Document
... 1. Characteristics of a cell depend on which genes are expressed within it 2. Tissue-specific gene expression vs. house-keeping genes (picture only 20.14) 3. Genes are regulated in a variety of ways (18.6) 4. Genes can be regulated by turning on/off transcription a. Epigenetic factors regulate chrom ...
... 1. Characteristics of a cell depend on which genes are expressed within it 2. Tissue-specific gene expression vs. house-keeping genes (picture only 20.14) 3. Genes are regulated in a variety of ways (18.6) 4. Genes can be regulated by turning on/off transcription a. Epigenetic factors regulate chrom ...
16.6 * Locating and Sequencing Genes
... template, countless nucleotides, and a good supply of the specific terminator nucleotide. Due to this, you get a variety of ‘partially completed’ DNA strands, because they have been ‘terminated’ at different points. ...
... template, countless nucleotides, and a good supply of the specific terminator nucleotide. Due to this, you get a variety of ‘partially completed’ DNA strands, because they have been ‘terminated’ at different points. ...
Genetics and Heredity
... of DNA is a sugar-phosphate bond. It provides support for the “steps” or base pairs. The base pairs or “Steps” are made up of four nitrogen ...
... of DNA is a sugar-phosphate bond. It provides support for the “steps” or base pairs. The base pairs or “Steps” are made up of four nitrogen ...
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
pdf version
... Cyril Ribeyre and David Shore, from the Department of Molecular biology of the UNIGE, have discovered that Rif1 and Rif2, two related proteins that bind telomeres, deactivate the alarm of the DNA repair surveillance system. ʻTelomeres interact with many molecules. We had identified several biochemic ...
... Cyril Ribeyre and David Shore, from the Department of Molecular biology of the UNIGE, have discovered that Rif1 and Rif2, two related proteins that bind telomeres, deactivate the alarm of the DNA repair surveillance system. ʻTelomeres interact with many molecules. We had identified several biochemic ...
Biology Common Assessment Name
... 6. Code created during transcription from the DNA blueprint a. Replication b. gene ...
... 6. Code created during transcription from the DNA blueprint a. Replication b. gene ...
11-03-11 st bio3 notes
... -thus considered universal code for all life on Earth -bc everything has DNA and has the same function/rules -the language of DNA is universal -not all DNA contrain's info for protein-making -amount of DNA in organism does not ...
... -thus considered universal code for all life on Earth -bc everything has DNA and has the same function/rules -the language of DNA is universal -not all DNA contrain's info for protein-making -amount of DNA in organism does not ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
code sequence practice
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
Chapter 12 Test Review
... Watson and Crick – _________________________________________________________________ 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polym ...
... Watson and Crick – _________________________________________________________________ 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polym ...
Student Worksheet
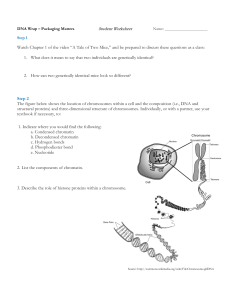
... structural proteins) and three-dimensional structure of chromosomes. Individually, or with a partner, use your textbook if necessary, to: 1. Indicate where you would find the following: a. Condensed chromatin b. Decondensed chromatin c. Hydrogen bonds d. Phosphodiester bond e. Nucleotide 2. List the ...
... structural proteins) and three-dimensional structure of chromosomes. Individually, or with a partner, use your textbook if necessary, to: 1. Indicate where you would find the following: a. Condensed chromatin b. Decondensed chromatin c. Hydrogen bonds d. Phosphodiester bond e. Nucleotide 2. List the ...
Transformation and Cloning
... Transformed bacteria can then be isolated and grown in bulk with appropriate antibiotic. Bacteria multiply to produce ...
... Transformed bacteria can then be isolated and grown in bulk with appropriate antibiotic. Bacteria multiply to produce ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... Genomics, bioinformatics, proteomics, homeobox, Hox genes, apoptosis, human genome project You may have multiple choice, true/false, matching, definitions, short answer, essays and fill-in-the-blanks, and "yes" spelling counts!!!! Sample Essays 1. It is very likely you will have genetics problems on ...
... Genomics, bioinformatics, proteomics, homeobox, Hox genes, apoptosis, human genome project You may have multiple choice, true/false, matching, definitions, short answer, essays and fill-in-the-blanks, and "yes" spelling counts!!!! Sample Essays 1. It is very likely you will have genetics problems on ...
How is DNA packed in the nucleus?
... chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
... chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
A8xb1e3x8x1 (2)
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
Unit 10 Biotechnology review guide 2014
... in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve desirable traits is referred to as _______________________. 15. In a test cross, if one parent’s genotype is homozygous dominant, what fraction o ...
... in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve desirable traits is referred to as _______________________. 15. In a test cross, if one parent’s genotype is homozygous dominant, what fraction o ...
Microbial Genetics - DrMinkovskyScienceWiki
... • Addition or deletion of 1 or 2 bases knocks the sequence out of frame • The whole amino acid sequence changes, usually results in a truncated (shortened) protein • If the gene is essential, the mutation is lethal. • Insertions or deletions in multiples of three may be tolerated • These are back in ...
... • Addition or deletion of 1 or 2 bases knocks the sequence out of frame • The whole amino acid sequence changes, usually results in a truncated (shortened) protein • If the gene is essential, the mutation is lethal. • Insertions or deletions in multiples of three may be tolerated • These are back in ...
15.2_Recombinant_DNA
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
Chapter Objectives: Chapter 20 Biotechnology
... 3. Describe how restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis are used to isolate DNA fragments 4. Explain how the creation of sticky ends by restriction enzymes is useful in producing a recombinant DNA molecule 5. Outline the procedures for producing plasmid and phage vectors 6. Explain how vectors a ...
... 3. Describe how restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis are used to isolate DNA fragments 4. Explain how the creation of sticky ends by restriction enzymes is useful in producing a recombinant DNA molecule 5. Outline the procedures for producing plasmid and phage vectors 6. Explain how vectors a ...
File - Ms. Wilson`s Biology Class
... Read the text below and answer the following questions: 1. In order to speed up the copying process (replication), DNA replication begins at ___________ locations along each chromosome. 2. The two DNA strands are pulled apart and copied in both directions at the rate of about _________ nucleotides p ...
... Read the text below and answer the following questions: 1. In order to speed up the copying process (replication), DNA replication begins at ___________ locations along each chromosome. 2. The two DNA strands are pulled apart and copied in both directions at the rate of about _________ nucleotides p ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.