Slide 1
... Management of occupational exposure to HCV baseline serology and HCV serology at 3 months HCV PCR at 6 weeks in high risk exposures monitor LFTs every 2 weeks no prophylaxis available early interferon treatment of acute Hepatitis C may ...
... Management of occupational exposure to HCV baseline serology and HCV serology at 3 months HCV PCR at 6 weeks in high risk exposures monitor LFTs every 2 weeks no prophylaxis available early interferon treatment of acute Hepatitis C may ...
Intestinal Pathogens Flyer - Medical Diagnostic Laboratories
... Clinical Significance: Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive, facultative intracellular parasite and is the causative agent of listeriosis. L. monocytogenes infections can cause septicemia, encephalitis, meningitis, and gastroenteritis. The bacteria is capable of entering most cells. Transmissio ...
... Clinical Significance: Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive, facultative intracellular parasite and is the causative agent of listeriosis. L. monocytogenes infections can cause septicemia, encephalitis, meningitis, and gastroenteritis. The bacteria is capable of entering most cells. Transmissio ...
Information Cascade
... Question: How to select a subset of persons such that maximum number of persons can be influenced? ...
... Question: How to select a subset of persons such that maximum number of persons can be influenced? ...
lecture1
... In the case of the fungal infection, the fungus keeps growing until it reaches the reproductive phase and starts to reproduce. The time that passes between the infected spot is known as the latency period. The latency period is followed by the infection period during when the fungus produces a certa ...
... In the case of the fungal infection, the fungus keeps growing until it reaches the reproductive phase and starts to reproduce. The time that passes between the infected spot is known as the latency period. The latency period is followed by the infection period during when the fungus produces a certa ...
Humabs BioMed and the Institute for Research in Biomedicine
... therapeutics company, and the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB) affiliated to the Università della Svizzera Italiana today announced the identification, isolation and characterization of two Ebola virus neutralizing monoclonal antibodies from the blood of a survivor of an Ebola infection. ...
... therapeutics company, and the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB) affiliated to the Università della Svizzera Italiana today announced the identification, isolation and characterization of two Ebola virus neutralizing monoclonal antibodies from the blood of a survivor of an Ebola infection. ...
Lesson Virology. Morphology and structure of viruses. Methods of
... (A) *The vaccine should not be given in conjunction with other viral vaccines because interference can occur (B) The vaccine contains live, attenuated virus (C) Virus in the vaccine contains only one serotype (D) The vaccine should not be given prior to 15 months of age because maternal antibodies c ...
... (A) *The vaccine should not be given in conjunction with other viral vaccines because interference can occur (B) The vaccine contains live, attenuated virus (C) Virus in the vaccine contains only one serotype (D) The vaccine should not be given prior to 15 months of age because maternal antibodies c ...
... 101 children (3-6y; F=52, M=49) nutritionally eutrophic. Sixty two children free of G. lamblia and 39 infected. The serum concentration of IFN-gamma, IL-4 and IL-10 (pg/mL) were determined by ELISA method and IL-2 (U/mL) by EAISA method. The Student’s t test was applied to compare the groups. We con ...
kdscl - Pathways Kelowna
... Pathways Abilities Society is committed to ensuring the safe keeping of all individuals and staff. Implementation of the following measures and procedures are required in order to uphold a safe and practiced level of Universal Precautions. Universal Precautions is the practice of stopping the spread ...
... Pathways Abilities Society is committed to ensuring the safe keeping of all individuals and staff. Implementation of the following measures and procedures are required in order to uphold a safe and practiced level of Universal Precautions. Universal Precautions is the practice of stopping the spread ...
Skin condition info (USA Wrestling)
... - Folliculitis: Mild superficial bacterial infection of the hair follicles. Presents with "pus" filled lesions around the base of the hair. In normal healthy individuals, the immune system will neutralize the bacteria. If no "pus" filled blisters present not considered infectious. - Boil (Furuncle): ...
... - Folliculitis: Mild superficial bacterial infection of the hair follicles. Presents with "pus" filled lesions around the base of the hair. In normal healthy individuals, the immune system will neutralize the bacteria. If no "pus" filled blisters present not considered infectious. - Boil (Furuncle): ...
Vaccination
... prevention of disease. • Immunization: is the process of inducing immunity artificially by either vaccination or administration of antibody. • Immunizing agents include vaccines, toxoids, antitoxins, and immune globulins derived from human or animal donors. ...
... prevention of disease. • Immunization: is the process of inducing immunity artificially by either vaccination or administration of antibody. • Immunizing agents include vaccines, toxoids, antitoxins, and immune globulins derived from human or animal donors. ...
Bloodbourne Pathogens
... and clinicians. Standard precautions apply to contact with blood, all body fluids, secretions and excretions except sweat, regardless of whether they contain blood, non-intact skin and mucous membranes. ...
