Particle bombardment
... Electroporated pollen can supposedly germinate at 30% efficiency. However, no transgenic plant has so far been reported using this concept, even though it has been shown that pollen grains can be permeated with macromolecules such as DNA. Electroporation method is very efficient in permeating DNA in ...
... Electroporated pollen can supposedly germinate at 30% efficiency. However, no transgenic plant has so far been reported using this concept, even though it has been shown that pollen grains can be permeated with macromolecules such as DNA. Electroporation method is very efficient in permeating DNA in ...
lec-09-forensic-dna-analysis-chem-195h-2017
... 5. Add DNA polymerase and all four types of nucleotides. The polymerase (enzyme used in DNA replication) will fill in the rest of the two strands. ...
... 5. Add DNA polymerase and all four types of nucleotides. The polymerase (enzyme used in DNA replication) will fill in the rest of the two strands. ...
DNA–DNA hybridisation
... have the identical sequence of amino acids in their haemoglobin and so they are more closely related than humans and gibbons, which have three differences. www.mpg.de ...
... have the identical sequence of amino acids in their haemoglobin and so they are more closely related than humans and gibbons, which have three differences. www.mpg.de ...
4.4.1 Evidence to support the theory of evolution
... have the identical sequence of amino acids in their haemoglobin and so they are more closely related than humans and gibbons, which have three differences. www.mpg.de ...
... have the identical sequence of amino acids in their haemoglobin and so they are more closely related than humans and gibbons, which have three differences. www.mpg.de ...
Protein synthesis test review key
... 12. What happens to the mRNA sequence if the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the sequence of amino acids of the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the final protein if the DNA sequence changes? If the DNA sequence changes, then the mRNA sequence will change. The amino acids may or may not c ...
... 12. What happens to the mRNA sequence if the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the sequence of amino acids of the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the final protein if the DNA sequence changes? If the DNA sequence changes, then the mRNA sequence will change. The amino acids may or may not c ...
File
... deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromosomes, that patch of fur may be black while another with both of its chromosomes activated w ...
... deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromosomes, that patch of fur may be black while another with both of its chromosomes activated w ...
PLASMIDS AND RESTRICTION ENZYMES
... A fourth feature of plasmids that is critical for genetic engineering is that they can be passed on from one bacterial strain to another in a process called bacterial conjugation, which enables bacteria to share and exchange genetic information. When a plasmid with a gene for antibiotic resistance ...
... A fourth feature of plasmids that is critical for genetic engineering is that they can be passed on from one bacterial strain to another in a process called bacterial conjugation, which enables bacteria to share and exchange genetic information. When a plasmid with a gene for antibiotic resistance ...
Protein Synthesis - Elgin High School
... • When a cell makes a copy of itself (either thru mitosis or meiosis), it must make a copy of the DNA or the new cell won’t have the instructions it needs. ...
... • When a cell makes a copy of itself (either thru mitosis or meiosis), it must make a copy of the DNA or the new cell won’t have the instructions it needs. ...
Lesson 3
... Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) • RNA is made in the nucleus from DNA • RNA is a single strand • RNA has the nitrogen bases A, G, C, and ...
... Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) • RNA is made in the nucleus from DNA • RNA is a single strand • RNA has the nitrogen bases A, G, C, and ...
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
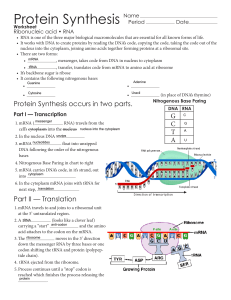
... 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
... 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
AP Bio Review - Genetics Jeopardy
... a nucleotide with a base complimentary to the base on the template strand is added to the new DNA strand ...
... a nucleotide with a base complimentary to the base on the template strand is added to the new DNA strand ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in which the DNA sequence is copied to form an additional DNA molecule A segment of ...
... The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in which the DNA sequence is copied to form an additional DNA molecule A segment of ...
Biotechnology - BeautyinScience.com
... Step 1 A restriction enzyme is used to cut a gene such as human insulin out of a DNA strand. The gene has sticky ends. Step 2 A bacterial plasmid is taken out of its cell and the circle is cut open using a restriction enzyme. The cut plasmid has sticky ends. Step 3 The gene and a genetic marker gene ...
