Grade 9 Science Ch 4 - Answers to Comprehensive Questions
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
Supplemental File S6. You and Your Oral Microflora
... 3. (1 point) Your friend learned in class recently that some antibiotics work because they target the ribosomal subunits of prokaryotes but don’t affect the ribosomes of eukaryotes. Your friend isn’t sure how this can be true, since both eukaryotes and prokaryotes use ribosomes to make proteins. You ...
... 3. (1 point) Your friend learned in class recently that some antibiotics work because they target the ribosomal subunits of prokaryotes but don’t affect the ribosomes of eukaryotes. Your friend isn’t sure how this can be true, since both eukaryotes and prokaryotes use ribosomes to make proteins. You ...
Mini lab 11.1 and 11.2
... the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic knowledge Fails to complete ...
... the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic knowledge Fails to complete ...
Name:
... Scientific Method & The Science of Biology Steps of the scientific method; Hypothesis v. Theory; dependent v. independent variable; control group Observations v. Inferences; Qualitative v. Quantitative Observations Characteristics of life; Levels of organization ...
... Scientific Method & The Science of Biology Steps of the scientific method; Hypothesis v. Theory; dependent v. independent variable; control group Observations v. Inferences; Qualitative v. Quantitative Observations Characteristics of life; Levels of organization ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
Chapter 24 Applied Genetics I. Plant and animal
... 2. Offspring contain those desirable traits B. Hybridization 1. Crossing of two genetically different related species 2. Produce organism with best traits of both parents (hybrid) C. Inbreeding 1. Crossing of two organisms with the same or similar sets of genes 2. Leads to purebred organisms 3. Able ...
... 2. Offspring contain those desirable traits B. Hybridization 1. Crossing of two genetically different related species 2. Produce organism with best traits of both parents (hybrid) C. Inbreeding 1. Crossing of two organisms with the same or similar sets of genes 2. Leads to purebred organisms 3. Able ...
Fertilisation, development and DNA
... I can state that DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell. ...
... I can state that DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell. ...
DNA & Heredity
... large number of events. However it can not predict the precise outcome of an individual event Multiple Alleles- have more than 2 allele possibilities in the population. Doesn’t mean that a person can have more than 2 alleles. Ex. (blood type) Polygenic traits- traits controlled by two or more genes. ...
... large number of events. However it can not predict the precise outcome of an individual event Multiple Alleles- have more than 2 allele possibilities in the population. Doesn’t mean that a person can have more than 2 alleles. Ex. (blood type) Polygenic traits- traits controlled by two or more genes. ...
Honors Biology Final Outline
... Mutations that result in insertions and deletions of information can significantly alter information when it is expressed. Environmental agents such as mutagens can cause mutations in cells. Viruses differ in structure and ways of entering host cells. Viruses are obligate intracellular genet ...
... Mutations that result in insertions and deletions of information can significantly alter information when it is expressed. Environmental agents such as mutagens can cause mutations in cells. Viruses differ in structure and ways of entering host cells. Viruses are obligate intracellular genet ...
Introduction
... isolated from Thermus aquaticus and has a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. HyTaq DNA Polymerase has both a 5'→3' DNA polymerase and a 5'→3' exonuclease activity. The enzyme lacks a 3'→5' exonuclease activity (no proofreading ability). Taq DNA Polymerase leaves an A′ overhang, which makes th ...
... isolated from Thermus aquaticus and has a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. HyTaq DNA Polymerase has both a 5'→3' DNA polymerase and a 5'→3' exonuclease activity. The enzyme lacks a 3'→5' exonuclease activity (no proofreading ability). Taq DNA Polymerase leaves an A′ overhang, which makes th ...
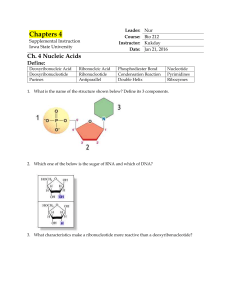
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... STR — short tandem repeats. Short sequences (2–8 base pairs) able to repeat up to 100 times. Humans have many microsatellites and the number of repeats varies between people. This is used to gene profile people using PCR ...
