DNA -‐ Compsci 201
... strand of DNA data, or to ecoli.dat which is larger. Both are files in the data directory you download/snarf with Eclipse. You’ll probably need to create your own file of DNA, e.g., with ...
... strand of DNA data, or to ecoli.dat which is larger. Both are files in the data directory you download/snarf with Eclipse. You’ll probably need to create your own file of DNA, e.g., with ...
ADVANTAGES OF FETAL CELLS IN NON
... genomes but may not be linked directly to a specific disease Polymorphic segments of DNA that vary between the maternal and paternal genomes, such as short tandem repeats (STRs) Epigenetic modifications, specifically DNA methylation of certain genes, which differs between cells of the mother versus ...
... genomes but may not be linked directly to a specific disease Polymorphic segments of DNA that vary between the maternal and paternal genomes, such as short tandem repeats (STRs) Epigenetic modifications, specifically DNA methylation of certain genes, which differs between cells of the mother versus ...
From Genes to Proteins
... from a gene and delivers it to the site of translation. The information is translated from the language of RNA—nucleotides—to the language of proteins—amino acids. The RNA instructions are written as a series of three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA called codons (KOH dahnz). Each codon along the m ...
... from a gene and delivers it to the site of translation. The information is translated from the language of RNA—nucleotides—to the language of proteins—amino acids. The RNA instructions are written as a series of three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA called codons (KOH dahnz). Each codon along the m ...
Aberrant Epigenetic Regulation Could Explain the Relationship of
... system.24–26 Genes are differentially marked during gametogenesis after the methylation patterns of the previous generation are ‘‘erased’’ and the new parent of origin-specific methylation and additional changes in chromatin are established.27,28 This differential marking silences or imprints the ma ...
... system.24–26 Genes are differentially marked during gametogenesis after the methylation patterns of the previous generation are ‘‘erased’’ and the new parent of origin-specific methylation and additional changes in chromatin are established.27,28 This differential marking silences or imprints the ma ...
FEMS Microbiology Ecology
... is known about the impact of these biologically diverse and often specific infections on the recently detected bacterial community in lichens. To address this question, we studied the arctic–alpine ‘chocolate chip lichen’ Solorina crocea, which is frequently infected by Rhagadostoma lichenicola. We ...
... is known about the impact of these biologically diverse and often specific infections on the recently detected bacterial community in lichens. To address this question, we studied the arctic–alpine ‘chocolate chip lichen’ Solorina crocea, which is frequently infected by Rhagadostoma lichenicola. We ...
Chromosome Variations
... • Some duplications are “dispersed”, found in very different locations from each other. • Other duplications are “tandem”, found next to each other. • Tandem duplications play a major role in evolution, because it is easy to generate extra copies of the duplicated genes through the process of unequa ...
... • Some duplications are “dispersed”, found in very different locations from each other. • Other duplications are “tandem”, found next to each other. • Tandem duplications play a major role in evolution, because it is easy to generate extra copies of the duplicated genes through the process of unequa ...
GENETICS TEST II - Daytona State College
... • A region of the mammalian X chromosome that is the major control unit of inactivation. Located on the proximal end of the p arm in human. Its genetic expression occurs only on the X chromosome that is inactivated. • It consists of the X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) gene which is critical fo ...
... • A region of the mammalian X chromosome that is the major control unit of inactivation. Located on the proximal end of the p arm in human. Its genetic expression occurs only on the X chromosome that is inactivated. • It consists of the X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) gene which is critical fo ...
Sequence Information Encoded in DNA that May Influence Long
... the occurrence, distribution, and relative sizes of the $300 kb clusters of nearly-consecutive signals (black bars) and $1 Mb clusters with no signals (grey bars) across chromosome 1 are shown as an example. The higher resolution shown in the expanded 2.5 Mb region indicates the presence of one $1 M ...
... the occurrence, distribution, and relative sizes of the $300 kb clusters of nearly-consecutive signals (black bars) and $1 Mb clusters with no signals (grey bars) across chromosome 1 are shown as an example. The higher resolution shown in the expanded 2.5 Mb region indicates the presence of one $1 M ...
