Topic 16 Some non-metals and their compounds notes
... gas which is less dense than air and extremely reactive. Unfortunately it is so light that there is none of it in our atmosphere. We can, however, produce hydrogen fairly easily by the electrolysis of water (H2O is broken down into the elements hydrogen and oxygen) or by the reaction of methane with ...
... gas which is less dense than air and extremely reactive. Unfortunately it is so light that there is none of it in our atmosphere. We can, however, produce hydrogen fairly easily by the electrolysis of water (H2O is broken down into the elements hydrogen and oxygen) or by the reaction of methane with ...
... comprised bristle oat ( Avena strigosa Schreb), yellow oat ( Avena byzantina C. Koch), triticale ( X Triticosecale Wittmack), bristle oat + yellow oat, bristle oat + triticale, yellow oat + tritic ale, bristle oat + yellow oat + triticale seeded in Tifton 85 and sole crop (control). Experimental des ...
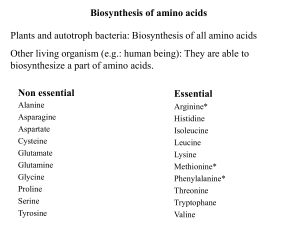
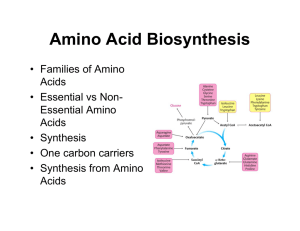
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
metabolism of amino acids
... • Normal condition- nitrogen intake match nitrogen excreted • Positive nitrogen balance- an excess of ingested over excreted nitrogen- during growth and pregnancy • Negative nitrogen balance – output exceeds intakeduring surgery, advanced cancer or malnutrition ...
... • Normal condition- nitrogen intake match nitrogen excreted • Positive nitrogen balance- an excess of ingested over excreted nitrogen- during growth and pregnancy • Negative nitrogen balance – output exceeds intakeduring surgery, advanced cancer or malnutrition ...
10 NH4 - ISLSOhio
... Some trees and grasses are able to absorb ammonium ions directly, but most require their conversion to nitrate. This process, called nitrification, is usually accomplished by bacteria in the soil or water. In the first step of nitrification, ammonium ions are oxidized into nitrite. The nitrite is th ...
... Some trees and grasses are able to absorb ammonium ions directly, but most require their conversion to nitrate. This process, called nitrification, is usually accomplished by bacteria in the soil or water. In the first step of nitrification, ammonium ions are oxidized into nitrite. The nitrite is th ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... Anaerobes – Live in the absence of oxygen. Catabolize nutrients without molecular oxygen. Obligate anaerobes- are poisoned by oxygen. Facultative – Some organisms can live in either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. They are called faculatives. Examples are yeast and E. coli. III. Nitrogen All living ...
... Anaerobes – Live in the absence of oxygen. Catabolize nutrients without molecular oxygen. Obligate anaerobes- are poisoned by oxygen. Facultative – Some organisms can live in either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. They are called faculatives. Examples are yeast and E. coli. III. Nitrogen All living ...
File
... Nitrogen dioxide + water(l) nitric acid + nitrogen monoxide Nitrogen dioxide(g) + water(l) nitric acid(aq) + nitrogen monoxide(g) NO2(g) + H2O(l) HNO3(aq) + NO(g) 3 NO2(g) + H2O(l) 2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) ...
... Nitrogen dioxide + water(l) nitric acid + nitrogen monoxide Nitrogen dioxide(g) + water(l) nitric acid(aq) + nitrogen monoxide(g) NO2(g) + H2O(l) HNO3(aq) + NO(g) 3 NO2(g) + H2O(l) 2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) ...
Heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen
... In this experiment we will measure the heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen and calculate the entropy change per nitrogen molecule of the vaporization process. Theory The heat of vaporization of a liquid is the energy that must be supplied in order to convert a unit mass of the liquid to the gas ...
... In this experiment we will measure the heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen and calculate the entropy change per nitrogen molecule of the vaporization process. Theory The heat of vaporization of a liquid is the energy that must be supplied in order to convert a unit mass of the liquid to the gas ...
Nitrogen Acquisition and Amino Acid Metabolism
... a. Through assimilation, inorganic forms of nitrogen like nitrate (NO 3-) gets reduced to nitrite (NO2-). b. The fully reduced form is ammonium ion with protons on it (NH 4+). c. Through a series of reactions, NH4+ will get cycled into organic nitrogen that’s combined with other atoms. d. Through fi ...
... a. Through assimilation, inorganic forms of nitrogen like nitrate (NO 3-) gets reduced to nitrite (NO2-). b. The fully reduced form is ammonium ion with protons on it (NH 4+). c. Through a series of reactions, NH4+ will get cycled into organic nitrogen that’s combined with other atoms. d. Through fi ...
nitrogen cycle
... this created niches occupied by organisms that could reduce NO3 to NH3 (many higher plants can do this) converting NO3 back to N2 (denitrification) is an arduous process and has evolved more recently ...
... this created niches occupied by organisms that could reduce NO3 to NH3 (many higher plants can do this) converting NO3 back to N2 (denitrification) is an arduous process and has evolved more recently ...
