Winchester Hospital B2 Infection Prevention Team
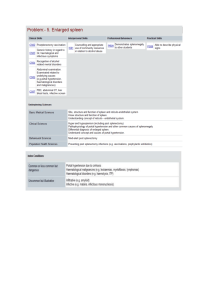
... Aim – Reduce hospital acquired multidrug resistant organisms on one unit in three phases over one year. ...
... Aim – Reduce hospital acquired multidrug resistant organisms on one unit in three phases over one year. ...
DISEASES SPREAD THROUGH BLOOD AND BODY FLUIDS
... B. Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Ninety per cent of those infected with HBV recover completely from the disease. Three to 10 per cent of cases go on to be chronic carriers of the virus (i.e., individuals who are not able to develop antibo ...
... B. Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Ninety per cent of those infected with HBV recover completely from the disease. Three to 10 per cent of cases go on to be chronic carriers of the virus (i.e., individuals who are not able to develop antibo ...
Equine Influenza: A Highly Contagious Respiratory Disease
... that affects horses, H7N7 (also known as A1), and H3N8 (also known as A2). This viral disease is spread by inhalation of drops of infective material. When an infected horse coughs or has nasal discharge, and another horse comes in contact with the infective material, that horse is exposed. The virus ...
... that affects horses, H7N7 (also known as A1), and H3N8 (also known as A2). This viral disease is spread by inhalation of drops of infective material. When an infected horse coughs or has nasal discharge, and another horse comes in contact with the infective material, that horse is exposed. The virus ...
2017 Meeting -Zika Virus GP Update
... 47 cases with antibody evidence indicating recent infection [seroconversion] and 90 cases that have antibody evidence highly indicative of recent infection (Zika-specific IgM) [probable cases]. ...
... 47 cases with antibody evidence indicating recent infection [seroconversion] and 90 cases that have antibody evidence highly indicative of recent infection (Zika-specific IgM) [probable cases]. ...
Vertical Transmission of Murine Cytomegalovirus
... Embryo cells from uninfected mice, and cells infected with MCMV in vitro and harvested at 2o h p.i. were used as controls (Fig. 2a and b). The results show very low numbers of background grains in uninfected cells (a) while in contrast the infected cells at 2o h.p.i. contained many grains concentrat ...
... Embryo cells from uninfected mice, and cells infected with MCMV in vitro and harvested at 2o h p.i. were used as controls (Fig. 2a and b). The results show very low numbers of background grains in uninfected cells (a) while in contrast the infected cells at 2o h.p.i. contained many grains concentrat ...
Nervous System Infections - Biology Online Learning
... • Develop gradually in healthy individuals • Generally consist of ...
... • Develop gradually in healthy individuals • Generally consist of ...
Immune System Review
... How can Diseases be caused by pathogens, fungi, and cigarette smoke? Give examples of each. An example of an infectious disease that is spread by viruses in the air is How do Antibiotics fight infections? The inflammatory response can cause, three general symptoms, what are they? If the skin is cut ...
... How can Diseases be caused by pathogens, fungi, and cigarette smoke? Give examples of each. An example of an infectious disease that is spread by viruses in the air is How do Antibiotics fight infections? The inflammatory response can cause, three general symptoms, what are they? If the skin is cut ...
How vaccines work.
... work fast enough to prevent the antigen from causing disease, so the child still gets sick. • However, the immune system “remembers” that antigen. If it ever enters the body again, even after many years, the immune system can produce antibodies fast enough to keep it from causing disease a second ti ...
... work fast enough to prevent the antigen from causing disease, so the child still gets sick. • However, the immune system “remembers” that antigen. If it ever enters the body again, even after many years, the immune system can produce antibodies fast enough to keep it from causing disease a second ti ...
HIV Disease
... Person may not know they have HIV Person may suspect they have HIV but will not get tested so they can say, “I do not know if I have the disease.” Sexual activity may continue, increase, or decrease ...
... Person may not know they have HIV Person may suspect they have HIV but will not get tested so they can say, “I do not know if I have the disease.” Sexual activity may continue, increase, or decrease ...
