Mutations & DNA Technology Worksheet
... Little mutations with big effects: Mutations to control genes --- Some regions of DNA control other genes, determining when and where other genes are turned "on". Mutations in these parts of the genome can substantially change the way the organism is built and have a greater impact. For example, Hox ...
... Little mutations with big effects: Mutations to control genes --- Some regions of DNA control other genes, determining when and where other genes are turned "on". Mutations in these parts of the genome can substantially change the way the organism is built and have a greater impact. For example, Hox ...
Cell division: mitosis and meiosis I. Cell division -
... - a cell spends most of its life in interphase • G1 phase ...
... - a cell spends most of its life in interphase • G1 phase ...
The History of Molecular Biology
... By the 1930s, geneticists began speculating as to what sort of molecules could have the kind of stability that the gene demanded, yet be capable of permanent, sudden change to the mutant forms that must provide the basis of evolution... It was generally assumed that genes would be composed of amino ...
... By the 1930s, geneticists began speculating as to what sort of molecules could have the kind of stability that the gene demanded, yet be capable of permanent, sudden change to the mutant forms that must provide the basis of evolution... It was generally assumed that genes would be composed of amino ...
Bio212-01-Alu Lab Part1
... The Target of Our PCR: Recall that we humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or a total of 46 chromosomes. These chromosomes contain somewhere between 30,000 and 50,000 genes. Interestingly, these genes occupy only ~5% of our DNA. The other 95 % of our DNA consists of non-coding DNA, or DNA that doesn ...
... The Target of Our PCR: Recall that we humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or a total of 46 chromosomes. These chromosomes contain somewhere between 30,000 and 50,000 genes. Interestingly, these genes occupy only ~5% of our DNA. The other 95 % of our DNA consists of non-coding DNA, or DNA that doesn ...
Great Discoveries in Science: The Double Helix [JUDSON:] In the
... [JUDSON:] The year ended with Watson and Crick thinking about DNA, Franklin taking pictures of DNA, Wilkins avoiding Franklin, and Pauling a distant but worrisome presence. Then, in January 1953, everything changed. News came that Pauling was indeed preparing a paper on the structure of DNA. Watson ...
... [JUDSON:] The year ended with Watson and Crick thinking about DNA, Franklin taking pictures of DNA, Wilkins avoiding Franklin, and Pauling a distant but worrisome presence. Then, in January 1953, everything changed. News came that Pauling was indeed preparing a paper on the structure of DNA. Watson ...
Mutations booklet MutationsAND Consequences
... Mutations are changes in the DNA. Mutations occur frequently, but these changes may or may not impact the protein that the DNA codes for. Therefore, mutations may have negative consequences, positive consequences, or may be neutral (inconsequential/no effect). In the table below, Use the single st ...
... Mutations are changes in the DNA. Mutations occur frequently, but these changes may or may not impact the protein that the DNA codes for. Therefore, mutations may have negative consequences, positive consequences, or may be neutral (inconsequential/no effect). In the table below, Use the single st ...
REVIEW for the Spring Final Fill In
... 2. The average leaf length of one plant is 2.5 cm with a standard deviation of 0.5 cm. What does this indicate? A. 95 % of all leaves fall within 2.0 to 3.0 cm B. 68 % of all leaves fall within 1.5 to 3.5 cm C. 68 % of all leaves fall within 2.5 to 3.0 cm D. 95 % of all leaves fall within 1.5 to 3.5 ...
... 2. The average leaf length of one plant is 2.5 cm with a standard deviation of 0.5 cm. What does this indicate? A. 95 % of all leaves fall within 2.0 to 3.0 cm B. 68 % of all leaves fall within 1.5 to 3.5 cm C. 68 % of all leaves fall within 2.5 to 3.0 cm D. 95 % of all leaves fall within 1.5 to 3.5 ...
Dr Ishtiaq Lecture at GC Faisalabad
... • Irinotecan is used as chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. • It produces adverse drug reactions in some patients. • genotyping assay is carried out to mutations in UGT1A1 gene for irinotecan prescribing. (Personalized Medicine 2006, 3(4): 415-419) ...
... • Irinotecan is used as chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. • It produces adverse drug reactions in some patients. • genotyping assay is carried out to mutations in UGT1A1 gene for irinotecan prescribing. (Personalized Medicine 2006, 3(4): 415-419) ...
Unit 1
... 9. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which prevent peptidoglycan cross-linking. a. Negative…more b. Negative…less c. Positive…less d. Positive…more 10. Bacterial cells, but not eukaryotic cells, possess _____ ...
... 9. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which prevent peptidoglycan cross-linking. a. Negative…more b. Negative…less c. Positive…less d. Positive…more 10. Bacterial cells, but not eukaryotic cells, possess _____ ...
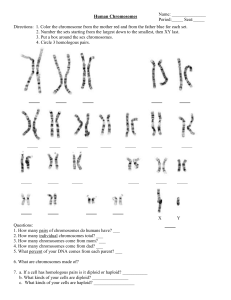
Human Chromosomes
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
Role of Tension and Twist in Single
... does not elastically deform the DNA, but transforms regions of the molecule from B-form DNA into an alternate structure [24]. Similarly, regime (iii) can be explained by the transition of part of the DNA to P-DNA with 2.6 bases per turn. This has been reported to occur at F 3 pN and a degree of su ...
