* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Y 1
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian economics wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
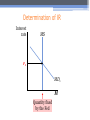
Orange Brigade Theory of Liquidity Preference- Keynes's Theory that Interest rate adjusts to bring Money Supply and demand into Balance 1. Money Supply- Fixed by Central Bank, unresponsive to interest rate 2. Money Demand- recall components that affect AD curve As real income rises, Households purchase more goods and services, so demand for money increases. Households sell bonds to increase money holdings Increase in IR increases cost of holding money. Therefore, quantity of money demanded decreases. Decreasing IR decreases cost of holding money, so money demand increases As a result, Money Demand curve slopes downwards 3. Equilibrium in Money Market- If interest rate isn’t at equilibrium, people will buy or sell assets to drive market towards equilibrium. Determination of IR Interest rate MS r1 MD1 M Quantity fixed by the Fed Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand Fed uses monetary policy to shift the aggregate Demand curve by altering the money supply. Recall that the Fed adjusts the interest rate by changing the Fed Funds Rate Fed uses Open Market operations to change the interest rate and to shift the AD curve The Effects of Reducing the Money Supply The Fed can raise r by reducing the money supply. P Interest MS2 MS1 rate r2 P1 r1 AD1 MD M AD2 Y2 Y1 Y An increase in r reduces the quantity of g&s demanded. THE INFLUENCE OF MONETARY AND FISCAL POLICY 5 Fiscal Policy- Setting of the level of government spending and taxation Expansionary policies shift AD rightwards increase in government purchases or decrease in taxation Contractionary policies shift AD leftwards decrease in government purchases or increase in taxation Multiplier effect- additional shifts in AD resulting when fiscal policy increases income and thereby consumer spending. Increase in real income increases consumer spending, ` shifting AD rightwards Marginal Propensity to Consume- Fraction of extra income households consume rather than save Formula for the multiplier: G is the change in G, Y and C are the ultimate changes in Y and C Y = C + I + G + NX Y = C + G identity I and NX do not change Y = MPC Y + G MPC Y 1 Y = Y 1 – MPC G because C = solved for The Multiplier Effect P AD1 AD2 AD3 P1 Y1 Y Crowding-Out Effect is also affected by Fiscal Policy Expansionary policy increases interest rate, which reduces investment, which reduces the net increase in aggregate demand. So, the size of the AD shift may be smaller than the initial fiscal expansion. Changes in Taxes Tax cuts increase take-home pay for households, increasing consumer spending and shifting AD to the right. If household perceives tax cut to be permanent, shift is larger. Using policy to stabilize the economy Booms, recessions, and crashes cause fluctuations in the market Active stabilization- supporters of active stabilization believe it is the government’s responsibility to regulate the economy. Expansionary policy should be used during a recession, contractionary policy should be used during periods of rapid inflation Against Active stabilization- critics of active stabilization claim that monetary and fiscal policy affects economy with a long lag Because firms create investment plans in advance, investment takes time to respond to changes in IR Because government purchases and taxes require congressional approval, G and T require time These lags can destabilize the economy Automatic stabilizers- changes in fiscal policy that stimulate AD when economy goes into recession, without policymakers having to take any deliberate action Include tax system and government spending