Quiz- Dengue Fever Week - Ipswich-Year2-Med-PBL-Gp-2
... mass) then to a schizont which has multiple chromatin masses, each of which develops into a merozoite. – Red Blood cell lyse, releasing merozoites that can infect additional red cells. – Some however develop into sexual forms called gametocytes that infect the mosquito ...
... mass) then to a schizont which has multiple chromatin masses, each of which develops into a merozoite. – Red Blood cell lyse, releasing merozoites that can infect additional red cells. – Some however develop into sexual forms called gametocytes that infect the mosquito ...
Infection Control Quiz #1 Your client is a 40 year old man who has
... b. Indirect contact with a contaminated instrument such as dental instruments c. Direct contact with blood and oral fluids d. Inhalation of chemical fumes in the radiology darkroom e. Inhalation of airborne microorganisms that can remain suspended in the air 14. Reservoirs in the chain of infection ...
... b. Indirect contact with a contaminated instrument such as dental instruments c. Direct contact with blood and oral fluids d. Inhalation of chemical fumes in the radiology darkroom e. Inhalation of airborne microorganisms that can remain suspended in the air 14. Reservoirs in the chain of infection ...
Foodborne Viruses in the European Union
... • Common source outbreaks due to contaminated food or water also occur • Quite contagious when spread from person to person (R0 HAV= 1.3) • Acute disease – does not have a chronic form. Protective antibodies develop after infection • Vaccine preventable • Clinical severity tends to increase with age ...
... • Common source outbreaks due to contaminated food or water also occur • Quite contagious when spread from person to person (R0 HAV= 1.3) • Acute disease – does not have a chronic form. Protective antibodies develop after infection • Vaccine preventable • Clinical severity tends to increase with age ...
13- 2012common_child..
... severities of croup, single dose is usually all that is required. Moderate to severe croup may be improved temporarily with nebulized epinephrine ...
... severities of croup, single dose is usually all that is required. Moderate to severe croup may be improved temporarily with nebulized epinephrine ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Training Kit Presentation
... The average incubation period for hepatitis C is generally 6-7 weeks with a range of 2 weeks to 26 weeks. About 80% of persons having an acute infection show no signs or symptoms, with about 20% having jaundice and mild symptoms. It’s rare that death from acute liver failure from hepatitis C occurs ...
... The average incubation period for hepatitis C is generally 6-7 weeks with a range of 2 weeks to 26 weeks. About 80% of persons having an acute infection show no signs or symptoms, with about 20% having jaundice and mild symptoms. It’s rare that death from acute liver failure from hepatitis C occurs ...
Immunity to infection_vibuntita
... Location of infectious agents in host tissue is of the essence for development and differentiation of immune responses ...
... Location of infectious agents in host tissue is of the essence for development and differentiation of immune responses ...
Judul
... • Information has value, it can affect our lives and our livelihood • Information has become an integral part of the structure of society • Information needs to be trusted if it is to be useful, the breakdown of trust removes value from the information protected. ...
... • Information has value, it can affect our lives and our livelihood • Information has become an integral part of the structure of society • Information needs to be trusted if it is to be useful, the breakdown of trust removes value from the information protected. ...
Document
... New TB cases are driven by the reservoir of latently infected people. If we want to stop active TB cases, we need to eliminate this reservoir of infection. ...
... New TB cases are driven by the reservoir of latently infected people. If we want to stop active TB cases, we need to eliminate this reservoir of infection. ...
Topic Library – Hepatitis C - Australian Indigenous HealthInfoNet
... Medical Journal of Australia;166(3):127-130 Butler T, Spencer J, Cui JS, Vickery K, Zou J, et al. (1999) Seroprevalence of markers for hepatitis B, C and G in male and female prisoners NSW, 1996. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health;23(4):377-384 Colman A, Crombie I (2001) Hepatitis C ...
... Medical Journal of Australia;166(3):127-130 Butler T, Spencer J, Cui JS, Vickery K, Zou J, et al. (1999) Seroprevalence of markers for hepatitis B, C and G in male and female prisoners NSW, 1996. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health;23(4):377-384 Colman A, Crombie I (2001) Hepatitis C ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Atypical Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
... "Patterns of acute and persistent infections" from Mims. Medical Microbiology ...
... "Patterns of acute and persistent infections" from Mims. Medical Microbiology ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.