Chapter 12 Cell Cycle Functions of cell division. . Phases of the cell
... explained by the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis. 9. Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, pleiotropy, epistasis, multiple inheritance. Describe how environmental conditions can influence the phenotypic expression of a character. Explain what is meant by "a norm of reaction." 10. Distinguish be ...
... explained by the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis. 9. Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, pleiotropy, epistasis, multiple inheritance. Describe how environmental conditions can influence the phenotypic expression of a character. Explain what is meant by "a norm of reaction." 10. Distinguish be ...
GENETICS I. Review of DNA/RNA – A. Basic Structure – DNA 3
... a) The two genes controlling these traits are sex-linked b) The two genes controlling these traits might be on different chromosomes c) The two genes controlling these traits are linked with no crossing over d) The two genes controlling these traits are nearby on the same chromosome e) The two genes ...
... a) The two genes controlling these traits are sex-linked b) The two genes controlling these traits might be on different chromosomes c) The two genes controlling these traits are linked with no crossing over d) The two genes controlling these traits are nearby on the same chromosome e) The two genes ...
BIO.6
... carries a specific amino acid that is coded for by the 3 nucleotide sequence (anticodon). These tRNA molecules will bond to the mRNA, matching codons (3 nucleotide sequences on the mRNA) from the 5’ to the 3” direction. When two tRNAs are bonded to the mRNA side by side, their amino acids form a pep ...
... carries a specific amino acid that is coded for by the 3 nucleotide sequence (anticodon). These tRNA molecules will bond to the mRNA, matching codons (3 nucleotide sequences on the mRNA) from the 5’ to the 3” direction. When two tRNAs are bonded to the mRNA side by side, their amino acids form a pep ...
DNA / RNA / PROTEIN SYNTHESIS / AP Biology
... phosphate) construct the following DNA and RNA molecules; transcribe the message into RNA when asked to do so; and translate the message into amino acids (protein) when directed. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Cons ...
... phosphate) construct the following DNA and RNA molecules; transcribe the message into RNA when asked to do so; and translate the message into amino acids (protein) when directed. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Cons ...
DNA Sequencing
... and transfer them between species Cloning technology is used to find carriers of genetic disorders, perform gene therapy, and create disease-resistant plants ...
... and transfer them between species Cloning technology is used to find carriers of genetic disorders, perform gene therapy, and create disease-resistant plants ...
Biology Final Review
... _____42. A child is diagnosed with a genetic disease. Neither parent has the disease. How might the child have inherited the disease? A. disorder dominant – carried by a single parent B. disorder is sex-linked – carried by the father C. disorder is recessive – carried by both parents D. None of the ...
... _____42. A child is diagnosed with a genetic disease. Neither parent has the disease. How might the child have inherited the disease? A. disorder dominant – carried by a single parent B. disorder is sex-linked – carried by the father C. disorder is recessive – carried by both parents D. None of the ...
Gregor Mendel - father of Genetics and 18th century Austrian monk
... Each codon codes for an amino acid. These amino acids made in ribosome make up proteins. ...
... Each codon codes for an amino acid. These amino acids made in ribosome make up proteins. ...
Chapter 10 Nucleic Acids and Protein synthesis
... transcription by binding to “PROMOTER REGIONS” ( these regions have lots of A-T base pairs) on the DNA. Promoter Region – marks the beginning of the DNA portion that will be transcribed RNA polymerase attaches to 1 strand of unzipped DNA and begins pasting together complementary RNA nucleotides to f ...
... transcription by binding to “PROMOTER REGIONS” ( these regions have lots of A-T base pairs) on the DNA. Promoter Region – marks the beginning of the DNA portion that will be transcribed RNA polymerase attaches to 1 strand of unzipped DNA and begins pasting together complementary RNA nucleotides to f ...
Genetics Vocabulary Review2
... sex of offspring as well as other traits; it is made up of DNA and protein ...
... sex of offspring as well as other traits; it is made up of DNA and protein ...
Press Release, February 15, 2016 - Max-Planck
... The genetic material of cancer cells is unstable. For example, the number of chromosomes, which are the individual elements of packed DNA, is changed in so called aneuploidies. This imbalance in chromosomes, which often occurs early in tumor development, leads to cell stress and promotes disease. Ho ...
... The genetic material of cancer cells is unstable. For example, the number of chromosomes, which are the individual elements of packed DNA, is changed in so called aneuploidies. This imbalance in chromosomes, which often occurs early in tumor development, leads to cell stress and promotes disease. Ho ...
Genetics study guide answers
... 11. The different forms of a gene are called _alleles____. 12. Which of the following best describes the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells? a. More-complex eukaryotes have more chromosomes than simpler eukaryotes do b. Different kinds of eukaryotes have different numbers of chromosomes. c. The chromos ...