... STR — short tandem repeats. Short sequences (2–8 base pairs) able to repeat up to 100 times. Humans have many microsatellites and the number of repeats varies between people. This is used to gene profile people using PCR ...
Biotechnology Applications
... • DNA sequencing of base pairs – Many organisms have been sequenced – Human Genome Project • Know the entire human genome at base pair level ...
... • DNA sequencing of base pairs – Many organisms have been sequenced – Human Genome Project • Know the entire human genome at base pair level ...
DNA functions worksheet
... DNA Structure and Replication: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the st ...
... DNA Structure and Replication: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the st ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... Significance of genetic variation • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intellig ...
... Significance of genetic variation • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intellig ...
File
... 3 types of mutations: • 2. Frameshift mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA – This would cause every codon to be wrong from that point on in protein coding – Example: • THE CAT ATE THE FAT RAT • THE ATA TET HEF ATR ATT ...
... 3 types of mutations: • 2. Frameshift mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA – This would cause every codon to be wrong from that point on in protein coding – Example: • THE CAT ATE THE FAT RAT • THE ATA TET HEF ATR ATT ...
What I`ve done this summer
... The allelic diversity arises from unequal homologous crossing-over or gene conversions rather than point mutations. The incidence of the allelic diversity across the world appears to be characteristic of the ethnic or geographic origin of the subjects. The evolution of the three identified hot spots ...
... The allelic diversity arises from unequal homologous crossing-over or gene conversions rather than point mutations. The incidence of the allelic diversity across the world appears to be characteristic of the ethnic or geographic origin of the subjects. The evolution of the three identified hot spots ...
INSERT A-3c
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... paper). Apply radioactive probe designed to detect (bind to) harmful allele / gene of interest. Unattached probes are rinsed off. Photographic film used to form a image that compares individuals. In this picture I had the harmful allele. If any individual matches the banding pattern of I, then they ...
... paper). Apply radioactive probe designed to detect (bind to) harmful allele / gene of interest. Unattached probes are rinsed off. Photographic film used to form a image that compares individuals. In this picture I had the harmful allele. If any individual matches the banding pattern of I, then they ...
What is a protein?
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
Name
... 8. What is DNA replication? DNA unzips and the nitrogen bases that are floating in the nucleus pair up with each half of the DNA molecule. One DNA strands becomes two . 9. One section of a strand of a DNA strand has the base sequence AGATTC. What is the base sequence on the other strand? TCTAAG ...
... 8. What is DNA replication? DNA unzips and the nitrogen bases that are floating in the nucleus pair up with each half of the DNA molecule. One DNA strands becomes two . 9. One section of a strand of a DNA strand has the base sequence AGATTC. What is the base sequence on the other strand? TCTAAG ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Recombinant DNA Technology: Using the above tools, genes are combined from two or more different sources. The recombinant fragment is introduced into a cell that can express that gene. Uses: Mass production of biochemicals needed by other species Creation of new strains of living organisms Pro ...
... Recombinant DNA Technology: Using the above tools, genes are combined from two or more different sources. The recombinant fragment is introduced into a cell that can express that gene. Uses: Mass production of biochemicals needed by other species Creation of new strains of living organisms Pro ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... ABO blood groups, Rh factor, pedigree, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, Huntington's disease, sickle-cell disease, carriers, amniocentesis, chorionic villi, ultrasound, fetoscopy Be able to work genetics problems (make punnett squares for monohybrid and dihybrid crosses) and be able to correctly ...
... ABO blood groups, Rh factor, pedigree, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, Huntington's disease, sickle-cell disease, carriers, amniocentesis, chorionic villi, ultrasound, fetoscopy Be able to work genetics problems (make punnett squares for monohybrid and dihybrid crosses) and be able to correctly ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... • Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs in about 1 out of 1,000 males. ...
... • Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs in about 1 out of 1,000 males. ...