... and clinicians. Standard precautions apply to contact with blood, all body fluids, secretions and excretions except sweat, regardless of whether they contain blood, non-intact skin and mucous membranes. ...
EBOLA VIRUS WHAT NURSES NEED TO KNOW
... o residence in, or travel to, an area where EVD transmission is active; o or direct handling of bats, rodents, or primates from disease-endemic areas. Malaria diagnostics should also be a part of initial testing because it is a common cause of febrile illness in persons with a travel history to the ...
... o residence in, or travel to, an area where EVD transmission is active; o or direct handling of bats, rodents, or primates from disease-endemic areas. Malaria diagnostics should also be a part of initial testing because it is a common cause of febrile illness in persons with a travel history to the ...
Saint Louis Encephalitis Virus, another re
... Figure 1 - Worldwide distribution and trends in time of scientific production on Saint Louis Encephalitis Virus (from GoPubMed®). ...
... Figure 1 - Worldwide distribution and trends in time of scientific production on Saint Louis Encephalitis Virus (from GoPubMed®). ...
A proactive approach to infection control
... prior to cleaning being undertaken. Ventilated. Some form of hazard warning tape/signage is recommended to prevent access. Remember viral particles can travel a long way, so don’t confine the cordoned off area to just the immediate area of contamination. Where possible the areas to be cleaned and co ...
... prior to cleaning being undertaken. Ventilated. Some form of hazard warning tape/signage is recommended to prevent access. Remember viral particles can travel a long way, so don’t confine the cordoned off area to just the immediate area of contamination. Where possible the areas to be cleaned and co ...
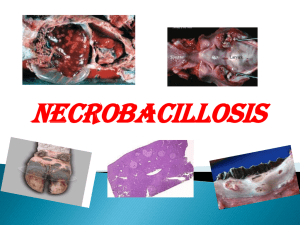
necrobacillosis_0
... Calf diphtheria Bronchopneumonia, purulent or necrotic pneumonia and pleurisy Acute catarrhal, ulcerative or necrotic enteritis Calf usually dies after 4-5 days due to pneumonia and toxemia ...
... Calf diphtheria Bronchopneumonia, purulent or necrotic pneumonia and pleurisy Acute catarrhal, ulcerative or necrotic enteritis Calf usually dies after 4-5 days due to pneumonia and toxemia ...
Lecture GuideViruses(Ch13)–7e
... their genome and also an envelope. The influenza virus is a virus in this family with 8 segments of ssRNA that make up its genome. There are two key spikes found on the envelope, an H spike and an N spike. The H spike (hemagglutinin) is used by the virus to enter/bind to target host cells. The N spi ...
... their genome and also an envelope. The influenza virus is a virus in this family with 8 segments of ssRNA that make up its genome. There are two key spikes found on the envelope, an H spike and an N spike. The H spike (hemagglutinin) is used by the virus to enter/bind to target host cells. The N spi ...
LACTOFERRIN MODULATES HSV-1 INFECTION AT EARLY
... Department of Virology, 2Department of Cariology, University of Turku, Turku, Finland The abstract should describe the purpose of the study and the major results and conclusions. If you prefer breaking the text into paragraphs, please do not leave space between them. Oral mucosa is a frequent site o ...
... Department of Virology, 2Department of Cariology, University of Turku, Turku, Finland The abstract should describe the purpose of the study and the major results and conclusions. If you prefer breaking the text into paragraphs, please do not leave space between them. Oral mucosa is a frequent site o ...
Virus-Linked Cancers
... argon gas to destroy the abnormal tissue. Maria is fine now and cancer-free, but has to go in more often for routine pap tests over the next few years to make sure that cancerous cells do not form. ...
... argon gas to destroy the abnormal tissue. Maria is fine now and cancer-free, but has to go in more often for routine pap tests over the next few years to make sure that cancerous cells do not form. ...
Serology testing
... For a selection of infectious agents, a multiplex EvalutionTM1 serology prototype assay was developed. The assay detects and measures antibodies against different types of pathogens present in the blood of postinfected specimens (table 1). For each infectious agent, one or ...
... For a selection of infectious agents, a multiplex EvalutionTM1 serology prototype assay was developed. The assay detects and measures antibodies against different types of pathogens present in the blood of postinfected specimens (table 1). For each infectious agent, one or ...
New Zealand Health Declaration
... an infectious nature: fever accompanied by prostration or persisting for several days, or attended with glandular swelling; or any acute skin rash or eruption with or without fever; severe diarrhoea with symptoms of collapse; jaundice accompanied by fever. ...
... an infectious nature: fever accompanied by prostration or persisting for several days, or attended with glandular swelling; or any acute skin rash or eruption with or without fever; severe diarrhoea with symptoms of collapse; jaundice accompanied by fever. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.