Biogeochemical Cycles
... Plants and animals are broken down by still other bacteria that convert nitrogen containing organic molecules in organisms to an inorganic form of nitrogen (NH3 or NH41+) This is ammonification Once this ammonia is formed, still another group of bacteria can perform denitrification: NH3 or NH4 ...
... Plants and animals are broken down by still other bacteria that convert nitrogen containing organic molecules in organisms to an inorganic form of nitrogen (NH3 or NH41+) This is ammonification Once this ammonia is formed, still another group of bacteria can perform denitrification: NH3 or NH4 ...
Living organisms require between 30 to 40 elements for their normal
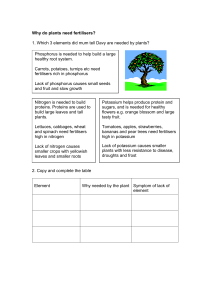
... a result of weathering. The cycle has no gaseous phase and it moves very slowly. Phosphorus is a vital component of DNA, RNA and ATP, therefore necessary for all living cells. Phosphorus is the most important ecologically element, and its deficiency tends to limit the productivity of any region, par ...
... a result of weathering. The cycle has no gaseous phase and it moves very slowly. Phosphorus is a vital component of DNA, RNA and ATP, therefore necessary for all living cells. Phosphorus is the most important ecologically element, and its deficiency tends to limit the productivity of any region, par ...
DNA and RNA Replication
... 1. Observe the unwoven DNA molecule. One of the DNA strands is exposed, showing a sequence of nitrogen bases. 2. Click the Legend button for information about how nitrogen bases pair. 3. Build a mRNA molecule by pairing up free nitrogen bases in the nucleus with the nitrogen bases on the exposed str ...
... 1. Observe the unwoven DNA molecule. One of the DNA strands is exposed, showing a sequence of nitrogen bases. 2. Click the Legend button for information about how nitrogen bases pair. 3. Build a mRNA molecule by pairing up free nitrogen bases in the nucleus with the nitrogen bases on the exposed str ...
Drugs Discovered through Serendipity in the Laboratory
... subsequently becoming unpalpable. On cessation of treatment, there was no sign of its return until a month had passed, whereupon it gradually reappeared. A second course of injections afforded a shorter respite than before; the lymphoma ultimately killed the mouse 84 days after transplantation. Such ...
... subsequently becoming unpalpable. On cessation of treatment, there was no sign of its return until a month had passed, whereupon it gradually reappeared. A second course of injections afforded a shorter respite than before; the lymphoma ultimately killed the mouse 84 days after transplantation. Such ...
The Mole Ratio · the ratio between the molar amounts of any two
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
Nitrogen Anabolism
... N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated from the Haber-Bos ...
... N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated from the Haber-Bos ...
File
... 4. The formula for sulfurous acid is. a. SF2 b. H2SO4 c. HSO3 d. HSF 5. Which of the following bonds is most negatively charged? a. C-H b. C-S c.C-N d. C-O 6. Based on symmetry which one of these molecules is non-polar? a. H3O+ b. PCl5 c. H2O d. NH3 7. The molecular shape of PH3 would be. a. Trigona ...
... 4. The formula for sulfurous acid is. a. SF2 b. H2SO4 c. HSO3 d. HSF 5. Which of the following bonds is most negatively charged? a. C-H b. C-S c.C-N d. C-O 6. Based on symmetry which one of these molecules is non-polar? a. H3O+ b. PCl5 c. H2O d. NH3 7. The molecular shape of PH3 would be. a. Trigona ...
10/31
... Sulfate (SO42) is often used as a source of sulfur Sulfate must be reduced before assimilation ...
... Sulfate (SO42) is often used as a source of sulfur Sulfate must be reduced before assimilation ...
Nitrogen in Lakes
... iv. summer blooms of Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Nostoc, Microcystis, Oscillatoria when N is low. Nitrogen fixation is important in lakes. a. In Eutrophic lakes fixation is a major process as first NH4+ then NO3- are used and BGA's begin to bloom as they can fix N2. In Clear Lake CA overy 1/2 of the an ...
... iv. summer blooms of Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Nostoc, Microcystis, Oscillatoria when N is low. Nitrogen fixation is important in lakes. a. In Eutrophic lakes fixation is a major process as first NH4+ then NO3- are used and BGA's begin to bloom as they can fix N2. In Clear Lake CA overy 1/2 of the an ...
Practice Problems
... nitrogen gas, water vapor and chromium (III) oxide. Hint: Dichromate = Cr2O72How many grams of ammonium dichromate would be needed to generate 400. grams of water from this decomposition? ...
... nitrogen gas, water vapor and chromium (III) oxide. Hint: Dichromate = Cr2O72How many grams of ammonium dichromate would be needed to generate 400. grams of water from this decomposition? ...
Assn5
... 5. Describe a biochemical procedure that selectively inhibits DNA synthesis, but has no affect on RNA synthesis. Answer this question by identifying a compound that inhibits one of the enzymes you showed in question 4. 5 Point Bonus 1. Beginning with NaNO2, trace the path of nitrogen into the struct ...
... 5. Describe a biochemical procedure that selectively inhibits DNA synthesis, but has no affect on RNA synthesis. Answer this question by identifying a compound that inhibits one of the enzymes you showed in question 4. 5 Point Bonus 1. Beginning with NaNO2, trace the path of nitrogen into the struct ...
