EDITORIAL Ebola virus disease in West Africa: outbreak or epidemic?
... By definition, a disease “outbreak” is “the occurrence of cases of disease in a community or region where it would not normally be expected, or at a much greater level than expected”, while an “epidemic” is “the occurrence of disease at a level greater than would normally be expected”.1 In other wor ...
... By definition, a disease “outbreak” is “the occurrence of cases of disease in a community or region where it would not normally be expected, or at a much greater level than expected”, while an “epidemic” is “the occurrence of disease at a level greater than would normally be expected”.1 In other wor ...
meningitis - Infectious Diseases
... Antibiotics are given to close contacts of patients with meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis. “Close contacts include household members, child care center contacts, and anyone directly exposed to the patient’s oral secretions (e.g., through kissing, mouth-tomouth resuscitation, endotracheal ...
... Antibiotics are given to close contacts of patients with meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis. “Close contacts include household members, child care center contacts, and anyone directly exposed to the patient’s oral secretions (e.g., through kissing, mouth-tomouth resuscitation, endotracheal ...
The Cycle of Infection
... individual in a health care facility which is transmitted by health care workers to the patient. D. Opportunistic- means the infections are those that occur when the body’s defenses are weak. II. Infections are also classified as Aerobic or Anaerobic: A. Aerobic- means the organism requires oxygen ...
... individual in a health care facility which is transmitted by health care workers to the patient. D. Opportunistic- means the infections are those that occur when the body’s defenses are weak. II. Infections are also classified as Aerobic or Anaerobic: A. Aerobic- means the organism requires oxygen ...
When It Comes to Vaccines - National Foundation for Infectious
... When It Comes to Vaccines: Doctors and Patients Aren’t Hearing One Another Most physicians say “I talk to all of my patients about vaccines” ...
... When It Comes to Vaccines: Doctors and Patients Aren’t Hearing One Another Most physicians say “I talk to all of my patients about vaccines” ...
CATEGORY A
... Primarily a pathogen of birds, elementary bodies are excreted in droppings. Humans inhale elementary bodies, causing a flu-like illness (“parrot fever”- ornithosis) After an incubation period of 5 to 14 days the human develops ...
... Primarily a pathogen of birds, elementary bodies are excreted in droppings. Humans inhale elementary bodies, causing a flu-like illness (“parrot fever”- ornithosis) After an incubation period of 5 to 14 days the human develops ...
scarlet fever * frequently asked questions
... Most mild cases of scarlet fever will clear up on their own, but it is still best to see your GP if you, or your child, are showing symptoms. Having treatment for the illness speeds recovery and reduces the risk of complications. You will also become non-contagious more quickly. In most cases, docto ...
... Most mild cases of scarlet fever will clear up on their own, but it is still best to see your GP if you, or your child, are showing symptoms. Having treatment for the illness speeds recovery and reduces the risk of complications. You will also become non-contagious more quickly. In most cases, docto ...
SCARLET FEVER FAQs - Curbar Primary School
... Most mild cases of scarlet fever will clear up on their own, but it is still best to see your GP if you, or your child, are showing symptoms. Having treatment for the illness speeds recovery and reduces the risk of complications. You will also become non-contagious more quickly. In most cases, docto ...
... Most mild cases of scarlet fever will clear up on their own, but it is still best to see your GP if you, or your child, are showing symptoms. Having treatment for the illness speeds recovery and reduces the risk of complications. You will also become non-contagious more quickly. In most cases, docto ...
SCARLET-FEVER-FAQs - Moir Medical Centre, Long Eaton
... vomiting. After 12 to 48 hours the characteristic fine red rash develops (if you touch it, it feels like sandpaper). Typically, it first appears on the chest and stomach, rapidly spreading to other parts of the body. On more darkly-pigmented skin, the scarlet rash may be harder to spot, although the ...
... vomiting. After 12 to 48 hours the characteristic fine red rash develops (if you touch it, it feels like sandpaper). Typically, it first appears on the chest and stomach, rapidly spreading to other parts of the body. On more darkly-pigmented skin, the scarlet rash may be harder to spot, although the ...
ebola: facts and fiction
... website, PLOS current, outbreaks is a publication channel that seeks to minimize the time between the generation and publication of new research, without threatening its integrity in relation to peer-reviewing, citations, and other legitimizing processes. ...
... website, PLOS current, outbreaks is a publication channel that seeks to minimize the time between the generation and publication of new research, without threatening its integrity in relation to peer-reviewing, citations, and other legitimizing processes. ...
Abstinence PowerPoint
... What is abstinence? • The conscious decision not to participate in sexual activity of any kind ...
... What is abstinence? • The conscious decision not to participate in sexual activity of any kind ...
Raising awareness about Kawasaki disease
... Associate Professor David Burgner, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist and co-chair of the International Kawasaki Disease Consortium Kawasaki disease is a relatively rare condition in Australia; there is probably a case diagnosed every 2 days or so. But it is also an extremely important diseas ...
... Associate Professor David Burgner, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist and co-chair of the International Kawasaki Disease Consortium Kawasaki disease is a relatively rare condition in Australia; there is probably a case diagnosed every 2 days or so. But it is also an extremely important diseas ...
Pneumococcal Pneumonia
... – Pathogens taken up by alveolar macrophages • fusion of phagosome with lysosomes prevented – Pathogen replicates inside macrophages slowly killing ...
