination is used • Inexpensive, reliable, and high t ...
... partners that livestock have not been exposed to infectious virus i.e. differentiate vaccinated only and vaccinated and then infected poultry • Can also be used as surveillance tool for low virulence AIV to determine incidence of infection when vaccination is used • Inexpensive, reliable, and high t ...
Herpes viruses
... Herpes viruses Introduction The Herpetoviridae family is a complicated family of viruses. In this family we have 25 different viruses which infect both humans and different species of animals. Only 8 of the viruses are known to cause infections in humans. Each one causes different clinical manifesta ...
... Herpes viruses Introduction The Herpetoviridae family is a complicated family of viruses. In this family we have 25 different viruses which infect both humans and different species of animals. Only 8 of the viruses are known to cause infections in humans. Each one causes different clinical manifesta ...
Our aim - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... the properties of living systems such a s having a genome and being able to adapt to changing environments • However, viruses cannot capture or store free energy and they are not functionally active outside their host cells. • A virus has both intrinsic properties (e.g. its size) and extrinsic prope ...
... the properties of living systems such a s having a genome and being able to adapt to changing environments • However, viruses cannot capture or store free energy and they are not functionally active outside their host cells. • A virus has both intrinsic properties (e.g. its size) and extrinsic prope ...
Equine Viral Diseases
... Vaccination –95% control rate WNV Antibody for horses already infected (from Novartis Animal Vaccines, Inc.) ...
... Vaccination –95% control rate WNV Antibody for horses already infected (from Novartis Animal Vaccines, Inc.) ...
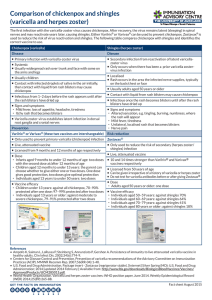
Comparison of chickenpox and shingles (varicella and herpes zoster)
... The first infection with the varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox. After recovery, the virus remains latent (sleeping) in spinal nerves and may reactivate years later, causing shingles. Either Varilrix® or Varivax® can be used to prevent chickenpox. Zostavax® is used to reduce the risk of virus ...
... The first infection with the varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox. After recovery, the virus remains latent (sleeping) in spinal nerves and may reactivate years later, causing shingles. Either Varilrix® or Varivax® can be used to prevent chickenpox. Zostavax® is used to reduce the risk of virus ...
Water Borne Microbial Diseases
... • Water, sodium, and other electrolytes follow and leave the body as diarrhoea. • Characteristic rice water stools, causes dehydration; life-threatening if untreated ...
... • Water, sodium, and other electrolytes follow and leave the body as diarrhoea. • Characteristic rice water stools, causes dehydration; life-threatening if untreated ...
Inflammation & the Immune Response Unit VIII
... Bacteria adapt in ways which make an antibiotic less effective or ineffective MRSA ...
... Bacteria adapt in ways which make an antibiotic less effective or ineffective MRSA ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.