Lecture Topic: Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Nitrogen is an essential element found in proteins, nucleic acids and many other molecules Biologically available nitrogen is scarce Nitrogen incorporation begins with fixation (reduction) of N2 by prokaryotic microorganisms to form ammonia (NH3) Nitrogen supply is often the rate-limiting factor in ...
... Nitrogen is an essential element found in proteins, nucleic acids and many other molecules Biologically available nitrogen is scarce Nitrogen incorporation begins with fixation (reduction) of N2 by prokaryotic microorganisms to form ammonia (NH3) Nitrogen supply is often the rate-limiting factor in ...
Grade 11 Chemistry E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... g. Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + NaCl(aq) h. CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) 25. Classify each of the above according to the 5 types of reactions (composition, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion). 26. Write the formula for each material correctly and then b ...
... g. Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + NaCl(aq) h. CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) 25. Classify each of the above according to the 5 types of reactions (composition, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion). 26. Write the formula for each material correctly and then b ...
Solar protein
... method monitors a parallel reductionthat of acetylene (C2H2) to ethylene (C2H4) by the enzyme nitrogenase. One technician, using a gas chromatograph, can measure up to 200 samples a day in the soybean field. Measurement of nitrogen-fixation rates under different field conditions led ...
... method monitors a parallel reductionthat of acetylene (C2H2) to ethylene (C2H4) by the enzyme nitrogenase. One technician, using a gas chromatograph, can measure up to 200 samples a day in the soybean field. Measurement of nitrogen-fixation rates under different field conditions led ...
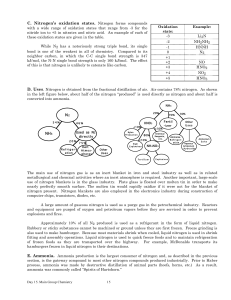
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... The structure of ammonia, predicted by VSEPR is that of a trigonal pyramid. At room temperature ammonia molecules undergo an inversion or flip via a trigonal planar transition state. The lone pair on nitrogen and the three hydrogens invert to the opposite side. At room temperature the inversion rate ...
... The structure of ammonia, predicted by VSEPR is that of a trigonal pyramid. At room temperature ammonia molecules undergo an inversion or flip via a trigonal planar transition state. The lone pair on nitrogen and the three hydrogens invert to the opposite side. At room temperature the inversion rate ...
Intermediary Nitrogen Metabolism, Vol 16. Biochemistry of Plants Brochure
... J.K. Bryan, Recent Advances in the Biochemistry of Amino Acid Biosynthesis. K.R. Schubert and M.J. Boland, The Ureides. A.F. Tiburcio, R. Kaur-Sawhney, Sr., and A.W. Galston, Polyamine Metabolism. J.W. Anderson, Sulfur Metabolism in Plants. ...
... J.K. Bryan, Recent Advances in the Biochemistry of Amino Acid Biosynthesis. K.R. Schubert and M.J. Boland, The Ureides. A.F. Tiburcio, R. Kaur-Sawhney, Sr., and A.W. Galston, Polyamine Metabolism. J.W. Anderson, Sulfur Metabolism in Plants. ...
The Elements of Group 15 (5A, V, VA) The Nitrogen Group
... Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our atmosphere (78%), found as a diatomic gas. N2(g) exhibits low reactivity, and is isolated from condensed air. N2 boils at 77K(-196oC) and is can thus serve as a refrigerant. ...
... Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our atmosphere (78%), found as a diatomic gas. N2(g) exhibits low reactivity, and is isolated from condensed air. N2 boils at 77K(-196oC) and is can thus serve as a refrigerant. ...
The Nitrogen Cycle and why you should know about it.
... Nitrogen is a key constituent of living tissue. ...
... Nitrogen is a key constituent of living tissue. ...
The Nitrogen Cycle - The Angelfish Society
... The general structure of an “alpha” amino acid. (Figure from Wikipedia.) ...
... The general structure of an “alpha” amino acid. (Figure from Wikipedia.) ...
fiii Fli I`.,
... bacteria that atmospheric nitrogen enters the biosphere-the domain of living things. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are organisms that reduce atnxospheric nitrogen to ammonia, a water-solubleform of nitrogen that can be usedbyplants and animak. N2+3H2-+2NHs ...
... bacteria that atmospheric nitrogen enters the biosphere-the domain of living things. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are organisms that reduce atnxospheric nitrogen to ammonia, a water-solubleform of nitrogen that can be usedbyplants and animak. N2+3H2-+2NHs ...
Document
... change N2 gas into ammonia in soil. Other soil bacteria can change ammonia into nitrates/nitrites. 2. How do humans get the nitrogen they need? Plants can take up these forms of nitrogen and use it to make their molecules (see below). Heterotrophs (like humans) get their nitrogen FROM EATING plants ...
... change N2 gas into ammonia in soil. Other soil bacteria can change ammonia into nitrates/nitrites. 2. How do humans get the nitrogen they need? Plants can take up these forms of nitrogen and use it to make their molecules (see below). Heterotrophs (like humans) get their nitrogen FROM EATING plants ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... stock 280 tables, 1750 chairs, 550 bookshelves, 300 china cabinets, and 325 sideboards. He asked his assistant to figure out how many dining room sets they could sell, how much money they would make if they sold all the sets possible, and what they would have left that could not be sold as part of t ...
... stock 280 tables, 1750 chairs, 550 bookshelves, 300 china cabinets, and 325 sideboards. He asked his assistant to figure out how many dining room sets they could sell, how much money they would make if they sold all the sets possible, and what they would have left that could not be sold as part of t ...