Electronic Structure of Atoms
... E.g. determine the energies of photons with wavelengths of 650 nm, 700 nm and frequencies 4.50x1014 s1, 6.50x1014 s1 Photoelectric effect: E = h where = constant the energy of the electron is directly related to the energy of the photon. the threshold of energy must be exceeded for electron ...
... E.g. determine the energies of photons with wavelengths of 650 nm, 700 nm and frequencies 4.50x1014 s1, 6.50x1014 s1 Photoelectric effect: E = h where = constant the energy of the electron is directly related to the energy of the photon. the threshold of energy must be exceeded for electron ...
Wave mechanics and the Schrödinger equation
... quantum theory. When a metallic surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation, above a certain threshold frequency, the light is absorbed and electrons are emitted (see figure, right). In 1902, Philipp Eduard Anton von Lenard observed that the energy of individual emitted electrons increases with ...
... quantum theory. When a metallic surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation, above a certain threshold frequency, the light is absorbed and electrons are emitted (see figure, right). In 1902, Philipp Eduard Anton von Lenard observed that the energy of individual emitted electrons increases with ...
powerpoint slides
... A photon has passed through a vertical polarizer. It then passed through one at +45. What are the chances that the photon will be able to pass a third? a) 0% if it is vertical and 100% if it is horizontal b) 100% if it is vertical and 0% if it is horizontal c) 50% if it is vertical and 50% if it is ...
... A photon has passed through a vertical polarizer. It then passed through one at +45. What are the chances that the photon will be able to pass a third? a) 0% if it is vertical and 100% if it is horizontal b) 100% if it is vertical and 0% if it is horizontal c) 50% if it is vertical and 50% if it is ...
Discussion of Experimental Proof for the Paradox of Einstein, Rosen
... state, while the fluctuations of the other two components of the spin are uncorrelated to the Quctuations of these components of the spin of the other particle. In order to retain spherical symmetry in the statistical sense, we shall further suppose that in a large aggregate of similar cases, there ...
... state, while the fluctuations of the other two components of the spin are uncorrelated to the Quctuations of these components of the spin of the other particle. In order to retain spherical symmetry in the statistical sense, we shall further suppose that in a large aggregate of similar cases, there ...
Momentum Transfer to a Free Floating Double Slit
... We simultaneously measured the momentum transferred to a free-floating molecular double slit and the momentum change of the atom scattering from it. Our experimental results are compared to quantum mechanical and semiclassical models. The results reveal that a classical description of the slits, whi ...
... We simultaneously measured the momentum transferred to a free-floating molecular double slit and the momentum change of the atom scattering from it. Our experimental results are compared to quantum mechanical and semiclassical models. The results reveal that a classical description of the slits, whi ...
1 Hydrogen Atom: Wave Function Hydrogen Atom
... continuing this process of stimulated emission and amplification. ...
... continuing this process of stimulated emission and amplification. ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... The Quantum Model of the Atom Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
... The Quantum Model of the Atom Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
PowerPoint
... angular momentum = m·v·r = nh/2 m = mass of electron v = velocity of electron r = radius of orbit n = 1,2,3,4,...(energy levels) h = Planck’s constant ...
... angular momentum = m·v·r = nh/2 m = mass of electron v = velocity of electron r = radius of orbit n = 1,2,3,4,...(energy levels) h = Planck’s constant ...
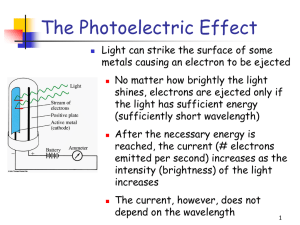
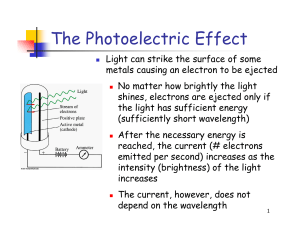
The Photoelectric Effect
... Light consists of photons, each with a particular amount of energy, called a quantum of energy Upon collision, each photon can transfer its energy to a single electron The more photons strike the surface of the metal, the more electrons are liberated and the higher is the current ...
... Light consists of photons, each with a particular amount of energy, called a quantum of energy Upon collision, each photon can transfer its energy to a single electron The more photons strike the surface of the metal, the more electrons are liberated and the higher is the current ...
Lecture 14
... and that the potential function was the usual electrostatic potential V(x,y,z) = -kZe2/r = -kZe2/ (x2+y2+z2)1/2, which is a function of the radial coordinate r only. The conclusion was that the natural variables are the spherical coordinates r,θ,φ. Today we draw the conclusions from these considerat ...
... and that the potential function was the usual electrostatic potential V(x,y,z) = -kZe2/r = -kZe2/ (x2+y2+z2)1/2, which is a function of the radial coordinate r only. The conclusion was that the natural variables are the spherical coordinates r,θ,φ. Today we draw the conclusions from these considerat ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.