ws: DNA Alphabet Activity
... Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________________________ #2: ...
... Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________________________ #2: ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
DNA Technology
... use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CRIMINALS as examples. Find something less common. 3. If this is a controversia ...
... use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CRIMINALS as examples. Find something less common. 3. If this is a controversia ...
It all started in the 700s when Chinese used fingerprints to launch
... DNA analysis whenever collected evidence contain deteriorated or degraded DNA. In my study, I attempted to design a sensitive and specific assay for both quantitative and qualitative profiling of gene including specific methylated spots in various tissues. This assay will help in the identification ...
... DNA analysis whenever collected evidence contain deteriorated or degraded DNA. In my study, I attempted to design a sensitive and specific assay for both quantitative and qualitative profiling of gene including specific methylated spots in various tissues. This assay will help in the identification ...
Genetic Engineering
... New Kinds of Plants • polyploid – chromosomes do not separate during meiosis • Use drugs that prevent chromosome separation • Plants are stronger, bigger than diploid • Polyploidy fatal in animals ...
... New Kinds of Plants • polyploid – chromosomes do not separate during meiosis • Use drugs that prevent chromosome separation • Plants are stronger, bigger than diploid • Polyploidy fatal in animals ...
Journey Into dna
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
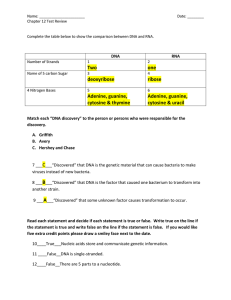
chapter 12 test review key
... occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries the mutation.________________ ...
... occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries the mutation.________________ ...
DNA Worksheet
... Worksheet on DNA name_____________________________ Date ____________ Period _____________ 1. What does DNA stand for? ______________________________________ ...
... Worksheet on DNA name_____________________________ Date ____________ Period _____________ 1. What does DNA stand for? ______________________________________ ...
Game 2
... of a reaction rate (product in moles vs. time) and indicate the initial reaction rate & explain why the asymptote that is approached as the reaction finishes is present ...
... of a reaction rate (product in moles vs. time) and indicate the initial reaction rate & explain why the asymptote that is approached as the reaction finishes is present ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expensive and only works for short strings, and the decoding process creates lot ...
... does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expensive and only works for short strings, and the decoding process creates lot ...
Chapter 10
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
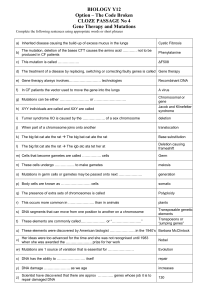
Ch 11 homework
... C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac operon when no lactose is present. (1) ...
... C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac operon when no lactose is present. (1) ...
What are multiple alleles
... These are the sex chromosomes. Among other things they code for the production of hormones that make males - males and females – females. In humans the sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair. ...
... These are the sex chromosomes. Among other things they code for the production of hormones that make males - males and females – females. In humans the sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair. ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 15. Watson & Crick used the X-Ray of a DNA molecule taken by _________________ __________________. 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? ...
... 15. Watson & Crick used the X-Ray of a DNA molecule taken by _________________ __________________. 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 9. A break in the chromosome occurred when a _______ randomly ____________ from one chromosome to another. 10. Which basketball hero has a transposon named for him? 11. When did Barbara McClintock finally win a Nobel Prize for Medicine? #5- DNA Carries Genetic Material ...
... 9. A break in the chromosome occurred when a _______ randomly ____________ from one chromosome to another. 10. Which basketball hero has a transposon named for him? 11. When did Barbara McClintock finally win a Nobel Prize for Medicine? #5- DNA Carries Genetic Material ...
Mutations
... • Mutation- any change in the gene or chromosome, it can be harmful or helpful • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms ...
... • Mutation- any change in the gene or chromosome, it can be harmful or helpful • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms ...
Prenatal Screening
... FORTE- Fetal-fraction Optimized Risk of Trisomy Evaluation Algorithm that takes into account additional data: prior risk (based on maternal age and gestational age) as well as fetal fraction Enables determination of chromosome proportion and fetal fraction at same time ...
... FORTE- Fetal-fraction Optimized Risk of Trisomy Evaluation Algorithm that takes into account additional data: prior risk (based on maternal age and gestational age) as well as fetal fraction Enables determination of chromosome proportion and fetal fraction at same time ...
When to Refer Patients
... pregnancy losses on a repetitive basis. Couples requiring assisted reproduction techniques to achieve pregnancy, or individuals donating eggs or sperm for those purposes. Couples interested in undergoing preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Couples with difficulty achieving a pregnancy due to male fac ...
... pregnancy losses on a repetitive basis. Couples requiring assisted reproduction techniques to achieve pregnancy, or individuals donating eggs or sperm for those purposes. Couples interested in undergoing preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Couples with difficulty achieving a pregnancy due to male fac ...