RHD - Labex
... A very early detection of the fetal RHD genotyping is possible starting with the 12th gestational week In some rare cases even earlier ...
... A very early detection of the fetal RHD genotyping is possible starting with the 12th gestational week In some rare cases even earlier ...
localization of histone gene transcripts in newt lampbrush
... attempt resulted in the regular labelling of a few pairs of loops on bivalent X and one pair of loops on bivalent I; the second attempt resulted in a far more complex distribution of label over the chromosome complement, altogether too complex to justify a detailed analysis. The first attempt indica ...
... attempt resulted in the regular labelling of a few pairs of loops on bivalent X and one pair of loops on bivalent I; the second attempt resulted in a far more complex distribution of label over the chromosome complement, altogether too complex to justify a detailed analysis. The first attempt indica ...
CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Antonella Spinazzola Nationality
... The study showed that MNGIE results from a deficiency of thymidine phosphorylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible breakdown of thymidine to thymine plus deoxyribose-1-phosphate. The report underlies the importance of understanding the nature and sources of mitochondrial DNA precursor pools s ...
... The study showed that MNGIE results from a deficiency of thymidine phosphorylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible breakdown of thymidine to thymine plus deoxyribose-1-phosphate. The report underlies the importance of understanding the nature and sources of mitochondrial DNA precursor pools s ...
BioACTS Quarter THREE
... a nucleic acid is called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are made up of THREE parts—a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose) and one of four nitrogen bases. Diagram I Draw and label ONE nucleotide using the highlighters below your entry task. ...
... a nucleic acid is called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are made up of THREE parts—a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose) and one of four nitrogen bases. Diagram I Draw and label ONE nucleotide using the highlighters below your entry task. ...
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION 1
... Transgenes integrated within a methylated chromosome area are more likely to get methylated and silenced. Genes inserted within a CG rich chromosome region or high gene ...
... Transgenes integrated within a methylated chromosome area are more likely to get methylated and silenced. Genes inserted within a CG rich chromosome region or high gene ...
Semiconservative Replication in the Quasispecies Model
... p(σ, σ ′ )p((σ, σ ′ ), (σ ′′ , σ̄ ′′ )). Write σ = b1 . . . bL , σ = b′1 . . . b′L , and σ” = b1 ” . . . bL ”. Let l ≡ HD(σ, σ”). Let us consider some i for which bi = bi ”. Then b′i can take on any value, for if b′i = b̄i ”, then no repair is necessary, and we obtain bi → (bi ”, b̄i ”). If b′i 6= b ...
... p(σ, σ ′ )p((σ, σ ′ ), (σ ′′ , σ̄ ′′ )). Write σ = b1 . . . bL , σ = b′1 . . . b′L , and σ” = b1 ” . . . bL ”. Let l ≡ HD(σ, σ”). Let us consider some i for which bi = bi ”. Then b′i can take on any value, for if b′i = b̄i ”, then no repair is necessary, and we obtain bi → (bi ”, b̄i ”). If b′i 6= b ...
Probing b-Lactamase Structure and Function Using Random Replacement Mutagenesis.
... those for the wild-type enzyme. We also found a few exceptional regions where only a few random sequences function. Examination of the Xray structures of homologous p-lactamases indicates that the regions most sensitive to substitution are in the vicinity of the active site pocket or buried in the h ...
... those for the wild-type enzyme. We also found a few exceptional regions where only a few random sequences function. Examination of the Xray structures of homologous p-lactamases indicates that the regions most sensitive to substitution are in the vicinity of the active site pocket or buried in the h ...
ThermalAce™ DNA Polymerase
... -20°C until use. Analyze 5–10 μl of sample by agarose gel electrophoresis. ...
... -20°C until use. Analyze 5–10 μl of sample by agarose gel electrophoresis. ...