... does not elastically deform the DNA, but transforms regions of the molecule from B-form DNA into an alternate structure [24]. Similarly, regime (iii) can be explained by the transition of part of the DNA to P-DNA with 2.6 bases per turn. This has been reported to occur at F 3 pN and a degree of su ...
G T A C A T C T T A A C G C A T A T
... DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) Deletion and insertion may cause what’s called a FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called ...
... DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) Deletion and insertion may cause what’s called a FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called ...
15 points each
... -DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded -The sugars are different -RNA has uracil instead of thymine -DNA can not leave the nucleus ...
... -DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded -The sugars are different -RNA has uracil instead of thymine -DNA can not leave the nucleus ...
Scientific Process Chapter 1
... _______________My dog ate his entire meal each of the 14 days in just under 3 minutes. 7. Name the control group, the experimental group, the manipulated variable, the responding variable and the controlled variables for the following experiment: Mrs. C.M. Run wants to find out if mice run faster wh ...
... _______________My dog ate his entire meal each of the 14 days in just under 3 minutes. 7. Name the control group, the experimental group, the manipulated variable, the responding variable and the controlled variables for the following experiment: Mrs. C.M. Run wants to find out if mice run faster wh ...
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in IsraelClinical and Genetic Features
... Mutation analysis in family 4. A, DNA sequence of K14 exon 6 in an affected child (upper panel), her mother (middle panel), and her father (lower panel). The R388H and Q396X mutation sites are marked with an arrow. B, Polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism confirmation of ...
... Mutation analysis in family 4. A, DNA sequence of K14 exon 6 in an affected child (upper panel), her mother (middle panel), and her father (lower panel). The R388H and Q396X mutation sites are marked with an arrow. B, Polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism confirmation of ...
STUDY GUIDE for Dr. Mohnen`s part of Exam #3
... Cis-acting element: DNA sequences that regulate expression of gene located on same DNA molecule Transcription initiation in eukaryotes: TFII: transcription factor for RNA Pol II (TF-D (with TBP),A,B,F (then initiate),E,H TFIIH: opens double helix & phosphorylated CTD of RNA PolII change from initiat ...
... Cis-acting element: DNA sequences that regulate expression of gene located on same DNA molecule Transcription initiation in eukaryotes: TFII: transcription factor for RNA Pol II (TF-D (with TBP),A,B,F (then initiate),E,H TFIIH: opens double helix & phosphorylated CTD of RNA PolII change from initiat ...
SOL Review Packet - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... 5. aerobic respiration occurs when there is oxygen present. All three steps (glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, and the electron transport chain) are involved in this type of respiration. 6. anaerobic respiration (aka fermentation) occurs when there is no oxygen present. Only glycolysis is involved in th ...
... 5. aerobic respiration occurs when there is oxygen present. All three steps (glycolysis, the Kreb’s cycle, and the electron transport chain) are involved in this type of respiration. 6. anaerobic respiration (aka fermentation) occurs when there is no oxygen present. Only glycolysis is involved in th ...
Biology II (Block III)
... 1) Messenger RNA: as its name says these are molecules of RNA that carry the instructions to build proteins found in genes. They carry the information from DNA (indide the nucleus) to other parts of the cell. 2) Ribosomal RNA: proteins ar assembled on ribosomes, small organelles composed of two subu ...
... 1) Messenger RNA: as its name says these are molecules of RNA that carry the instructions to build proteins found in genes. They carry the information from DNA (indide the nucleus) to other parts of the cell. 2) Ribosomal RNA: proteins ar assembled on ribosomes, small organelles composed of two subu ...
Leukaemia Section t(10;11)(p11.2;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... A. Partial Q-banded karyotype showing the t(10;11)(p11.2;q23), derivative chromosomes are on the right. B. FISH using RP13-31H8 (ABI1) shows one signal on the normal chromosome 10 and the another one split between the p arm of der(10) (arrowheads) and the q arm of der(11) (arrow). The BAC clone was ...
... A. Partial Q-banded karyotype showing the t(10;11)(p11.2;q23), derivative chromosomes are on the right. B. FISH using RP13-31H8 (ABI1) shows one signal on the normal chromosome 10 and the another one split between the p arm of der(10) (arrowheads) and the q arm of der(11) (arrow). The BAC clone was ...
Transcription - SCIS Teachers
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
Homework Assignment #1
... Answer: SL-1, TFIIIB, and TFIID all contain the TATA binding protein (TBP). Each of these transcription factors determine where the start site of transcription will be and thus must help either directly or indirectly position RNA polymerase over the start site. SL-1 and TFIIIB are both known to dir ...
... Answer: SL-1, TFIIIB, and TFIID all contain the TATA binding protein (TBP). Each of these transcription factors determine where the start site of transcription will be and thus must help either directly or indirectly position RNA polymerase over the start site. SL-1 and TFIIIB are both known to dir ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.




![Great Discoveries in Science: The Double Helix [JUDSON:] In the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002738145_1-0c9d37952d304a3f9a33f852da322160-300x300.png)