Georgia Credit Union Affiliates Annual Meeting May 8, 2004
... capacity utilization rates rise. Low core inflation will keep inflation expectations low and therefore also keep long-term interest rates low. The unemployment rate will fall below 6.0% by the end of 2014. Even so we do not expect them to raise the fed funds rate in 2014. The fed funds interest rate ...
... capacity utilization rates rise. Low core inflation will keep inflation expectations low and therefore also keep long-term interest rates low. The unemployment rate will fall below 6.0% by the end of 2014. Even so we do not expect them to raise the fed funds rate in 2014. The fed funds interest rate ...
Costa_Rica_en.pdf
... The growth rate remains high, however, especially in comparison with potential growth, estimated at 4.5%. Exports rose by 9% at constant prices and continued to show the greatest buoyancy. The open unemployment figure fell from 6.0% to 4.6%. Inflation picked up during the last months of 2007 and is ...
... The growth rate remains high, however, especially in comparison with potential growth, estimated at 4.5%. Exports rose by 9% at constant prices and continued to show the greatest buoyancy. The open unemployment figure fell from 6.0% to 4.6%. Inflation picked up during the last months of 2007 and is ...
Ass no. 3 2017
... Q# 5 Define monetary neutrality. Show that, after prices adjust completely, money is neutral in the ISLM model. What are the classical and Keynesian views about whether money is neutral in the short run? In the long run? Q#6 Drive aggregate demand (AD) curve? Why does the AD curve slope downward? Gi ...
... Q# 5 Define monetary neutrality. Show that, after prices adjust completely, money is neutral in the ISLM model. What are the classical and Keynesian views about whether money is neutral in the short run? In the long run? Q#6 Drive aggregate demand (AD) curve? Why does the AD curve slope downward? Gi ...
Y 1
... rate adjusts to bring Money Supply and demand into Balance 1. Money Supply- Fixed by Central Bank, unresponsive to interest rate 2. Money Demand- recall components that affect AD curve As real income rises, Households purchase more goods and services, so demand for money increases. Households sell b ...
... rate adjusts to bring Money Supply and demand into Balance 1. Money Supply- Fixed by Central Bank, unresponsive to interest rate 2. Money Demand- recall components that affect AD curve As real income rises, Households purchase more goods and services, so demand for money increases. Households sell b ...
PDF Download
... rate and especially the real effective exchange rate of the euro. From its low in June 2001 at 86.3 (19991 Q! = 100) it rose to 91.5 in May 2002. From August 2001 to April 2002 the real effective exchange rate had moved around the 90 mark which has now been significantly exceeded for the first time. ...
... rate and especially the real effective exchange rate of the euro. From its low in June 2001 at 86.3 (19991 Q! = 100) it rose to 91.5 in May 2002. From August 2001 to April 2002 the real effective exchange rate had moved around the 90 mark which has now been significantly exceeded for the first time. ...
market moves 12.20.2013
... Recession. This further suggests that the “money creation” concerns of the monetarists have not occurred and hence their associated inflation concerns have not been realized. At some future point the reserve money may make its way into the system, however, we doubt this will happen anytime soon. For ...
... Recession. This further suggests that the “money creation” concerns of the monetarists have not occurred and hence their associated inflation concerns have not been realized. At some future point the reserve money may make its way into the system, however, we doubt this will happen anytime soon. For ...
Macro practice FRQs
... • S affected by savings; D affected by increased budget deficit (increasing G or decreasing taxes) • Upward sloping S curve • Increase in budget deficit raises interest rates (decreases I and C – crowding out) • Increase in savings lowers interest rates • Changes in income affect BOTH savings and co ...
... • S affected by savings; D affected by increased budget deficit (increasing G or decreasing taxes) • Upward sloping S curve • Increase in budget deficit raises interest rates (decreases I and C – crowding out) • Increase in savings lowers interest rates • Changes in income affect BOTH savings and co ...
Big Boom for Stocks
... to value stocks, consistently said US equities were undervalued. This was even true when we used a higher discount rate. These days we use a 3.5% 10-year Treasury yield (higher than the current 2.3%) and the model still says stocks are undervalued by almost 25%. But that’s just the beginning. Even t ...
... to value stocks, consistently said US equities were undervalued. This was even true when we used a higher discount rate. These days we use a 3.5% 10-year Treasury yield (higher than the current 2.3%) and the model still says stocks are undervalued by almost 25%. But that’s just the beginning. Even t ...
SECTION 5: The Financial Sector Need to Know
... which funds are borrowed and lent in the federal funds market, plays a key role in modern monetary policy. • Discount Rate is the rate of interest the Fed charges on loans to banks that do not meet their reserve requirements (set 1 percentage point above the federal funds rate – that is why t ...
... which funds are borrowed and lent in the federal funds market, plays a key role in modern monetary policy. • Discount Rate is the rate of interest the Fed charges on loans to banks that do not meet their reserve requirements (set 1 percentage point above the federal funds rate – that is why t ...
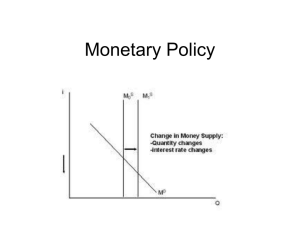
Monetary Policy
... Expansionary monetary policy • Fed buys bonds, lowers reserve requirements, or lowers discount rate • Real interest rates decrease • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices in ...
... Expansionary monetary policy • Fed buys bonds, lowers reserve requirements, or lowers discount rate • Real interest rates decrease • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices in ...
Master Entrance Exam
... b. The country of Past has a steady-state growth rate of real GDP of 4 percent per year. Capital typically lasts for 20 years, and the marginal product of capital is 9 percent of the value of each unit of capital. ______ (above, below, or at the Golden Rule steady state) 5. During the global economi ...
... b. The country of Past has a steady-state growth rate of real GDP of 4 percent per year. Capital typically lasts for 20 years, and the marginal product of capital is 9 percent of the value of each unit of capital. ______ (above, below, or at the Golden Rule steady state) 5. During the global economi ...
what are the instruments of monetary policy
... inflation rate), full employment, and growth in aggregate income. This is necessary because money is a medium of exchange and changes in its demand relative to supply, necessitate spending adjustments. To conduct monetary policy, some monetary variables which the Central Bank controls are adjusted-a ...
... inflation rate), full employment, and growth in aggregate income. This is necessary because money is a medium of exchange and changes in its demand relative to supply, necessitate spending adjustments. To conduct monetary policy, some monetary variables which the Central Bank controls are adjusted-a ...
Annual contribution policy
... For the purposes hereof, RBC Prime Rate means the annual interest rate announced from time to time by the Royal Bank of Canada as its prime rate then applicable in the determination of interest rates applicable to commercial loans made in Canadian Dollars in Canada. ...
... For the purposes hereof, RBC Prime Rate means the annual interest rate announced from time to time by the Royal Bank of Canada as its prime rate then applicable in the determination of interest rates applicable to commercial loans made in Canadian Dollars in Canada. ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.