Microarray-based comparative genomic hybridisation (array CGH)
... array CGH. This is because balanced chromosome rearrangements do not result in any loss or gain of chromosome material. It will also not detect some types of polyploidy (more than the usual 2 sets of chromosomes), such as triploidy (three sets of chromosomes). A standard karyotype is still available ...
... array CGH. This is because balanced chromosome rearrangements do not result in any loss or gain of chromosome material. It will also not detect some types of polyploidy (more than the usual 2 sets of chromosomes), such as triploidy (three sets of chromosomes). A standard karyotype is still available ...
Ends-out, or replacement, gene targeting in Drosophila
... the same as those used for ends-in targeting: heat-inducible FLP recombinase (13) and I-SceI endonuclease (3) transgenes (70FLP and 70I-SceI). We also constructed donor transgenes that carry sequence from the locus to be targeted. We first made and transformed a y⫹ P element donor construct to rescu ...
... the same as those used for ends-in targeting: heat-inducible FLP recombinase (13) and I-SceI endonuclease (3) transgenes (70FLP and 70I-SceI). We also constructed donor transgenes that carry sequence from the locus to be targeted. We first made and transformed a y⫹ P element donor construct to rescu ...
Meiosis
... Meiosis II – Division of sister chromatids Telophase II : -nuclear membrane reforms -chromatin forms -cytokinesis produces 4 haploid (n) cells ...
... Meiosis II – Division of sister chromatids Telophase II : -nuclear membrane reforms -chromatin forms -cytokinesis produces 4 haploid (n) cells ...
repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in pseudomonas
... suggest that genome fragments lacking REP sequences could be pointing to regions recently acquired from other organisms and REP sequences could be a new tracer for getting insight into the key aspects of bacterial genome evolution, especially for studying pathogenicity acquisition. In addition, as t ...
... suggest that genome fragments lacking REP sequences could be pointing to regions recently acquired from other organisms and REP sequences could be a new tracer for getting insight into the key aspects of bacterial genome evolution, especially for studying pathogenicity acquisition. In addition, as t ...
A simple set of rules for primer sequence design is as follows
... the Tm, a prime consideration is that the primers should be complex enough so that the likelihood of annealing to sequences other than the chosen target is very low. For example, there is a ¼ chance of finding an A, G, C or T in any given DNA sequence; there is a 1/16 chance of finding any dinucleot ...
... the Tm, a prime consideration is that the primers should be complex enough so that the likelihood of annealing to sequences other than the chosen target is very low. For example, there is a ¼ chance of finding an A, G, C or T in any given DNA sequence; there is a 1/16 chance of finding any dinucleot ...
The energetic basis of the DNA double helix: a
... Considering the apparent heat capacity function of the DNA duplex (Figure 1, left panel), one notes that it starts to increase from the very beginning of heating, namely in the temperature range from 0 to 45◦ C, over which the duplex is generally regarded as still being fully folded. The observed ri ...
... Considering the apparent heat capacity function of the DNA duplex (Figure 1, left panel), one notes that it starts to increase from the very beginning of heating, namely in the temperature range from 0 to 45◦ C, over which the duplex is generally regarded as still being fully folded. The observed ri ...
Mapping the histone code at hMLH1. - JScholarship
... methylation patterns during development (Okano et al., 1999). Dnmt1 appears to be the main enzyme required for the maintenance of these methylation patterns (Bestor et al., 1988). In addition, Dnmt1 may also play a role in de novo methylation (Jair et al., 2006) and may cooperate with Dnmt3b to main ...
... methylation patterns during development (Okano et al., 1999). Dnmt1 appears to be the main enzyme required for the maintenance of these methylation patterns (Bestor et al., 1988). In addition, Dnmt1 may also play a role in de novo methylation (Jair et al., 2006) and may cooperate with Dnmt3b to main ...
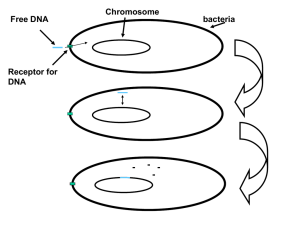
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.