DNA Discovery - Biology Junction
... Frederick Griffith – bacterial transformation Oswald Avery – DNA = key to transformation Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase – Bacteriophage transformation experiment Erwin Chargaff – base-pairing rules ...
... Frederick Griffith – bacterial transformation Oswald Avery – DNA = key to transformation Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase – Bacteriophage transformation experiment Erwin Chargaff – base-pairing rules ...
Genetics 1
... Heredity: is the study of the natural law or property of organisms whereby their offspring have various physical and mental traits of their parents or ancestors i.e. certain traits are transmitted from one generation to the next. Genetic information is carried on the DNA molecule as a gene. Gene: is ...
... Heredity: is the study of the natural law or property of organisms whereby their offspring have various physical and mental traits of their parents or ancestors i.e. certain traits are transmitted from one generation to the next. Genetic information is carried on the DNA molecule as a gene. Gene: is ...
Recombination
... C. altering plants to make them resistant to pests. D. treatment of human genetic disorders. ...
... C. altering plants to make them resistant to pests. D. treatment of human genetic disorders. ...
here - St Vincent College
... Term that means the DNA has 2 strands that are twisted together (dh) There are 23 pairs of these in most human cells (c) ...
... Term that means the DNA has 2 strands that are twisted together (dh) There are 23 pairs of these in most human cells (c) ...
Evolution and Genetics
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
Honors Biology Final Outline
... Viruses differ in structure and ways of entering host cells. Viruses are obligate intracellular genetic parasites. Viruses cause infectious diseases including HIV/AIDS Genomics involves the study of genes, gene functions, and entire genomes. Technology allows the study and comparison of bo ...
... Viruses differ in structure and ways of entering host cells. Viruses are obligate intracellular genetic parasites. Viruses cause infectious diseases including HIV/AIDS Genomics involves the study of genes, gene functions, and entire genomes. Technology allows the study and comparison of bo ...
centromere
... Eukaryotic chromosomes • In metaphase of mitosis, chromosomes can be seen under microscope they have a compact rod-like structure • The ends of chromosome are called telomeres, function is to protect the ends of the DNA • Near the middle is the centromere, function is to attach to spindles during c ...
... Eukaryotic chromosomes • In metaphase of mitosis, chromosomes can be seen under microscope they have a compact rod-like structure • The ends of chromosome are called telomeres, function is to protect the ends of the DNA • Near the middle is the centromere, function is to attach to spindles during c ...
ib biology………………
... Pathogenic — disease causing organism. Lytic cycle - reproductive cycle of virus. Virus attaches to host cell, injects its hereditary material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Compose ...
... Pathogenic — disease causing organism. Lytic cycle - reproductive cycle of virus. Virus attaches to host cell, injects its hereditary material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Compose ...
microbio 40 [4-20
... Aids transmissibility and makes them resistant to detergents, dessication, and heat usually by direct skin to skin contact, and even then it requires a skin break can also be spread by exfoliation onto inanimate objects 3. What is the result when HPV is transferred to a child during birth? Wha ...
... Aids transmissibility and makes them resistant to detergents, dessication, and heat usually by direct skin to skin contact, and even then it requires a skin break can also be spread by exfoliation onto inanimate objects 3. What is the result when HPV is transferred to a child during birth? Wha ...
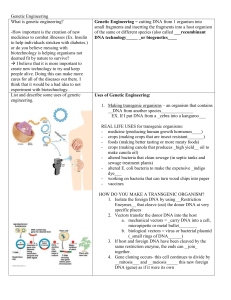
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (_small rings of DNA______) 3. If host and foreign ...
... Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (_small rings of DNA______) 3. If host and foreign ...
Document
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
Honors Biology Final Exam-‐Part 2-‐Semester 2
... 5. Both mitosis and meiosis start with diploid cells with _______________ chromosomes. 6. Where in the body would meiosis occur? 7. A picture of all the chromosomes in one cell arranged in pairs ...
... 5. Both mitosis and meiosis start with diploid cells with _______________ chromosomes. 6. Where in the body would meiosis occur? 7. A picture of all the chromosomes in one cell arranged in pairs ...
ANSWER KEY BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA
... BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA (17 QUESTIONS) 1. (2006-7) One strand of DNA could be as long as a football field if it were stretched out lengthwise. One of the factors allowing DNA to fit inside the nucleus of a cell is its ability to a. denature from the effect of an enzyme b. break apart into sepa ...
... BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA (17 QUESTIONS) 1. (2006-7) One strand of DNA could be as long as a football field if it were stretched out lengthwise. One of the factors allowing DNA to fit inside the nucleus of a cell is its ability to a. denature from the effect of an enzyme b. break apart into sepa ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA (17 QUESTIONS) 1. (2006-7) One strand of DNA could be as long as a football field if it were stretched out lengthwise. One of the factors allowing DNA to fit inside the nucleus of a cell is its ability to a. denature from the effect of an enzyme b. break apart into sepa ...
... BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA (17 QUESTIONS) 1. (2006-7) One strand of DNA could be as long as a football field if it were stretched out lengthwise. One of the factors allowing DNA to fit inside the nucleus of a cell is its ability to a. denature from the effect of an enzyme b. break apart into sepa ...
Unit 3 Practice Exam
... d. building a new species by combining genes of different organisms. 9. Although controversial, DNA fingerprinting has been used in criminal investigations because a. criminals leave DNA samples behind them when they touch an object at a crime scene. b. DNA analysis is believed to allow investigator ...
... d. building a new species by combining genes of different organisms. 9. Although controversial, DNA fingerprinting has been used in criminal investigations because a. criminals leave DNA samples behind them when they touch an object at a crime scene. b. DNA analysis is believed to allow investigator ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
CH-13 Sect 1
... 18. Is the following sentence true or false? The pattern of colored bands on an electrophoresis gel tells the exact sequence of bases in DNA. ____ ...
... 18. Is the following sentence true or false? The pattern of colored bands on an electrophoresis gel tells the exact sequence of bases in DNA. ____ ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.