6CH02 - MPPE
... 10 There would be a major peak in the mass spectrum for butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, but not for butan-2-ol, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3, at m/e value A ...
... 10 There would be a major peak in the mass spectrum for butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, but not for butan-2-ol, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3, at m/e value A ...
Formulae/ Equations homework - St Peter the Apostle High School
... Which of the following pairs of elements would form a compound with a formula X2Y3? X is a metal and Y is a non-metal. ...
... Which of the following pairs of elements would form a compound with a formula X2Y3? X is a metal and Y is a non-metal. ...
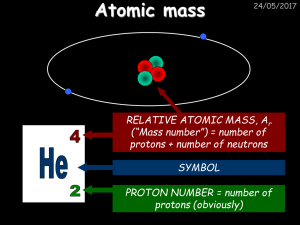
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
11.lec11_biochemical-cycles - Lightweight OCW University of
... that few organisms can use. (It takes a great deal of energy to split the N2 molecule.) Therefore, it must be converted to an organic form, or fixed, in a process called nitrogen fixation. A small amount of nitrogen is fixed through high energy fixation, primarily lighting strikes that convert atmos ...
... that few organisms can use. (It takes a great deal of energy to split the N2 molecule.) Therefore, it must be converted to an organic form, or fixed, in a process called nitrogen fixation. A small amount of nitrogen is fixed through high energy fixation, primarily lighting strikes that convert atmos ...
Nitrogen cycle
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
lect4
... Pyruvate is usually abundant in active muscle Muscle uses pyruvate as an acceptor keto acid alanine aminotransferase ...
... Pyruvate is usually abundant in active muscle Muscle uses pyruvate as an acceptor keto acid alanine aminotransferase ...
Detoxification of ammonia and biosynthesis of urea
... The liver takes up the alanine and converts it back into pyruvate by transamination. The glutamate formed in the liver is deaminated and ammonia is utilized in urea cycle. ...
... The liver takes up the alanine and converts it back into pyruvate by transamination. The glutamate formed in the liver is deaminated and ammonia is utilized in urea cycle. ...
8. Nitrogen Monoxide and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO and NO2 )
... balance and, by reproducing OH, the oxidization capacity of the atmosphere. NOx thus play a great role in controlling greenhouse gas concentrations (CH4, HCFCs, etc.). Sources of NOx include fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning, and soil (IPCC, 1990; IPCC, 1995). The oxides’ dominant sink in the ...
... balance and, by reproducing OH, the oxidization capacity of the atmosphere. NOx thus play a great role in controlling greenhouse gas concentrations (CH4, HCFCs, etc.). Sources of NOx include fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning, and soil (IPCC, 1990; IPCC, 1995). The oxides’ dominant sink in the ...
Reading Guide
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
PART VI
... 95-99% of N is in organic compounds, unavailable to higher plants, but protected from loss 1. Soil microbes attack these organic molecules, (proteins, nucleic acids, amino sugars, urea), forming amino compounds 2. The amine groups are hydrolyzed, with N released as NH4+ (ammonium ions; See pg. 548) ...
... 95-99% of N is in organic compounds, unavailable to higher plants, but protected from loss 1. Soil microbes attack these organic molecules, (proteins, nucleic acids, amino sugars, urea), forming amino compounds 2. The amine groups are hydrolyzed, with N released as NH4+ (ammonium ions; See pg. 548) ...
02/01/05 1 Cellulose-Degrading Symbioses BI 358 I. Intro: Guts of
... (a) if symbiont oxidized them all the way to CO2 via aerobic respiration then the host could not derive any nourishment (5) VFAs then absorbed and used in metabolism. So almost no soluble sugars are absorbed d) Methanogenic bacteria - derive energy from producing methane from CO2 and hydrogen. Contr ...
... (a) if symbiont oxidized them all the way to CO2 via aerobic respiration then the host could not derive any nourishment (5) VFAs then absorbed and used in metabolism. So almost no soluble sugars are absorbed d) Methanogenic bacteria - derive energy from producing methane from CO2 and hydrogen. Contr ...
Block III - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open University
... them contains iron, is known as Heme- Protein or denitrogen reductase and the other one which contains both molybdenum and iron at its reactive site is known as iron molybdenum protein or dinitrogenase. The conversion takes place at the surface of nitrogenase N2 bonds to both metals at the reactive ...
... them contains iron, is known as Heme- Protein or denitrogen reductase and the other one which contains both molybdenum and iron at its reactive site is known as iron molybdenum protein or dinitrogenase. The conversion takes place at the surface of nitrogenase N2 bonds to both metals at the reactive ...
100 Most Important Chemical Compounds : A
... components to characterize their behavior. Thus dates of discovery of gases are often ambiguous, with multiple dates being cited in the literature. For example, the year of discovery for nitrous oxide ranges between 1772 and 1793. Humphrey Davy (1778–1829) examined the physiological effects of nitrou ...
... components to characterize their behavior. Thus dates of discovery of gases are often ambiguous, with multiple dates being cited in the literature. For example, the year of discovery for nitrous oxide ranges between 1772 and 1793. Humphrey Davy (1778–1829) examined the physiological effects of nitrou ...