... – Pathogens taken up by alveolar macrophages • fusion of phagosome with lysosomes prevented – Pathogen replicates inside macrophages slowly killing ...
TUBERCULOSIS - UA Campus Health Service
... system, this can occur slowly or quickly (+ PPD, + CXR*) • There is a 10% lifetime risk of converting from latent TB infection to active TB disease, without treatment ...
... system, this can occur slowly or quickly (+ PPD, + CXR*) • There is a 10% lifetime risk of converting from latent TB infection to active TB disease, without treatment ...
Contagious disease
... A disease is a particular abnormal condition, a disorder of a structure or function, that affects part or all of an organism. The causal study of disease is called pathology. Disease is often construed as a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs.[1] It may be caused by factors ...
... A disease is a particular abnormal condition, a disorder of a structure or function, that affects part or all of an organism. The causal study of disease is called pathology. Disease is often construed as a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs.[1] It may be caused by factors ...
Endemic Diseases Involving Nervous System OBJECTIVES
... Immunity following infection is fairly solid, although reinfection can occur. EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS 3. ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS. ...
... Immunity following infection is fairly solid, although reinfection can occur. EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS 3. ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS. ...
Host-Microbe Relationships
... them It has been calculated that the normal human houses about 10^12 bacteria on the skin, 10^10 in the mouth, and 10^14 in the gastrointestinal tract. The latter number is far in excess of the number of eukaryotic cells in all organs which comprise the human host. ...
... them It has been calculated that the normal human houses about 10^12 bacteria on the skin, 10^10 in the mouth, and 10^14 in the gastrointestinal tract. The latter number is far in excess of the number of eukaryotic cells in all organs which comprise the human host. ...
Disease Transmission
... entrance of the infectious disease agent into the body until the first signs and symptoms of the disease appear. ...
... entrance of the infectious disease agent into the body until the first signs and symptoms of the disease appear. ...
Principles of Infection
... from one individual to another, certain conditions must be met. If any one condition is not met, the transmission of the disease will not happen. Pathogens are everywhere and preventing their transmission is a continuous process. ...
... from one individual to another, certain conditions must be met. If any one condition is not met, the transmission of the disease will not happen. Pathogens are everywhere and preventing their transmission is a continuous process. ...
Chlamydia trachomatis testing
... positive test results. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test is an example of a nucleic acid amplification test. This test can also be done on a urine sample. ...
... positive test results. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test is an example of a nucleic acid amplification test. This test can also be done on a urine sample. ...
Infection Control Strategies for an
... Professional should be consulted in situations in which there are inadequate single bedded rooms, or to assist in creating a plan for cohorting patients who are diagnosed with the same disease. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Healthcare workers entering an airborne isolation precaution room, cl ...
... Professional should be consulted in situations in which there are inadequate single bedded rooms, or to assist in creating a plan for cohorting patients who are diagnosed with the same disease. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Healthcare workers entering an airborne isolation precaution room, cl ...
Sexually Transmitted Infections
... • Using alcohol or other drugs bc they cause inhibitions to lower • Being sexually active with more than one person at a time or over time • Choosing high-risk partners who have a history of being sexually active ...
... • Using alcohol or other drugs bc they cause inhibitions to lower • Being sexually active with more than one person at a time or over time • Choosing high-risk partners who have a history of being sexually active ...
Infection and Disease
... (Yersinia pestis) and influenza. Opportunistic infections cause disease in some cases, but can be part of normal flora at other times e.g. Pseudomonas, Candida ...
... (Yersinia pestis) and influenza. Opportunistic infections cause disease in some cases, but can be part of normal flora at other times e.g. Pseudomonas, Candida ...
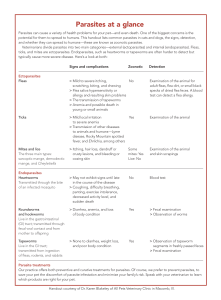
Parasites at a glance - Low Cost Pet Vaccinations
... Parasites at a glance Parasites can cause a variety of health problems for your pet—and even death. One of the biggest concerns is the potential for them to spread to humans. This handout lists common parasites in cats and dogs, the signs, detection, and whether they can spread to humans—these are k ...
... Parasites at a glance Parasites can cause a variety of health problems for your pet—and even death. One of the biggest concerns is the potential for them to spread to humans. This handout lists common parasites in cats and dogs, the signs, detection, and whether they can spread to humans—these are k ...
Infectious Cells & Single Cell Organisms
... The bacteria that is resistant survives & passes its genetic information on to the next generation. This makes it difficult to treat some bacterial diseases and has caused an increase in some diseases due to lack of ...
... The bacteria that is resistant survives & passes its genetic information on to the next generation. This makes it difficult to treat some bacterial diseases and has caused an increase in some diseases due to lack of ...
Animal and Livestock Water Concerns
... forage. Pets will consume 1 to 5 % of their body weight. Animals will not forage as well when it is dry, and don’t go as far from water, so supplemental feeding has to occur. The importance of water tanks and ponds becomes more critical, but heat and intense ultra violet light encourages bacterial a ...
... forage. Pets will consume 1 to 5 % of their body weight. Animals will not forage as well when it is dry, and don’t go as far from water, so supplemental feeding has to occur. The importance of water tanks and ponds becomes more critical, but heat and intense ultra violet light encourages bacterial a ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.