Restriction Mapping Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
... Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype ...
... Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype ...
recombinant dna technology
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
Genetics - true or false
... Most of your DNA is found in the cell nucleus. Mitochondria (types of cell organelle) also have a small amount of their own DNA. All human cells contain DNA (except for mature red blood cells). If students consider the statement is false, they are technically correct but be aware of the common misun ...
... Most of your DNA is found in the cell nucleus. Mitochondria (types of cell organelle) also have a small amount of their own DNA. All human cells contain DNA (except for mature red blood cells). If students consider the statement is false, they are technically correct but be aware of the common misun ...
electroporation of a - The Steve Clough Lab
... 5. Apply a single 2.5kV electrical pulse (field strength of 12.5 kV/cm) by simultaneously pressing both red buttoms on face of gene pulser. Pulser will beep when finished. Time reading ideally will be above 9.3, but lower values may still be ok. Time will be lower the more salt (remember that DNA is ...
... 5. Apply a single 2.5kV electrical pulse (field strength of 12.5 kV/cm) by simultaneously pressing both red buttoms on face of gene pulser. Pulser will beep when finished. Time reading ideally will be above 9.3, but lower values may still be ok. Time will be lower the more salt (remember that DNA is ...
Unit 2 MI Study Guide
... a. caused by changes or mutations in the DNA sequence of one gene which results in the production of a non-functional protein ...
... a. caused by changes or mutations in the DNA sequence of one gene which results in the production of a non-functional protein ...
NOVA Online Cancer Tutorial
... 1. Which process do body cells use to replicate? 2. How do mutated cells replicated differently than normal cells? E.)Spread and Second Mutation: 1. What do the mutated cells do to the normal cells? 2. How do the mutated cells end up with more than one mutant genes? F.)Third/Fourth Mutations: 1. How ...
... 1. Which process do body cells use to replicate? 2. How do mutated cells replicated differently than normal cells? E.)Spread and Second Mutation: 1. What do the mutated cells do to the normal cells? 2. How do the mutated cells end up with more than one mutant genes? F.)Third/Fourth Mutations: 1. How ...
BI 200 – Final Exam
... DNA is supercoiled around histone proteins DNA is single stranded There is one copy of each chromosome Chromosomes are usually circular rather than linear There are usually more chromosomes than plasmids ...
... DNA is supercoiled around histone proteins DNA is single stranded There is one copy of each chromosome Chromosomes are usually circular rather than linear There are usually more chromosomes than plasmids ...
FREE Sample Here
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA pr ...
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA pr ...
Uses for transgenic organisms (also called GMO`s or genetically
... Genome—the complete set of genes for an organism. The human genome contains approximately 20,000-23,000 genes, made up of about 3 billion base pairs. (ATACGACCTG, etc., 3 billion times!) All bases have been sequenced (as of 2001) but exactly what each gene is or does isn’t yet known. Up until 2001, ...
... Genome—the complete set of genes for an organism. The human genome contains approximately 20,000-23,000 genes, made up of about 3 billion base pairs. (ATACGACCTG, etc., 3 billion times!) All bases have been sequenced (as of 2001) but exactly what each gene is or does isn’t yet known. Up until 2001, ...
Genetics
... Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
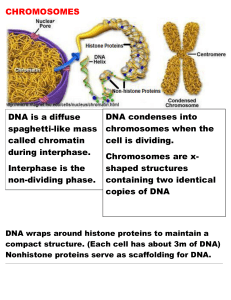
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
Genomes and their evolution
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
Review - Jeopardy PowerPoint
... This process occurs when the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei, each with an exact copy of DNA ...
... This process occurs when the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei, each with an exact copy of DNA ...
How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
Variation exists within individuals, within populations, and among
... What is meant by ‘redundancy’ in the genetic code? What is the function of tRNA? What is meant by ‘base pair’? Gene expression – be familiar with the various ways in which phenotypes can be derived from genotype, from simple dominance:recessive relationships of alleles to multi-gene interactions Wha ...
... What is meant by ‘redundancy’ in the genetic code? What is the function of tRNA? What is meant by ‘base pair’? Gene expression – be familiar with the various ways in which phenotypes can be derived from genotype, from simple dominance:recessive relationships of alleles to multi-gene interactions Wha ...
IV. Diagnosing Gene Disorders
... Normal development of sexual traits and are _____________. 3. Turner Syndrome females with only one affects 1/2000 live female births. Only 1 in ___________ affected zygotes develops to term. Individuals are short in stature, generally lack prominent female secondary sexual characteristics, ...
... Normal development of sexual traits and are _____________. 3. Turner Syndrome females with only one affects 1/2000 live female births. Only 1 in ___________ affected zygotes develops to term. Individuals are short in stature, generally lack prominent female secondary sexual characteristics, ...
Document
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
Brainpop Genetics questions Weinmann ANSWERS
... 2. Which of the following depicts (shows) a molecule of DNA? - B 3. What is the relationship between DNA and chromosomes? - A. chromosomes are made out of DNA 4. How many PAIRS of chromosomes exist in each of your cells? - D. 23 pairs (46 individual) 5. Why are your chromosomes arranged in pairs? - ...
... 2. Which of the following depicts (shows) a molecule of DNA? - B 3. What is the relationship between DNA and chromosomes? - A. chromosomes are made out of DNA 4. How many PAIRS of chromosomes exist in each of your cells? - D. 23 pairs (46 individual) 5. Why are your chromosomes arranged in pairs? - ...
Epigenetics
... Two genetically identical agouti mice, one whose mother was fed a diet with folic acid and other methyl-rich supplements during pregnancy and one whose mother has a normal diet. The brown mouse’s agouti gene has been shut off, whereas her genetically identical sister is yellow and has a higher rate ...
... Two genetically identical agouti mice, one whose mother was fed a diet with folic acid and other methyl-rich supplements during pregnancy and one whose mother has a normal diet. The brown mouse’s agouti gene has been shut off, whereas her genetically identical sister is yellow and has a higher rate ...
Chapter 12: Genetic Engineering
... Genetic engineering could not have come about without the development of a ______________________________ to support the process o A way to carefully _________________________ containing the gene away from the genes surrounding it o Find a way to ________________________________ with a piece of DNA ...
... Genetic engineering could not have come about without the development of a ______________________________ to support the process o A way to carefully _________________________ containing the gene away from the genes surrounding it o Find a way to ________________________________ with a piece of DNA ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.