... Step 1 A restriction enzyme is used to cut a gene such as human insulin out of a DNA strand. The gene has sticky ends. Step 2 A bacterial plasmid is taken out of its cell and the circle is cut open using a restriction enzyme. The cut plasmid has sticky ends. Step 3 The gene and a genetic marker gene ...
Modern Genetics Meets the Dodo and the Solitaire
... 6. The same color-blind man has four granddaughters. Would you predict the granddaughters to be colorblind? Explain why or why not. Use the terms in the vocabulary box. ...
... 6. The same color-blind man has four granddaughters. Would you predict the granddaughters to be colorblind? Explain why or why not. Use the terms in the vocabulary box. ...
Cell Line Characterization - Sigma
... multi-locus probe – an appropriate assay for cell line identity testing This DNA fingerprinting assay uses a single restriction endonuclease (HinfI) with MLP 33.15. In addition to the test article, a positive control standard consisting of cells of the same origin and an unrelated negative control a ...
... multi-locus probe – an appropriate assay for cell line identity testing This DNA fingerprinting assay uses a single restriction endonuclease (HinfI) with MLP 33.15. In addition to the test article, a positive control standard consisting of cells of the same origin and an unrelated negative control a ...
DNA TRANSFORMATION - Library Video Company
... nucleotide — The basic building block of DNA comprised of a molecule of sugar, a molecule of phosphoric acid, and a molecule called a base. Groups of three nucleotides, called “codons,” direct a cell to produce a specific amino acid to form proteins. base pair — Two nitrogenous bases which form a “r ...
... nucleotide — The basic building block of DNA comprised of a molecule of sugar, a molecule of phosphoric acid, and a molecule called a base. Groups of three nucleotides, called “codons,” direct a cell to produce a specific amino acid to form proteins. base pair — Two nitrogenous bases which form a “r ...
DNA as Drugs
... Natural DNA will be digested by enzymes, and also can cause immune response Synthetic DNA cannot be recognized by enzymes, so they are stable and may not cause immune response So, synthetic DNA can selectively block gene expression ...
... Natural DNA will be digested by enzymes, and also can cause immune response Synthetic DNA cannot be recognized by enzymes, so they are stable and may not cause immune response So, synthetic DNA can selectively block gene expression ...
DNA
... I. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) A. Found in almost all living cells –in the nucleus of eukaryotes (3 Feet/Cell) B. 2 primary functions 1. Control protein (enzyme) production (ie. ATPase)-These enzymes then control chemical reactions in cells. 2. Duplicate itself for new cells that are created ...
... I. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) A. Found in almost all living cells –in the nucleus of eukaryotes (3 Feet/Cell) B. 2 primary functions 1. Control protein (enzyme) production (ie. ATPase)-These enzymes then control chemical reactions in cells. 2. Duplicate itself for new cells that are created ...
TUTORIAL FIGURES: Basic Molecular Biology
... Figure 1: Chemical structure of DNA and RNA. A DNA molecule comprises of two chains consisting of nucleotide units. The basic structure of each nucleotide comprises of a phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar, and a base (nucleotide = P-S-Base). There are 4 DNA bases: A (adenine), G (guanine), T (thymine), ...
... Figure 1: Chemical structure of DNA and RNA. A DNA molecule comprises of two chains consisting of nucleotide units. The basic structure of each nucleotide comprises of a phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar, and a base (nucleotide = P-S-Base). There are 4 DNA bases: A (adenine), G (guanine), T (thymine), ...
GenTech Unit 2 DNA
... I. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) A. Found in almost all living cells –in the nucleus of eukaryotes (3 Feet/Cell) B. 2 primary functions 1. Control protein (enzyme) production (ie. ATPase)-These enzymes then control chemical reactions in cells. 2. Duplicate itself for new cells that are created ...
... I. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) A. Found in almost all living cells –in the nucleus of eukaryotes (3 Feet/Cell) B. 2 primary functions 1. Control protein (enzyme) production (ie. ATPase)-These enzymes then control chemical reactions in cells. 2. Duplicate itself for new cells that are created ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.