... 11. The different forms of a gene are called _alleles____. 12. Which of the following best describes the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells? a. More-complex eukaryotes have more chromosomes than simpler eukaryotes do b. Different kinds of eukaryotes have different numbers of chromosomes. c. The chromos ...
Genetics Vocabulary Review2
... sex of offspring as well as other traits; it is made up of DNA and protein ...
... sex of offspring as well as other traits; it is made up of DNA and protein ...
biology final review sheet answers
... 10. After replication, a DNA consists of one new strand and one old strand. 11. DNA replication occurs in the nucleus of the cell. 12. List 3 ways RNA differs from DNA: a. Shape (single stranded vs. double stranded) b. Base (uracil instead of thymine) c. Sugar (ribose instead of deoxyribose) 13. La ...
... 10. After replication, a DNA consists of one new strand and one old strand. 11. DNA replication occurs in the nucleus of the cell. 12. List 3 ways RNA differs from DNA: a. Shape (single stranded vs. double stranded) b. Base (uracil instead of thymine) c. Sugar (ribose instead of deoxyribose) 13. La ...
The process of meiosis - Deans Community High School
... The chromosome complement of a haploid cell is represented by the letter n and, therefore, that of a diploid cell by 2n. Since the members of each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell match one another gene for gene, they are said to be homologous. They may, however, possess different alleles (form ...
... The chromosome complement of a haploid cell is represented by the letter n and, therefore, that of a diploid cell by 2n. Since the members of each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell match one another gene for gene, they are said to be homologous. They may, however, possess different alleles (form ...
Answer Key
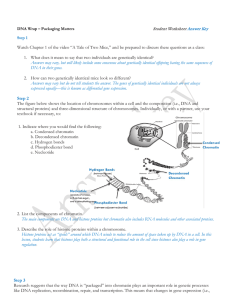
... 2. List the components of chromatin. The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of ...
... 2. List the components of chromatin. The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of ...
word
... Conjugation - Reproduction or "mating" of bacterial cells Example of how small amounts of recombinant DNA are “manufactured” through use of plasmids ...
... Conjugation - Reproduction or "mating" of bacterial cells Example of how small amounts of recombinant DNA are “manufactured” through use of plasmids ...
Teacher`s Guide for “Heredity” CT State Standards National Science
... 1. Heredity – the passing of traits from parents to offspring 2. Pedigree – a diagram which is used to map out genetic relationships within a family line 3. Chromosomes – an organized structure of DNA that contains genes 4. DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid – found in nucleus of cells which contains ...
... 1. Heredity – the passing of traits from parents to offspring 2. Pedigree – a diagram which is used to map out genetic relationships within a family line 3. Chromosomes – an organized structure of DNA that contains genes 4. DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid – found in nucleus of cells which contains ...
Lab 8
... In our cells, DNA is found inside the nucleus, wrapped around basic protein molecules called histones (kind of like thread wrapped around a spool). This combination of DNA and protein is called a nucleosome. The DNA does not leave the nucleus, so when new proteins or other structures need to be made ...
... In our cells, DNA is found inside the nucleus, wrapped around basic protein molecules called histones (kind of like thread wrapped around a spool). This combination of DNA and protein is called a nucleosome. The DNA does not leave the nucleus, so when new proteins or other structures need to be made ...
DNA Fingerprinting: The Code to Identification
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of almost all organisms, including humans. It has a very simple chemical composition, which includes four different nucleotides or bases called adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine which are commonly known by the letters A, T, C and G. The human ...
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of almost all organisms, including humans. It has a very simple chemical composition, which includes four different nucleotides or bases called adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine which are commonly known by the letters A, T, C and G. The human ...
Composite Transposons
... for transposition • Conservative transposition: The element itself moves from the donor site into the target site • Replicative transposition: The element moves a copy of itself to a new site via a DNA intermediate • Retrotransposition: The element makes an RNA copy of itself which is reversed-trans ...
... for transposition • Conservative transposition: The element itself moves from the donor site into the target site • Replicative transposition: The element moves a copy of itself to a new site via a DNA intermediate • Retrotransposition: The element makes an RNA copy of itself which is reversed-trans ...
Teacher Notes Protein Synthesis
... Teacher Notes: The intent of this activity is that the student will go through a process simulating proteins synthesis. (Transcription and translation) The end result is a key chain which represents a protein. 1. Print 2 DNA template pages. Use one to make the key - color each amino acid with the co ...
... Teacher Notes: The intent of this activity is that the student will go through a process simulating proteins synthesis. (Transcription and translation) The end result is a key chain which represents a protein. 1. Print 2 DNA template pages. Use one to make the key - color each amino acid with the co ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.