Niels Bohr`s Philosophy of Quantum
... was dependent on the kinematics of the design. So what Bohr called "spacetime representation" is no longer associated with only one kind of dynamics. The tracking of particles and the detection of waves correspond to different kinds of experiments, dynamically speaking. Consequently, the unity betwe ...
... was dependent on the kinematics of the design. So what Bohr called "spacetime representation" is no longer associated with only one kind of dynamics. The tracking of particles and the detection of waves correspond to different kinds of experiments, dynamically speaking. Consequently, the unity betwe ...
Chapter 3 de Broglie`s postulate: wavelike properties of particles
... sodium atoms are in two spectral lines at about 5890 A . What is the fractional width of either line, / ? (c) Calculate the uncertainty E in the energy of the excited state of the atom. (d) From the previous results determine, to within an accuracy E , the energy E of the excited state ...
... sodium atoms are in two spectral lines at about 5890 A . What is the fractional width of either line, / ? (c) Calculate the uncertainty E in the energy of the excited state of the atom. (d) From the previous results determine, to within an accuracy E , the energy E of the excited state ...
Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]
... The Nature of Light • electromagnetic radiation travels in waves • at the speed of light (in vacuum, c = "#) • intensity is either amplitude or number of photons/second • energy of light is quantized, E = h" • the energy of atom is also quantized, E = nh" h = 6.626$10-34 J•s ...
... The Nature of Light • electromagnetic radiation travels in waves • at the speed of light (in vacuum, c = "#) • intensity is either amplitude or number of photons/second • energy of light is quantized, E = h" • the energy of atom is also quantized, E = nh" h = 6.626$10-34 J•s ...
1 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
... But if an X-ray photon scatters from an electron, it will disturb the electron’s momentum by an amount δp. We expect δp to be of order the X-ray photon’s momentum, i.e. ...
... But if an X-ray photon scatters from an electron, it will disturb the electron’s momentum by an amount δp. We expect δp to be of order the X-ray photon’s momentum, i.e. ...
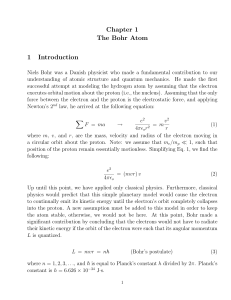
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
schoa - Schieck
... 8. What is meant by the term “ground state” 9. When creating his new atomic theory, Bohr used on important new idea (theoryP and primarily one important experimental area of study. Identify each. 10. State two differences between Excitation and Relaxation 11. What is the empirical (observed) distinc ...
... 8. What is meant by the term “ground state” 9. When creating his new atomic theory, Bohr used on important new idea (theoryP and primarily one important experimental area of study. Identify each. 10. State two differences between Excitation and Relaxation 11. What is the empirical (observed) distinc ...
Heisenberg, Matrix Mechanics, and the Uncertainty Principle 4
... Since the outcome of an experiment to measure a real observable IllUSt be a real number, Hermitian matrices would represent such observables (as their eigenvalues are real). If the result of a measurement is a certain eigenvalue, the corresponding eigenvector represents the state of the system immed ...
... Since the outcome of an experiment to measure a real observable IllUSt be a real number, Hermitian matrices would represent such observables (as their eigenvalues are real). If the result of a measurement is a certain eigenvalue, the corresponding eigenvector represents the state of the system immed ...
Glossary Chapter 4
... electromagnetic radiation a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space (91) electromagnetic spectrum all the forms of electromagnetic radiation (91) electron configuration the arrangement of electrons in an atom (105) excited state a state in which an atom has a highe ...
... electromagnetic radiation a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space (91) electromagnetic spectrum all the forms of electromagnetic radiation (91) electron configuration the arrangement of electrons in an atom (105) excited state a state in which an atom has a highe ...
constructive - Purdue Physics
... used to leave the metal (called W, work function), the rest becomes kinetic energy. ...
... used to leave the metal (called W, work function), the rest becomes kinetic energy. ...
midterm answers
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.










![Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016128835_1-aea3c1aec04363d6cbf538e8faf80e45-300x300.png)