File
... THE PHOSPHORUS CYCLE Phosphorus is essential for the formation of cell membranes, DNA, and the calcium phosphate of bones. The phosphorus cycle has a long-term cycle that involves the rocks of the Earth’s crust and can take millions of years. ...
... THE PHOSPHORUS CYCLE Phosphorus is essential for the formation of cell membranes, DNA, and the calcium phosphate of bones. The phosphorus cycle has a long-term cycle that involves the rocks of the Earth’s crust and can take millions of years. ...
Background
... plant growth. Animals get the nitrogen they need by consuming plants or other animals that contain organic molecules composed partially of nitrogen. When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into the oceans. As dead plants and animals decompose, nitrogen i ...
... plant growth. Animals get the nitrogen they need by consuming plants or other animals that contain organic molecules composed partially of nitrogen. When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into the oceans. As dead plants and animals decompose, nitrogen i ...
BioMI 2900
... Title: Nitrogen Fixation and Assimilation Keywords: Modularity, Biosynthesis, Nitrogen Cycle, Nitrification (Nitrogen Fixation), Nitrogenase, NifH, Protection from Oxygen, Heme, Heterocysts, Bacteroids, Gas Chromatograph, Ammonia, Ammonium, Hydrozene, Tetrapyrroles, Amino Acid Biosynthesis, Activate ...
... Title: Nitrogen Fixation and Assimilation Keywords: Modularity, Biosynthesis, Nitrogen Cycle, Nitrification (Nitrogen Fixation), Nitrogenase, NifH, Protection from Oxygen, Heme, Heterocysts, Bacteroids, Gas Chromatograph, Ammonia, Ammonium, Hydrozene, Tetrapyrroles, Amino Acid Biosynthesis, Activate ...
Quiz 2
... 1. The EPA limit for CO is 9 ppm. Express this number as a percentage. A. 90% B. 9% C. 0.09% D. 0.0009% Percent is parts per hundred. One hundred is 10,000 times less than one million. 2. The burning of coal produces sulfur dioxide, SO2, a pollutant that slowly reacts in air to form SO3. Sulfur trio ...
... 1. The EPA limit for CO is 9 ppm. Express this number as a percentage. A. 90% B. 9% C. 0.09% D. 0.0009% Percent is parts per hundred. One hundred is 10,000 times less than one million. 2. The burning of coal produces sulfur dioxide, SO2, a pollutant that slowly reacts in air to form SO3. Sulfur trio ...
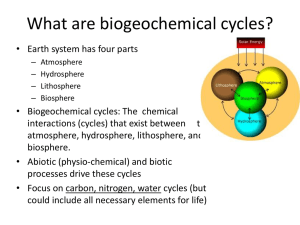
What are biogeochemical cycles?
... • Organic forms: amino acids and proteins (from plants or other animals) • Erosion • Fire (combustion) ...
... • Organic forms: amino acids and proteins (from plants or other animals) • Erosion • Fire (combustion) ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... >CO2 used to make calcium carbonate >sugars broken down & releasing CO2 >dead organisms decomposing or turning into fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) HUMAN INFLUENCE: >burning fossil fuels >clearing/burning forests & rainforests >mining fossils, minerals >planting crops, trees, etc. ...
... >CO2 used to make calcium carbonate >sugars broken down & releasing CO2 >dead organisms decomposing or turning into fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) HUMAN INFLUENCE: >burning fossil fuels >clearing/burning forests & rainforests >mining fossils, minerals >planting crops, trees, etc. ...
Cycles in Nature PowerPoint
... After plants have taken up nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate ions, the nitrogen is passed along the food chain. When those plants and animals dies, bacteria and fungi take up and use some of the nitrogen from the plant/animal protein and other nitrogen containing molecules. The remaining ...
... After plants have taken up nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate ions, the nitrogen is passed along the food chain. When those plants and animals dies, bacteria and fungi take up and use some of the nitrogen from the plant/animal protein and other nitrogen containing molecules. The remaining ...
The Nitrogen Cycle
... Description of the Nitrogen Cycle • N2 gas in the atmosphere must be taken in by symbiotic bacteria in the roots of plants (legumes) through nitrogen fixation. Then other bacteria change the nitrogen so it can be taken up by plants. Animals eat plants and get nitrogen. When plants and animals die, ...
... Description of the Nitrogen Cycle • N2 gas in the atmosphere must be taken in by symbiotic bacteria in the roots of plants (legumes) through nitrogen fixation. Then other bacteria change the nitrogen so it can be taken up by plants. Animals eat plants and get nitrogen. When plants and animals die, ...
Core Worksheet – Option E - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Discuss whether carbon dioxide or methane is a more effective greenhouse gas. ...
... Discuss whether carbon dioxide or methane is a more effective greenhouse gas. ...
Document
... farmers adding artificial fertilisers to the soil. farmers using natural fertilisers such as compost and manure. the decay of deal plants and animals. farmers planting peas and beans in their fields every 2 or 3 years. fa ...
... farmers adding artificial fertilisers to the soil. farmers using natural fertilisers such as compost and manure. the decay of deal plants and animals. farmers planting peas and beans in their fields every 2 or 3 years. fa ...
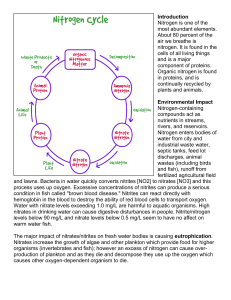
Introduction Nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements. About
... air we breathe is nitrogen. It is found in the cells of all living things and is a major component of proteins. Organic nitrogen is found in proteins, and is continually recycled by plants and animals. Environmental Impact Nitrogen-containing compounds act as nutrients in streams, rivers, and reserv ...
... air we breathe is nitrogen. It is found in the cells of all living things and is a major component of proteins. Organic nitrogen is found in proteins, and is continually recycled by plants and animals. Environmental Impact Nitrogen-containing compounds act as nutrients in streams, rivers, and reserv ...
leguminous plants question red
... Clover is a type of Legume. These are a group of plants that are adapted to take in nitrogen from the air. Other plants are not able to do this despite the high amount of nitrogen available in the air. They are able to do this due to the symbiotic relationship they have with the bacteria found on th ...
... Clover is a type of Legume. These are a group of plants that are adapted to take in nitrogen from the air. Other plants are not able to do this despite the high amount of nitrogen available in the air. They are able to do this due to the symbiotic relationship they have with the bacteria found on th ...
the nitrogen cycle: what a gas
... Although nitrogen gas makes up 79% of the Earth’s ___________________, it cannot be used in that form. Nitrogen is needed so cells can make ____________________ and genetic material like ____________________. For this to happen, the nitrogen gas must first be converted into ____________________, whi ...
... Although nitrogen gas makes up 79% of the Earth’s ___________________, it cannot be used in that form. Nitrogen is needed so cells can make ____________________ and genetic material like ____________________. For this to happen, the nitrogen gas must first be converted into ____________________, whi ...
Notes: The Nitrogen Cycle
... - All organisms need to make proteins and nucleic acids, both which contain nitrogen. - Nitrogen gas (N2) = 80% of the atmosphere. A. Nitrifying bacteria that live on the roots of plant and in the soil, “fix” the nitrogen into a form called nitrate B. Plants use the nitrate to make amino acids. - Pl ...
... - All organisms need to make proteins and nucleic acids, both which contain nitrogen. - Nitrogen gas (N2) = 80% of the atmosphere. A. Nitrifying bacteria that live on the roots of plant and in the soil, “fix” the nitrogen into a form called nitrate B. Plants use the nitrate to make amino acids. - Pl ...