TECHNICAL NOTE 4.1
... However, within the nucleus we find 46 chromosomes. These 46 chromosomes exist as pairs, with each pair containing the same sequence of DNA. Each pair of chromosomes contains one derived from the mother and the other from the father. Thus, for example, the gene coding for skin color (melanin content ...
... However, within the nucleus we find 46 chromosomes. These 46 chromosomes exist as pairs, with each pair containing the same sequence of DNA. Each pair of chromosomes contains one derived from the mother and the other from the father. Thus, for example, the gene coding for skin color (melanin content ...
Lesson Plan
... Guided Practice: Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab, Students will be given a lab report rubric and the lab report will be due Wednesday/Thursday for a major grade. ...
... Guided Practice: Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab, Students will be given a lab report rubric and the lab report will be due Wednesday/Thursday for a major grade. ...
Introduction o Except for identical twins, have the same DNA. o
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
Slide () - Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research
... (blue) attaches to a cell (see Subpanel B). Once attached, the DNA of the virus (see black vertical line) will be inserted into the cytoplasm of the host cell (see Subpanels 1C and 1D), where the viral DNA will incorporate into the DNA of the host cell (red; see Subpanel 1E). Viral DNA consists of s ...
... (blue) attaches to a cell (see Subpanel B). Once attached, the DNA of the virus (see black vertical line) will be inserted into the cytoplasm of the host cell (see Subpanels 1C and 1D), where the viral DNA will incorporate into the DNA of the host cell (red; see Subpanel 1E). Viral DNA consists of s ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
DNA Fingerprinting Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... biology. In an investigation, DNA samples from four organisms, A, B, C, and D, were cut into fragments. The number of bases in the resulting DNA fragments for each sample is shown below. ...
... biology. In an investigation, DNA samples from four organisms, A, B, C, and D, were cut into fragments. The number of bases in the resulting DNA fragments for each sample is shown below. ...
Study Guide for LS
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
Identify the three parts of cell theory All living things are made of
... mitosis the two strands of the chromosome divide and ar pulled by spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell ...
... mitosis the two strands of the chromosome divide and ar pulled by spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell ...
Lecture 18
... We need a copy of the gene, but with the introns removed. Copy the mRNA instead of the gene. - reverse transcriptase ...
... We need a copy of the gene, but with the introns removed. Copy the mRNA instead of the gene. - reverse transcriptase ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosome Quiz
... 23.) RNA is “read” and turned into a protein during the process of _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ...
... 23.) RNA is “read” and turned into a protein during the process of _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ...
Lecture 18
... We need a copy of the gene, but with the introns removed. Copy the mRNA instead of the gene. - reverse transcriptase ...
... We need a copy of the gene, but with the introns removed. Copy the mRNA instead of the gene. - reverse transcriptase ...
Ch. 18 – Microbial Models of DNA
... • Colds – epithelial cells in throat can repair themselves efficiently • Polio – attaches to nerve cells that cannot be repaired • 1796 – Edward Jenner – noticed that cow pox (mild) makes one immune to small pox (more harmful). • Used fluid from cow (vacca) pox blister to give people cow pox, making ...
... • Colds – epithelial cells in throat can repair themselves efficiently • Polio – attaches to nerve cells that cannot be repaired • 1796 – Edward Jenner – noticed that cow pox (mild) makes one immune to small pox (more harmful). • Used fluid from cow (vacca) pox blister to give people cow pox, making ...
Ch. 18 – Microbial Models of DNA
... The plague (emergent diseases aren’t all viral) – not currently emerging…. – Lyme disease – Asian Bird Flu – ???? Certain cancers ...
... The plague (emergent diseases aren’t all viral) – not currently emerging…. – Lyme disease – Asian Bird Flu – ???? Certain cancers ...
MS Word file
... Antibiotic resistance comes from the actions of genes located on R plasmids that can be transferred naturally. R plasmids have evolved in the past 60 years since the beginning of widespread use of antibiotics. The transfer of R plasmids is not restricted to bacteria of the same or even related speci ...
... Antibiotic resistance comes from the actions of genes located on R plasmids that can be transferred naturally. R plasmids have evolved in the past 60 years since the beginning of widespread use of antibiotics. The transfer of R plasmids is not restricted to bacteria of the same or even related speci ...
Review for Post Exam 10 on iLearn
... Review for DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter 10 Write the following questions on your own paper and answer them. 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. ...
... Review for DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter 10 Write the following questions on your own paper and answer them. 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. ...
Concept 18.3. How get genetic variation in prokaryotes: • E. coli is
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
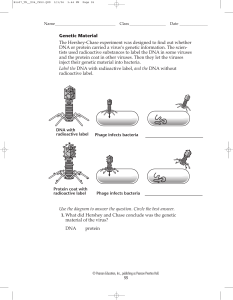
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
DNA Technology
... of the DNA chromosomal molecule • Subtle differences distinguish the gene from the surrounding material ...
... of the DNA chromosomal molecule • Subtle differences distinguish the gene from the surrounding material ...
dna microinjection
... • the super- ovulated females are mated and killed • the fertilized eggs are flushed from their oviducts • microinjection of the fertilized eggs ...
... • the super- ovulated females are mated and killed • the fertilized eggs are flushed from their oviducts • microinjection of the fertilized eggs ...
Basics of DNA
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...
DNA, genes and chromosomes
... Most bacteria contain a single, circular chromosome. (There are exceptions: some bacteria for example, the genus Streptomyces - possess linear chromosomes, and Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera, has two circular chromosomes.) The chromosome - together with ribosomes and proteins associ ...
... Most bacteria contain a single, circular chromosome. (There are exceptions: some bacteria for example, the genus Streptomyces - possess linear chromosomes, and Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera, has two circular chromosomes.) The chromosome - together with ribosomes and proteins associ ...
Genetics EOC Review
... Multiple alleles is when you have more than two forms (alleles) of a ________________ controlling a trait. Example = __________________. Polygenic inheritance is when you have two or more __________________ controlling a single trait. Example = _______________________. Sex Linked Traits Sex linked g ...
... Multiple alleles is when you have more than two forms (alleles) of a ________________ controlling a trait. Example = __________________. Polygenic inheritance is when you have two or more __________________ controlling a single trait. Example = _______________________. Sex Linked Traits Sex linked g ...
Genetic Engineering II
... – crops resistant to herbicides (but the weeds are not) – insulin gene from humans is put in the plasmid of E. coli which then makes insulin – a bacterium gene that codes for a protein called Bt toxin that kills moths that bore through corn is transferred to the DNA of corn ...
... – crops resistant to herbicides (but the weeds are not) – insulin gene from humans is put in the plasmid of E. coli which then makes insulin – a bacterium gene that codes for a protein called Bt toxin that kills moths that bore through corn is transferred to the DNA of corn ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.